4.3-4.4 Genetics and Biotechnology Study Guide File
... o Locus: the particular position on homologous chromosomes of a gene. o Homozygous: having two identical alleles of a gene. o Heterozygous: having two different alleles of a gene. o Carrier: an individual that has one copy of a recessive allele that causes a genetic disease in individuals that are h ...
... o Locus: the particular position on homologous chromosomes of a gene. o Homozygous: having two identical alleles of a gene. o Heterozygous: having two different alleles of a gene. o Carrier: an individual that has one copy of a recessive allele that causes a genetic disease in individuals that are h ...
Chapter 10
... of a single nucleotide 1. Substitution – a point mutation where one nucleotide in a codon is replaced with a different nucleotide, resulting in a new codon Ex. Sickle Cell Anemia – sub. Of A for T in a single codon ...
... of a single nucleotide 1. Substitution – a point mutation where one nucleotide in a codon is replaced with a different nucleotide, resulting in a new codon Ex. Sickle Cell Anemia – sub. Of A for T in a single codon ...
Recombinant DNA and Cloning The Impact of Biotechnology
... Terms to Know • Restriction enzymes: allow the DNA to be cut and spliced at VERY specific locations. • Vectors: carriers of DNA molecules; usually bacteria. • Plasmid: circular DNA found in bacteria. • Recombinant DNA: original carrier DNA + introduced sections of DNA. • Clones: when the bacteria d ...
... Terms to Know • Restriction enzymes: allow the DNA to be cut and spliced at VERY specific locations. • Vectors: carriers of DNA molecules; usually bacteria. • Plasmid: circular DNA found in bacteria. • Recombinant DNA: original carrier DNA + introduced sections of DNA. • Clones: when the bacteria d ...
LEQ: How do the events of meiosis account for Mendel`s laws?
... Sex Linked Genes Genes that are located on sex chromosomes Thomas Hunt Morgan identified sex linked traits by studying eye color in fruit flies ...
... Sex Linked Genes Genes that are located on sex chromosomes Thomas Hunt Morgan identified sex linked traits by studying eye color in fruit flies ...
wanted - Copenhagen Plant Science Centre
... DNA that does not code for proteins (non-coding DNA) makes up the vast majority of bases in many genomes yet we understand little about its role. Non-coding regions are actively transcribed by the same complex transcribing genes (RNA polymerase II, Pol II). Transcription of non-coding sequences resu ...
... DNA that does not code for proteins (non-coding DNA) makes up the vast majority of bases in many genomes yet we understand little about its role. Non-coding regions are actively transcribed by the same complex transcribing genes (RNA polymerase II, Pol II). Transcription of non-coding sequences resu ...
The Source of Heredity “Chapter 21”
... traced to the power of the males semen. He believed heredity factors from the male outweighed the female. ...
... traced to the power of the males semen. He believed heredity factors from the male outweighed the female. ...
What is a genome?
... The assembly starts when we generate the output of the sequencing machines This output can differ, but most of the time it will be a big FASTQ file maybe you know what a FASTA file is? ...
... The assembly starts when we generate the output of the sequencing machines This output can differ, but most of the time it will be a big FASTQ file maybe you know what a FASTA file is? ...
Genetics Since Mendel
... • A group of gene pairs acts together to produce a trait, which creates more variety in phenotypes. • Many human traits are controlled by polygenic inheritance, such as hair and eye color, height, body build, shape of eyes, lips and ears. ...
... • A group of gene pairs acts together to produce a trait, which creates more variety in phenotypes. • Many human traits are controlled by polygenic inheritance, such as hair and eye color, height, body build, shape of eyes, lips and ears. ...
File
... http://www.youtube.com/watch?list=EC3EE D4C1D684D3ADF&v=8kK2zwjRV0M&featur e=player_detailpage#t=547s ...
... http://www.youtube.com/watch?list=EC3EE D4C1D684D3ADF&v=8kK2zwjRV0M&featur e=player_detailpage#t=547s ...
Chapter 21. Development of Multicellular Organisms Sydney
... Zygotic genes Six gap genes: Coarse subdivision Pair rule genes: Segment alteration Segment-polarity genes: ...
... Zygotic genes Six gap genes: Coarse subdivision Pair rule genes: Segment alteration Segment-polarity genes: ...
Discussion-Activity-GATTACA
... How accurate are these predictions for the various disorders? Diagnosis is generally given based on studied correlation of what has happened to people with the same genetic allele in the past. Hence, it is a statistical statement. For example, 60% of people who have this gene combination have this m ...
... How accurate are these predictions for the various disorders? Diagnosis is generally given based on studied correlation of what has happened to people with the same genetic allele in the past. Hence, it is a statistical statement. For example, 60% of people who have this gene combination have this m ...
Mechanisms of Evolution
... portion of a population dies causing a significant decrease in the size of the gene pool. ...
... portion of a population dies causing a significant decrease in the size of the gene pool. ...
Genetics of MD - Myotonic Dystrophy Foundation
... Distinctive genetic mechanisms in DM Myotonic dystrophy is one of the most complex disorders known. In addition to the incredible variability of clinical symptoms, the disease also has several unique mechanistic features: • Autosomal dominant inheritance. The genes for DM1 and DM2 are dominant, mean ...
... Distinctive genetic mechanisms in DM Myotonic dystrophy is one of the most complex disorders known. In addition to the incredible variability of clinical symptoms, the disease also has several unique mechanistic features: • Autosomal dominant inheritance. The genes for DM1 and DM2 are dominant, mean ...
A Web based Database for Hypothetical Genes in the Human Genome
... annotation which involves identification of genes within the chromosome, its fine structure, determination of protein products encodes by the gene and understanding the function (Venter et al., 2001). A group of these genes may be involved in many pathological disorders and hence are of pharmaceutic ...
... annotation which involves identification of genes within the chromosome, its fine structure, determination of protein products encodes by the gene and understanding the function (Venter et al., 2001). A group of these genes may be involved in many pathological disorders and hence are of pharmaceutic ...
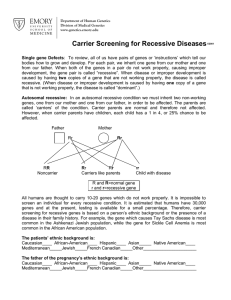
Carrier Screening for Recessive Diseases
... r and r=recessive gene All humans are thought to carry 10-20 genes which do not work properly. It is impossible to screen an individual for every recessive condition. It is estimated that humans have 30,000 genes and at the present, testing is available for a small percentage. Therefore, carrier scr ...
... r and r=recessive gene All humans are thought to carry 10-20 genes which do not work properly. It is impossible to screen an individual for every recessive condition. It is estimated that humans have 30,000 genes and at the present, testing is available for a small percentage. Therefore, carrier scr ...
SPoRE - LCQB
... may regulate several genes, and several TF may regulate a single gene. If a gene has no TFBS at all (it never appears in the “target” column) then the promoter position approximation of models 3-6 is used, so it is not a problem if the information is incomplete. In the extreme case, if TF.txt is emp ...
... may regulate several genes, and several TF may regulate a single gene. If a gene has no TFBS at all (it never appears in the “target” column) then the promoter position approximation of models 3-6 is used, so it is not a problem if the information is incomplete. In the extreme case, if TF.txt is emp ...
Homework: Mutations
... 8. Which of the following is a change that could be passed on to an organism’s offspring? A Damage to the DNA of gamete cells B Damage to skin cells from exposure to sunlight C Damage to DNA in the cytoplasm of cheek cells D Damage to hair pigment cells with permanent dyes 9. The diagram to the righ ...
... 8. Which of the following is a change that could be passed on to an organism’s offspring? A Damage to the DNA of gamete cells B Damage to skin cells from exposure to sunlight C Damage to DNA in the cytoplasm of cheek cells D Damage to hair pigment cells with permanent dyes 9. The diagram to the righ ...
Chapter 15 / Lecture Outline 36
... 1. Many DNA-binding proteins contain a helix-turn-helix motif 2. Most regulatory proteins are oligomeric and contain more than one binding domain 3. The looping of DNA is a common feature of regulatory systems 4. How regulatory proteins interact with RNA polymerase 5. In studying gene regulation, re ...
... 1. Many DNA-binding proteins contain a helix-turn-helix motif 2. Most regulatory proteins are oligomeric and contain more than one binding domain 3. The looping of DNA is a common feature of regulatory systems 4. How regulatory proteins interact with RNA polymerase 5. In studying gene regulation, re ...
Chromosomal mutations
... chromosome. If break occurs within a gene the function might be lost • Broken ands do not have telomeres that prevent degradation but the broken end is “sticky” and can adhere to other broken ends. ...
... chromosome. If break occurs within a gene the function might be lost • Broken ands do not have telomeres that prevent degradation but the broken end is “sticky” and can adhere to other broken ends. ...
Gene expression pipelining, applications and the wisdom
... • The images below show the correlation between some of the RNA-SEQ technologies, in order to compare gene expression consistency among them For Sample A, approximately 400 different samples were averaged for Illumina and 190 for Life Technologies ...
... • The images below show the correlation between some of the RNA-SEQ technologies, in order to compare gene expression consistency among them For Sample A, approximately 400 different samples were averaged for Illumina and 190 for Life Technologies ...
PG1007 Lecture 7 Anterior-Posterior Patterning, HOX Genes and
... "for their discoveries concerning the genetic control of early embryonic development". ...
... "for their discoveries concerning the genetic control of early embryonic development". ...
a 1
... HAR1F and HAR1R (black, with a chevroned line indicating introns), and the predicted RNA structure (green) based on the May 2004 human assembly in the UCSC Genome Browser41. The level of conservation in the orthologous region in other vertebrate species (blue) is plotted for this region using the Ph ...
... HAR1F and HAR1R (black, with a chevroned line indicating introns), and the predicted RNA structure (green) based on the May 2004 human assembly in the UCSC Genome Browser41. The level of conservation in the orthologous region in other vertebrate species (blue) is plotted for this region using the Ph ...
Genomic Library cDNA Library
... What is a genomic library and why is it important? A genomic library is a collection of cloned sequences which represents the entire genome. It allows the analysis of gene promoters which control how genes function (where and when they are expressed, and in response to which stimuli) ...
... What is a genomic library and why is it important? A genomic library is a collection of cloned sequences which represents the entire genome. It allows the analysis of gene promoters which control how genes function (where and when they are expressed, and in response to which stimuli) ...
Genome evolution

Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large.