Comparative Genomic Study of upstream Open Reading Frames
... The untranslated regions of mRNA molecules are involved in several posttranscriptional regulatory pathways. The 5’UTR is the sequence between the 5’ terminal cap structure and the initiation codon for protein synthesis. The 5’ end (the leader) can accurately regulate the amount of protein synthesise ...
... The untranslated regions of mRNA molecules are involved in several posttranscriptional regulatory pathways. The 5’UTR is the sequence between the 5’ terminal cap structure and the initiation codon for protein synthesis. The 5’ end (the leader) can accurately regulate the amount of protein synthesise ...
AP Bio Steps Wednesday February 25 SWBAT - APICA
... EU 3.A: Heritable information provides for continuity of life. EK 3.A.2: In eukaryotes, heritable information is passed to the next generation via processes that include the cell cycle and mitosis or meiosis plus fertilization. EK 3.A.3: The chromosomal basis of inheritance provides an understanding ...
... EU 3.A: Heritable information provides for continuity of life. EK 3.A.2: In eukaryotes, heritable information is passed to the next generation via processes that include the cell cycle and mitosis or meiosis plus fertilization. EK 3.A.3: The chromosomal basis of inheritance provides an understanding ...
Mendelian Genetics Student Objectives
... ● How can recombination during meiosis be explained? ● How can recombination during meiosis be utilized to locate genes on chromosomes and establish their relative distances? Learning Objectives: ● The student is able to construct an explanation, using visual representations or narratives, as to how ...
... ● How can recombination during meiosis be explained? ● How can recombination during meiosis be utilized to locate genes on chromosomes and establish their relative distances? Learning Objectives: ● The student is able to construct an explanation, using visual representations or narratives, as to how ...
If there are “CUES” listed within the question, please USE them and
... 2) E. coli bacteria are used in many genetic studies. Type A E. coli can live on a simple nutrient medium, because they have all the genes necessary to produce the chemicals they need. Type V E. coli can live only on a nutrient medium to which a certain vitamin has been added, because they lack a ge ...
... 2) E. coli bacteria are used in many genetic studies. Type A E. coli can live on a simple nutrient medium, because they have all the genes necessary to produce the chemicals they need. Type V E. coli can live only on a nutrient medium to which a certain vitamin has been added, because they lack a ge ...
7-2.5 Genetic Information is Passed from Parent to Offspring
... • Characteristics that are passed from parent to offspring. Examples of inherited traits may be eye color, eye shape, hair type, or face shape. • Some inherited traits are dominant and some are recessive. ...
... • Characteristics that are passed from parent to offspring. Examples of inherited traits may be eye color, eye shape, hair type, or face shape. • Some inherited traits are dominant and some are recessive. ...
DNA bracelet activity pack
... The best way to gauge understanding of participants is to ask them questions like »» Do you think everyone has the same colour eyes or hair? »» What colour are your eyes? Note that we don’t all have the same colour of eyes or hair because what we look like depends on information that we inherit from ...
... The best way to gauge understanding of participants is to ask them questions like »» Do you think everyone has the same colour eyes or hair? »» What colour are your eyes? Note that we don’t all have the same colour of eyes or hair because what we look like depends on information that we inherit from ...
chapter 18 microbial models: the genetics of viruses and bacteria
... Viruses and bacteria are the simplest biological systems—microbial models in which scientists find life’s fundamental molecular mechanisms in their most basic, accessible forms. Molecular biology was born in the laboratories of microbiologists studying viruses and bacteria. Microbes such as E. col ...
... Viruses and bacteria are the simplest biological systems—microbial models in which scientists find life’s fundamental molecular mechanisms in their most basic, accessible forms. Molecular biology was born in the laboratories of microbiologists studying viruses and bacteria. Microbes such as E. col ...
Introduction - Cedar Crest College
... Moving a section of cells from a region of an early frog embryo to another region causes the cells to differentiate appropriately for the new—not the old—location. (See Figure 19.2.) ...
... Moving a section of cells from a region of an early frog embryo to another region causes the cells to differentiate appropriately for the new—not the old—location. (See Figure 19.2.) ...
HEREDITY - Klahowya Secondary School
... Start with mom and the first X, bring it down & write it into each box it’s over. Do the same for the second X. Repeat this for dad’s traits bringing each trait across into the boxes it’s next to. ...
... Start with mom and the first X, bring it down & write it into each box it’s over. Do the same for the second X. Repeat this for dad’s traits bringing each trait across into the boxes it’s next to. ...
Classification
... Key Concept How are genes used to help scientists classify organisms? Scientists compare DNA of different organisms to establish similarities between them and reconstruct possible evolutionary relationships What is the principle behind cladistic analysis? traces the process of evolution in a group o ...
... Key Concept How are genes used to help scientists classify organisms? Scientists compare DNA of different organisms to establish similarities between them and reconstruct possible evolutionary relationships What is the principle behind cladistic analysis? traces the process of evolution in a group o ...
Self-Quiz Questions Activity 1: When is a Genome
... 8. Which of the following best explains why a genome project is not finished when the sequence has been completed? Genomes change too fast and must constantly be updated. Individuals within a species are so unique that having a single sequence is insufficient to characterize a species’ genome. Witho ...
... 8. Which of the following best explains why a genome project is not finished when the sequence has been completed? Genomes change too fast and must constantly be updated. Individuals within a species are so unique that having a single sequence is insufficient to characterize a species’ genome. Witho ...
Linkage mapping of the gpdA gene of
... In the last few years many genes of several Aspergillus species have been cloned and sequenced. For many of these genes mutant alleles and genetic linkage data are also available. However, for those genes for which no mutant alleles have been isolated, genetic mapping was not possible. Here we repor ...
... In the last few years many genes of several Aspergillus species have been cloned and sequenced. For many of these genes mutant alleles and genetic linkage data are also available. However, for those genes for which no mutant alleles have been isolated, genetic mapping was not possible. Here we repor ...
When Is a Genome Project Finished?
... 8. Which of the following best explains why a genome project is not finished when the sequence has been completed? Genomes change too fast and must constantly be updated. Individuals within a species are so unique that having a single sequence is insufficient to characterize a species’ genome. Witho ...
... 8. Which of the following best explains why a genome project is not finished when the sequence has been completed? Genomes change too fast and must constantly be updated. Individuals within a species are so unique that having a single sequence is insufficient to characterize a species’ genome. Witho ...
MB 206 Microbial Biotechnology2
... into host genome Phage M13 – allows cloned DNA to be isolated in single-stranded form Cosmids hybrids of plasmid-bacteriophage l Artificial chromosomes - Cloning of very large genomic fragments - BACs (bacterial artificial chromosomes) - YACs (yeast artificial chromosomes ...
... into host genome Phage M13 – allows cloned DNA to be isolated in single-stranded form Cosmids hybrids of plasmid-bacteriophage l Artificial chromosomes - Cloning of very large genomic fragments - BACs (bacterial artificial chromosomes) - YACs (yeast artificial chromosomes ...
Recitation Section 10 Answer Key Bacterial Genetics—Mutant Hunt
... In both uni- and mulit-cellular organisms, not every change in genetic material affects a trait of that organism. Any mutation you generate in unicellular organisms will be passed on to its progeny. In multicellular organisms, one mutant cell may or may not cause the organisms to display the changed ...
... In both uni- and mulit-cellular organisms, not every change in genetic material affects a trait of that organism. Any mutation you generate in unicellular organisms will be passed on to its progeny. In multicellular organisms, one mutant cell may or may not cause the organisms to display the changed ...
Slide 1
... •Most genes have 2 or more alleles, variations of genes that produce variations of a trait (FOR EXAMPLE: an allele for black fur and an allele for brown fur in mice – both affect fur color, but produce different colors) •Most organisms have 2 copies of each chromosome (one from the mother and the ot ...
... •Most genes have 2 or more alleles, variations of genes that produce variations of a trait (FOR EXAMPLE: an allele for black fur and an allele for brown fur in mice – both affect fur color, but produce different colors) •Most organisms have 2 copies of each chromosome (one from the mother and the ot ...
Tumor-Suppressor Genes
... • The basis of change at the genomic level is mutation, underlying much of genome evolution • The earliest forms of life likely had a minimal number of genes, including only those necessary for survival and reproduction • The size of genomes has increased over evolutionary time, with the extra genet ...
... • The basis of change at the genomic level is mutation, underlying much of genome evolution • The earliest forms of life likely had a minimal number of genes, including only those necessary for survival and reproduction • The size of genomes has increased over evolutionary time, with the extra genet ...
1 Antibiotic susceptibility Antibiotic: natural chemicals produced by
... and/or kills other microbes and/or cells Both work directly on the pathways which microbes use to grow and divide, including: DNA & RNA production, protein and cell wall synthesis, and pathways for other products needed for growth Antibiotic Resistance: Some members of a species become less suscepti ...
... and/or kills other microbes and/or cells Both work directly on the pathways which microbes use to grow and divide, including: DNA & RNA production, protein and cell wall synthesis, and pathways for other products needed for growth Antibiotic Resistance: Some members of a species become less suscepti ...
Gene ORGANizer: linking genes to the organs they
... data collected rarely capture the entire temporal and structural variation of organs. Third, expression analyses generally focus on specific cell types or tissues (e.g. cardiomyocytes), rather than on whole organs (e.g. heart), systems (e.g. the cardiovascular), or anatomical regions (e.g. the thora ...
... data collected rarely capture the entire temporal and structural variation of organs. Third, expression analyses generally focus on specific cell types or tissues (e.g. cardiomyocytes), rather than on whole organs (e.g. heart), systems (e.g. the cardiovascular), or anatomical regions (e.g. the thora ...
biological_approach.
... • It is a deterministic approach as it believes that we are determined by our physiological, genetic or evolutionary make-up. Thus stating that there is no free will. • This approach is reductionist by stating that all human behaviour can be explained through biological processes and we are therefor ...
... • It is a deterministic approach as it believes that we are determined by our physiological, genetic or evolutionary make-up. Thus stating that there is no free will. • This approach is reductionist by stating that all human behaviour can be explained through biological processes and we are therefor ...
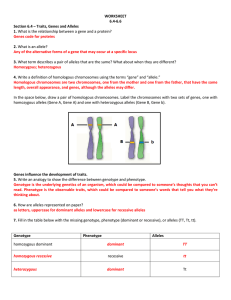
WORKSHEET 6.4-6.6 Section 6.4 – Traits, Genes and Alleles 1
... 7. If genes A and B are located on separate, nonhomologous chromosomes, will they follow Mendel’s law of independent assortment? Explain. Yes. The chromosomes carrying those genes will line up randomly and separate randomly during meiosis. 8. If genes A and B are located at opposite ends on the same ...
... 7. If genes A and B are located on separate, nonhomologous chromosomes, will they follow Mendel’s law of independent assortment? Explain. Yes. The chromosomes carrying those genes will line up randomly and separate randomly during meiosis. 8. If genes A and B are located at opposite ends on the same ...
No Slide Title
... partially or wholly compensates for telomere shortening. Telomerases in all eukaryotic species share at least two components essential for catalytic activity: a telomerase reverse transcriptase protein (TERT) and a telomerase RNA. The TERT encoding gene is a retroelement. In humans, this retroelemen ...
... partially or wholly compensates for telomere shortening. Telomerases in all eukaryotic species share at least two components essential for catalytic activity: a telomerase reverse transcriptase protein (TERT) and a telomerase RNA. The TERT encoding gene is a retroelement. In humans, this retroelemen ...