standards of
... hemodynamic consequences of pericardial effusion can range from relatively mild or nonexistent (if the pericardium has expanded; typically only occurs with chronic effusions) to severe and life-threatening. In the latter scenario, there is a marked increase in intrapericardial pressure resulting in ...
... hemodynamic consequences of pericardial effusion can range from relatively mild or nonexistent (if the pericardium has expanded; typically only occurs with chronic effusions) to severe and life-threatening. In the latter scenario, there is a marked increase in intrapericardial pressure resulting in ...
Acute Pain Management Part 2
... particularly for opioid medication, in the belief that it is safer. This belief is not supported by the literature. Drug absorption can be unpredictable, particularly in states of muscle hypoperfusion. It is also painful for the patient, and carries an infection risk. An alternative to the intramusc ...
... particularly for opioid medication, in the belief that it is safer. This belief is not supported by the literature. Drug absorption can be unpredictable, particularly in states of muscle hypoperfusion. It is also painful for the patient, and carries an infection risk. An alternative to the intramusc ...
Diagnosis of Acute HCV Infection - Core Concepts
... RNA and documented HCV antibody seroconversion and this scenario is the most definitive for diagnosing acute HCV infection. Some experts have suggested limiting the multiple possible terms to acute infection and recent infection: Acute Infection = estimated duration of infection less than 6 months R ...
... RNA and documented HCV antibody seroconversion and this scenario is the most definitive for diagnosing acute HCV infection. Some experts have suggested limiting the multiple possible terms to acute infection and recent infection: Acute Infection = estimated duration of infection less than 6 months R ...
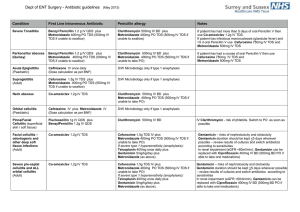
Condition
... use Co-amoxiclav 1.2g IV TDS. If patient has infectious mononucleosis (glandular fever) and >5 d oral Penicillin V use Cefuroxime 750mg IV TDS and Metronidazole 500mg IV TDS ...
... use Co-amoxiclav 1.2g IV TDS. If patient has infectious mononucleosis (glandular fever) and >5 d oral Penicillin V use Cefuroxime 750mg IV TDS and Metronidazole 500mg IV TDS ...
Acute appendicitis
... appendicectomy is the treatment of choice. No good evidence exists to support the notion that analgesia should be withheld on the grounds that it may cloud the clinical picture.12 w13 All patients should receive broad spectrum perioperative antibiotics (one to three doses), as they have been shown t ...
... appendicectomy is the treatment of choice. No good evidence exists to support the notion that analgesia should be withheld on the grounds that it may cloud the clinical picture.12 w13 All patients should receive broad spectrum perioperative antibiotics (one to three doses), as they have been shown t ...
Pleural Effusions
... • Reduced intravascular oncotic pressure (hypoalbuminemia, liver cirrhosis) • Increased oncotic pressure in pleural space • Increased capillary permeability or vascular disruption (neoplastic disease, infection or inflammation, pancreatitis) • Decreased lymphatic drainage (obstruction or damage) • R ...
... • Reduced intravascular oncotic pressure (hypoalbuminemia, liver cirrhosis) • Increased oncotic pressure in pleural space • Increased capillary permeability or vascular disruption (neoplastic disease, infection or inflammation, pancreatitis) • Decreased lymphatic drainage (obstruction or damage) • R ...
Zygomatic Mastoiditis with Extracranial Complications: An Extremely
... or conventional acute mastoiditis. Therefore, because of these atypical presentations, we first considered the possibility of a local skin infection such as cellulitis. Moreover, TBCT and PNS-MRI revealed no remarkable findings in the mastoid and tympanum. However, abscess formation with cortical bo ...
... or conventional acute mastoiditis. Therefore, because of these atypical presentations, we first considered the possibility of a local skin infection such as cellulitis. Moreover, TBCT and PNS-MRI revealed no remarkable findings in the mastoid and tympanum. However, abscess formation with cortical bo ...
Otitis media

Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. The two main types are acute otitis media (AOM) and otitis media with effusion (OME). AOM is an infection of abrupt onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, increased crying, and poor sleep. Decreased eating and a fever may also be present. OME is typically not associated with symptoms. Occasionally a feeling of fullness is described. It is defined as the presence of non-infectious fluid in the middle ear for more than three months. Chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) is middle ear inflammation of greater than two weeks that results in episodes of discharge from the ear. It may be a complication of acute otitis media. Pain is rarely present. All three may be associated with hearing loss. The hearing loss in OME, due to its chronic nature, may affect a child's ability to learn.The cause of AOM is related to childhood anatomy and immune function. Either bacteria or viruses may be involved. Risk factors include: exposure to smoke, use of pacifiers, and attending daycare. It occurs more commonly in those who are Native American or who have Down syndrome. OME frequently occurs following AOM but may also be related to viral upper respiratory infections, irritants such as smoke, or allergies. Looking at the eardrum is important for making the correct diagnosis. Signs of AOM include bulging or a lack of movement of the tympanic membrane from a puff of air. New discharge not related to otitis externa also indicates the diagnosis.A number of measures decrease the risk of otitis media including: pneumococcal and influenza vaccination, exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life, and avoiding tobacco smoke. In those with otitis media with effusion antibiotics do not generally speed recovery. The use of pain medications for AOM is important. This may include: paracetamol (acetaminophen), ibuprofen, benzocaine ear drops, or opioids. In AOM, antibiotics may speed recovery but may result in side effects. Antibiotics are often recommended in those with severe disease or under two years old. In those with less severe disease they may only be recommended in those who do not improve after two or three days. The initial antibiotic of choice is typically amoxicillin. In those with frequent infections tympanostomy tubes may decrease recurrence.Worldwide AOM affect about 11% of people a year (about 710 million cases). Half the cases involve children less than five years of age and it is more common among males. Of those affected about 4.8% or 31 million develop chronic suppurative otitis media. Before the age of ten OME affects about 80% of children at some point in time. Otitis media resulted in 2,400 deaths in 2013 – down from 4,900 deaths in 1990.