Epigenetics Theory www.AssignmentPoint.com In genetics
... have not been demonstrated to be heritable such as histone modification; there are therefore attempts to redefine it in broader terms that would avoid the constraints of requiring heritability. For example, Sir Adrian Bird defined epigenetics as "the structural adaptation of chromosomal regions so a ...
... have not been demonstrated to be heritable such as histone modification; there are therefore attempts to redefine it in broader terms that would avoid the constraints of requiring heritability. For example, Sir Adrian Bird defined epigenetics as "the structural adaptation of chromosomal regions so a ...
An excitingly predictable `omic future - Development
... availability and the renewed thrust towards improving human health will work out very well for the field of medical genetics, in which the recent launch of whole-exome sequencing for diagnostic purposes could reveal novel disease-causing mutations. This development promises to benefit other fields, ...
... availability and the renewed thrust towards improving human health will work out very well for the field of medical genetics, in which the recent launch of whole-exome sequencing for diagnostic purposes could reveal novel disease-causing mutations. This development promises to benefit other fields, ...
7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype
... • In incomplete dominance, neither allele is completely dominant nor completely recessive. – Heterozygous phenotype is intermediate between the two homozygous phenotypes – Homozygous parental phenotypes not seen in F1 offspring ...
... • In incomplete dominance, neither allele is completely dominant nor completely recessive. – Heterozygous phenotype is intermediate between the two homozygous phenotypes – Homozygous parental phenotypes not seen in F1 offspring ...
Gene Section ATM (ataxia telangiectasia mutated) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... functions similar to that of homologs in other species, e.g. telomere metabolism (see below). ...
... functions similar to that of homologs in other species, e.g. telomere metabolism (see below). ...
Autosomal Non-Mendelian Inheritance
... studied genes with fairly simple inheritance, many other genes do not follow such clear patterns, even when they are located on autosomes. In this lesson, we will discuss examples of inheritance of autosomal genes that differ from typical Mendelian inheritance. In the following lesson, we will discu ...
... studied genes with fairly simple inheritance, many other genes do not follow such clear patterns, even when they are located on autosomes. In this lesson, we will discuss examples of inheritance of autosomal genes that differ from typical Mendelian inheritance. In the following lesson, we will discu ...
Viruses - apbio107
... 8. Explain the significance of “sticky ends” and why they were given that name. ...
... 8. Explain the significance of “sticky ends” and why they were given that name. ...
Unit 3 PowerPoint
... • Dominant – the allele of a gene that masks or suppresses the expression of an alternate allele; the trait appears in the heterozygous condition. • Recessive – an allele that is masked by a dominant allele; does not appear in the heterozygous condition, only in homozygous. ...
... • Dominant – the allele of a gene that masks or suppresses the expression of an alternate allele; the trait appears in the heterozygous condition. • Recessive – an allele that is masked by a dominant allele; does not appear in the heterozygous condition, only in homozygous. ...
Data mining and Knowledge discovery in Biomedical literature
... Summary: CML data BMA applied to a microarray data consisting of patient samples in different phases of CML identified 6 signature genes (ART4, DDX47, IGSF2,LTB4R, SCARB1, SLC25A3). Results validated the gene signature using quantitative PCR: 6- ...
... Summary: CML data BMA applied to a microarray data consisting of patient samples in different phases of CML identified 6 signature genes (ART4, DDX47, IGSF2,LTB4R, SCARB1, SLC25A3). Results validated the gene signature using quantitative PCR: 6- ...
Epigenomics Workshop - Institute for Systems Genomics
... Lynch syndrome (LS). LS is caused by germline mutations in the genes of the DNA mismatch repair (MMR) pathway. His laboratory uses a variety of approaches to unravel the molecular mechanism of the MMR pathway and how defects in this pathway give rise to cancer. This work involves biochemical and bio ...
... Lynch syndrome (LS). LS is caused by germline mutations in the genes of the DNA mismatch repair (MMR) pathway. His laboratory uses a variety of approaches to unravel the molecular mechanism of the MMR pathway and how defects in this pathway give rise to cancer. This work involves biochemical and bio ...
Mendel Vocab
... Each different form of a characteristic, such as stem height or seed color, that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes. ...
... Each different form of a characteristic, such as stem height or seed color, that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes. ...
Nature/Nurture
... 1. Can drugs or psychotherapy or other environmental interventions alleviate human disorders that are largely caused by genes? a. No b. Yes c. Epigenetics is beginning to address these issues. 2. Scientists believe that molecular changes that determine the proteins that influence behavior: a. Only h ...
... 1. Can drugs or psychotherapy or other environmental interventions alleviate human disorders that are largely caused by genes? a. No b. Yes c. Epigenetics is beginning to address these issues. 2. Scientists believe that molecular changes that determine the proteins that influence behavior: a. Only h ...
Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes NOTES Cancer
... differentiation and survival. Ras is a molecular switch active when GTP-bound. In response to RTK signaling, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GNEF) is recruited to the membrane, promoting the release of Ras-GDP. This is replaced by Ras-GTP (active form). Ras is also regulated by GTPase activati ...
... differentiation and survival. Ras is a molecular switch active when GTP-bound. In response to RTK signaling, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GNEF) is recruited to the membrane, promoting the release of Ras-GDP. This is replaced by Ras-GTP (active form). Ras is also regulated by GTPase activati ...
Oncogenes And Tumor Suppressor Genes NOTES
... differentiation and survival. Ras is a molecular switch active when GTP-bound. In response to RTK signaling, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GNEF) is recruited to the membrane, promoting the release of Ras-GDP. This is replaced by Ras-GTP (active form). Ras is also regulated by GTPase activati ...
... differentiation and survival. Ras is a molecular switch active when GTP-bound. In response to RTK signaling, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GNEF) is recruited to the membrane, promoting the release of Ras-GDP. This is replaced by Ras-GTP (active form). Ras is also regulated by GTPase activati ...
File - Mrs. Harlin`s Website
... we call a gene. Genes are located on chromosomes in cells. Different forms of a gene are called alleles. Example: the gene for height could have alleles short and tall. ...
... we call a gene. Genes are located on chromosomes in cells. Different forms of a gene are called alleles. Example: the gene for height could have alleles short and tall. ...
REPRODUCTION and GENETICS
... • Organisms reproduce either sexually or asexually. • Asexual reproduction is the reproductive process in which offspring have only one parent. • Sexual reproduction involves two parents who combine their genetic material to produce a new organism. ...
... • Organisms reproduce either sexually or asexually. • Asexual reproduction is the reproductive process in which offspring have only one parent. • Sexual reproduction involves two parents who combine their genetic material to produce a new organism. ...
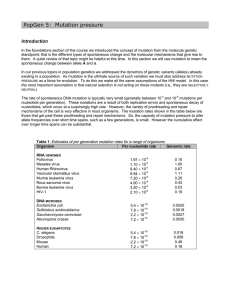
PopGen 5: Mutation pressure
... In the foundations section of this course we introduced the concept of mutation from the molecule genetic standpoint; that is the different types of spontaneous change and the molecular mechanisms that give rise to them. A quick review of that topic might be helpful at this time. In this section we ...
... In the foundations section of this course we introduced the concept of mutation from the molecule genetic standpoint; that is the different types of spontaneous change and the molecular mechanisms that give rise to them. A quick review of that topic might be helpful at this time. In this section we ...
SilverlightPivotViewerin Scientific Discovery
... Problem: DNA is 90% noise, so therefore zooming alone is not so useful (e.g. try some of the conventional viewers in the last slide). Semantic zooming given some good design ideas would probably work well. In the meantime… ...
... Problem: DNA is 90% noise, so therefore zooming alone is not so useful (e.g. try some of the conventional viewers in the last slide). Semantic zooming given some good design ideas would probably work well. In the meantime… ...
Against Maladaptationism - Open Research Exeter
... simplistic evolutionary models, and their apparent outputs can be almost entirely traced to these simplifications. The one important exception to this sceptical suggestion is the extent to which evolution legitimates comparative biology. Detection of homology, the common evolutionary origin of a fea ...
... simplistic evolutionary models, and their apparent outputs can be almost entirely traced to these simplifications. The one important exception to this sceptical suggestion is the extent to which evolution legitimates comparative biology. Detection of homology, the common evolutionary origin of a fea ...
Character and Origin of Species Created by Nature
... of the hybrid. This causes that among the descendants of the hybridplants individuals are to be found which show the species-foreign characters of the paternal parent and which sometimes also produce a few seeds. However, plants developed from such seeds were never fertile and with coccineus-tyipe. ...
... of the hybrid. This causes that among the descendants of the hybridplants individuals are to be found which show the species-foreign characters of the paternal parent and which sometimes also produce a few seeds. However, plants developed from such seeds were never fertile and with coccineus-tyipe. ...
notes (p.49-52)
... is the Wright-Fisher model. We imagine that, tracing back in time, each child chooses its single parent at random, independently of the other children. This resembles reality in the case in which every parent produced a very large number of offspring (much larger than N ), which are then randomly cu ...
... is the Wright-Fisher model. We imagine that, tracing back in time, each child chooses its single parent at random, independently of the other children. This resembles reality in the case in which every parent produced a very large number of offspring (much larger than N ), which are then randomly cu ...
Genotype and Phenotype Practice
... organism has is called genotype If the organism inherits two of the same gene, the genotype is homozygous. If it inherits two different genes, it is heterozygous. According to Mendel, one of these will be dominant and will be expressed if it is present. It can mask the recessive trait. An organism c ...
... organism has is called genotype If the organism inherits two of the same gene, the genotype is homozygous. If it inherits two different genes, it is heterozygous. According to Mendel, one of these will be dominant and will be expressed if it is present. It can mask the recessive trait. An organism c ...