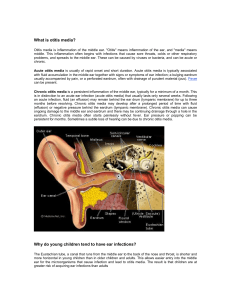
chronic otitis media
... o Concerns for intracranial or intra-temporal complications if reports of fever, vertigo and deep ear pain with headache o History of persistent chronic suppurative otitis media after appropriate medical treatment should raise suspicion for possible cholesteatoma1, 4, 5 2. Physical Exam o Otoscopy7 ...
... o Concerns for intracranial or intra-temporal complications if reports of fever, vertigo and deep ear pain with headache o History of persistent chronic suppurative otitis media after appropriate medical treatment should raise suspicion for possible cholesteatoma1, 4, 5 2. Physical Exam o Otoscopy7 ...
Acute Otitis Media
... Antibiotics should be prescribed when the patient does not improve with observation for 48 to 72 hours Adequate follow-up may include … ...
... Antibiotics should be prescribed when the patient does not improve with observation for 48 to 72 hours Adequate follow-up may include … ...
Tympanic Membrane Perforation - White
... welding, or from an open-handed slap to the ear. It may also be ruptured by barotrauma, which is pressureinduced damage, such as in scuba diving. The most common cause of rupture is from ear infections, however, which can cause increased fluid and pressure in the middle ear. Conversely, a perforatio ...
... welding, or from an open-handed slap to the ear. It may also be ruptured by barotrauma, which is pressureinduced damage, such as in scuba diving. The most common cause of rupture is from ear infections, however, which can cause increased fluid and pressure in the middle ear. Conversely, a perforatio ...
Sore throat, Sinusitis, Otitis media
... Acute Otitis Media Management “Uptodate” Otitis media is the most common diagnosis for which children receive antibiotics 1/Symptomatic therapy (Indicated to relieve pain) - Oral : Ibuprofen or Acetaminophen. - Topical : Benzocaine or Lidocaine (Alternative), only used in children > 2 years old “Ri ...
... Acute Otitis Media Management “Uptodate” Otitis media is the most common diagnosis for which children receive antibiotics 1/Symptomatic therapy (Indicated to relieve pain) - Oral : Ibuprofen or Acetaminophen. - Topical : Benzocaine or Lidocaine (Alternative), only used in children > 2 years old “Ri ...
ENT Emergencies
... • Hard to see – Hx of drainage • Usually from middle ear pressure secondary to fluid or barotrauma • Sometimes from external trauma • most heal uneventfully but all need otology follow-up • perfs with vertigo and facial nerve involvement need immediate referral • treat with antibiotics • drops contr ...
... • Hard to see – Hx of drainage • Usually from middle ear pressure secondary to fluid or barotrauma • Sometimes from external trauma • most heal uneventfully but all need otology follow-up • perfs with vertigo and facial nerve involvement need immediate referral • treat with antibiotics • drops contr ...
chronic suppurative otitis media
... and a permanent perforation. ( A perforation becomes permanent when its edges are covered by squamous epithelium) ...
... and a permanent perforation. ( A perforation becomes permanent when its edges are covered by squamous epithelium) ...
Otitis Media with Effusion
... for most children—hearing returns to normal after the fluid is gone from inside the ear. However, hearing loss may be more of a problem if the fluid stays in the ear for a long time. For a small number of children, reduced hearing can lead to problems with speech, language, and other developmental s ...
... for most children—hearing returns to normal after the fluid is gone from inside the ear. However, hearing loss may be more of a problem if the fluid stays in the ear for a long time. For a small number of children, reduced hearing can lead to problems with speech, language, and other developmental s ...
Ear Notes
... 1. Place vibrating tuning fork on top of skull 2. Ask patient to say if it is louder in either ear 3. Should be the same 4. If different, there is conduction deafness in ear in which it is not heard as loudly 5. Could be caused by wax (cerumen) or otitis media B. Rinne test 1. Place vibrating tuning ...
... 1. Place vibrating tuning fork on top of skull 2. Ask patient to say if it is louder in either ear 3. Should be the same 4. If different, there is conduction deafness in ear in which it is not heard as loudly 5. Could be caused by wax (cerumen) or otitis media B. Rinne test 1. Place vibrating tuning ...
Chronic Otitis Media and Cholesteatoma
... The operation is delicate and meticulous, and may take three to five hours to perform. Following surgery, a head dressing will be worn for five to seven days. Pain is usually mild, and a prescription is given for a pain medication and for an antibiotic. Aspirin or similar medications should NOT be t ...
... The operation is delicate and meticulous, and may take three to five hours to perform. Following surgery, a head dressing will be worn for five to seven days. Pain is usually mild, and a prescription is given for a pain medication and for an antibiotic. Aspirin or similar medications should NOT be t ...
What`s Going Around
... May be viral or bacterial. Slight discharge is usually viral, heavier discharge or eyes crusting shut is usually bacterial. Allergic conjunctivitis will cause redness and itching but little or no discharge. Bacterial infection should be treated with prescription drops. E ...
... May be viral or bacterial. Slight discharge is usually viral, heavier discharge or eyes crusting shut is usually bacterial. Allergic conjunctivitis will cause redness and itching but little or no discharge. Bacterial infection should be treated with prescription drops. E ...
Chronic Otitis Media/Cholesteatoma
... normally provides aeration of the middle ear cleft. When the eustachian tube functions poorly, negatively aerated middle ear space occurs. The negative pressure affect, not unlike a vacuum, may cause inward displacement of the skin lined tympanic membrane (ear drum) which can lead to reformation of ...
... normally provides aeration of the middle ear cleft. When the eustachian tube functions poorly, negatively aerated middle ear space occurs. The negative pressure affect, not unlike a vacuum, may cause inward displacement of the skin lined tympanic membrane (ear drum) which can lead to reformation of ...
Otitis Media With Effusion (Fluid in the Middle Ear) A doctor said
... Fluid may build up in the middle ear for two reasons. When a child has a cold, the middle ear makes fluid just as the nose does &151; it just doesn't run out as easily from the middle ear. After a middle ear infection, fluid may take a month or longer to go away. Are Antibiotics Ever Needed for OME? ...
... Fluid may build up in the middle ear for two reasons. When a child has a cold, the middle ear makes fluid just as the nose does &151; it just doesn't run out as easily from the middle ear. After a middle ear infection, fluid may take a month or longer to go away. Are Antibiotics Ever Needed for OME? ...
Otitis media

Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. The two main types are acute otitis media (AOM) and otitis media with effusion (OME). AOM is an infection of abrupt onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, increased crying, and poor sleep. Decreased eating and a fever may also be present. OME is typically not associated with symptoms. Occasionally a feeling of fullness is described. It is defined as the presence of non-infectious fluid in the middle ear for more than three months. Chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) is middle ear inflammation of greater than two weeks that results in episodes of discharge from the ear. It may be a complication of acute otitis media. Pain is rarely present. All three may be associated with hearing loss. The hearing loss in OME, due to its chronic nature, may affect a child's ability to learn.The cause of AOM is related to childhood anatomy and immune function. Either bacteria or viruses may be involved. Risk factors include: exposure to smoke, use of pacifiers, and attending daycare. It occurs more commonly in those who are Native American or who have Down syndrome. OME frequently occurs following AOM but may also be related to viral upper respiratory infections, irritants such as smoke, or allergies. Looking at the eardrum is important for making the correct diagnosis. Signs of AOM include bulging or a lack of movement of the tympanic membrane from a puff of air. New discharge not related to otitis externa also indicates the diagnosis.A number of measures decrease the risk of otitis media including: pneumococcal and influenza vaccination, exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life, and avoiding tobacco smoke. In those with otitis media with effusion antibiotics do not generally speed recovery. The use of pain medications for AOM is important. This may include: paracetamol (acetaminophen), ibuprofen, benzocaine ear drops, or opioids. In AOM, antibiotics may speed recovery but may result in side effects. Antibiotics are often recommended in those with severe disease or under two years old. In those with less severe disease they may only be recommended in those who do not improve after two or three days. The initial antibiotic of choice is typically amoxicillin. In those with frequent infections tympanostomy tubes may decrease recurrence.Worldwide AOM affect about 11% of people a year (about 710 million cases). Half the cases involve children less than five years of age and it is more common among males. Of those affected about 4.8% or 31 million develop chronic suppurative otitis media. Before the age of ten OME affects about 80% of children at some point in time. Otitis media resulted in 2,400 deaths in 2013 – down from 4,900 deaths in 1990.