pruitt_ppt_ch07
... possible candidates who are likely to suffer from a disease based on their nucleotide sequences. ...
... possible candidates who are likely to suffer from a disease based on their nucleotide sequences. ...
11-4 Meiosis - wvhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... NOTES: 14.1-14.2 - HUMAN HEREDITY; PEDIGREES Human Genes: ● The human genome is the complete set of genetic information -it determines characteristics such as eye color and how proteins function within cells Recessive and Dominant Alleles: • Some common genetic disorders are -This means that you nee ...
... NOTES: 14.1-14.2 - HUMAN HEREDITY; PEDIGREES Human Genes: ● The human genome is the complete set of genetic information -it determines characteristics such as eye color and how proteins function within cells Recessive and Dominant Alleles: • Some common genetic disorders are -This means that you nee ...
Lecture#5 - Introduction to gene regulation and operons in
... Central Dogma - Genetic Information and Genes Information flows: DNA -------> RNA ------> Protein Gene expression involves: 1) Transcription - Information is transferred from the DNA sequence into an RNA sequence - messenger RNA. 2) Translation - Information is transferred from the mRNA to protein s ...
... Central Dogma - Genetic Information and Genes Information flows: DNA -------> RNA ------> Protein Gene expression involves: 1) Transcription - Information is transferred from the DNA sequence into an RNA sequence - messenger RNA. 2) Translation - Information is transferred from the mRNA to protein s ...
Ch 6 Formative Test - Meiosis and Mendel
... a. the location of a specific set of genes b. the genes that make up an organism c. the genetic makeup of a chromosome ____ 11. Hair color and eye color are examples of a person's a. phenotype. b. genotype. c. recessive traits. ____ 12. When an organism has two alleles at a particular locus that are ...
... a. the location of a specific set of genes b. the genes that make up an organism c. the genetic makeup of a chromosome ____ 11. Hair color and eye color are examples of a person's a. phenotype. b. genotype. c. recessive traits. ____ 12. When an organism has two alleles at a particular locus that are ...
Exploring the genomic traits of fungus
... of genomic diversity between these strains. Each of the six genomes includes 125 to 835 orthologous groups that are unique (Fig. 2a). Species core orthologous clusters and strain-specific unique clusters within the three Collimonas species were examined, respectively (Fig. 2b-d). In the three specie ...
... of genomic diversity between these strains. Each of the six genomes includes 125 to 835 orthologous groups that are unique (Fig. 2a). Species core orthologous clusters and strain-specific unique clusters within the three Collimonas species were examined, respectively (Fig. 2b-d). In the three specie ...
Chapter 4- Genes and development
... of large genomes that participate in allele-specific expression, whereas differentiation does not depend on covalent modification. ...
... of large genomes that participate in allele-specific expression, whereas differentiation does not depend on covalent modification. ...
BIO 10 Lecture 2
... • Mutation is in the gene that codes for the chain polypeptide of the protein hemoglobin. • The mutation causes the substitution of one amino acid, causing the polypeptide chain to coalesce into crystals that distort the red blood cells. • Persons with one “s” allele and one normal S allele do not ...
... • Mutation is in the gene that codes for the chain polypeptide of the protein hemoglobin. • The mutation causes the substitution of one amino acid, causing the polypeptide chain to coalesce into crystals that distort the red blood cells. • Persons with one “s” allele and one normal S allele do not ...
Lecture #4 - College of Natural Resources, UC Berkeley
... • Selection of increased R in host? – Host: R to exotic may be significantly present because it identifies native pathogen. – R may be absent. – R may be present at low frequency. If host does not exchange genes long distance, but only in areas already infested there is a stronger selection process. ...
... • Selection of increased R in host? – Host: R to exotic may be significantly present because it identifies native pathogen. – R may be absent. – R may be present at low frequency. If host does not exchange genes long distance, but only in areas already infested there is a stronger selection process. ...
biology Ch. 13 Notes Part b Evolution
... o less common #’s go up from greater food 13.16 Explain what is meant by neutral variation. ✍ Mutations that have no effect, + or -, on the individual ✍ Mutation occurs in __________ region of DNA ✍ Occurs but doesn’t change ___________ significantly 13.17 Give four reasons why natural selec ...
... o less common #’s go up from greater food 13.16 Explain what is meant by neutral variation. ✍ Mutations that have no effect, + or -, on the individual ✍ Mutation occurs in __________ region of DNA ✍ Occurs but doesn’t change ___________ significantly 13.17 Give four reasons why natural selec ...
Ch5-Genetics - Medical School Pathology
... Expression determined by NUMBER of genes Overall 5% chance of 1st degree relatives having it ...
... Expression determined by NUMBER of genes Overall 5% chance of 1st degree relatives having it ...
Facing up to Complex Inheritance Patterns
... Influence of Life Stress on Depression: Moderation by a Polymorphism in the 5-HTT Gene In a prospective-longitudinal study of a representative birth cohort, we tested why stressful experiences lead to depression in some people but not in others. A functional polymorphism in the promoter region of th ...
... Influence of Life Stress on Depression: Moderation by a Polymorphism in the 5-HTT Gene In a prospective-longitudinal study of a representative birth cohort, we tested why stressful experiences lead to depression in some people but not in others. A functional polymorphism in the promoter region of th ...
Map of the Human β-Globin Gene – In Brief
... Because the genetic code is triplet, there are three forward reading frames on a strand of DNA. Eukaryotic genes have gaps, called introns, which must be removed from the mRNA before the protein is made. The number of introns, and their length, varies with different genes. Errors in removing introns ...
... Because the genetic code is triplet, there are three forward reading frames on a strand of DNA. Eukaryotic genes have gaps, called introns, which must be removed from the mRNA before the protein is made. The number of introns, and their length, varies with different genes. Errors in removing introns ...
Use of Gene Therapy in The Treatment of Disease
... • The goal of developing an effective genetic therapy for CF lung disease has led to the attainment of several milestones in the larger field of gene therapy. These include: • the first published in vivo gene transfers with adenovirus (Ad)7, and with recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV), and • ...
... • The goal of developing an effective genetic therapy for CF lung disease has led to the attainment of several milestones in the larger field of gene therapy. These include: • the first published in vivo gene transfers with adenovirus (Ad)7, and with recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV), and • ...
CHAPTER 14 THE HUMAN GENOME
... - biologists must identify an inherited trait controlled by a single gene(not easy) by establishing that it is an inherited trait and not the result of environmental influences - they then study how the trait is passed from generation to generation - to do this, they use a chart called a pedigree wh ...
... - biologists must identify an inherited trait controlled by a single gene(not easy) by establishing that it is an inherited trait and not the result of environmental influences - they then study how the trait is passed from generation to generation - to do this, they use a chart called a pedigree wh ...
Test Review
... a homozygous black guinea pig (BB) is crossed with a homozygous white guinea pig (bb), what is the probability that an offspring will have black fur? ...
... a homozygous black guinea pig (BB) is crossed with a homozygous white guinea pig (bb), what is the probability that an offspring will have black fur? ...
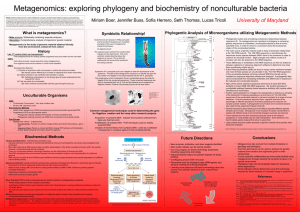
Metagenomics - University of Maryland, College Park
... genetic sequences of unidentified, unculturable bacteria to that of known, culturable ones, in order to come to a conclusion about the evolutionary origins of the unculturable bacteria. • The main source of genetic material used to study evolutionary relationships is the 16S rRNA subunit. The 16S rR ...
... genetic sequences of unidentified, unculturable bacteria to that of known, culturable ones, in order to come to a conclusion about the evolutionary origins of the unculturable bacteria. • The main source of genetic material used to study evolutionary relationships is the 16S rRNA subunit. The 16S rR ...
What organelle is responsible for storing DNA in eukaryotic cells
... order: the human species has 23 pairs, designated 1 to 22 in order of decreasing size and X and Y for the female and male sex chromosomes respectively. • Our definition: The place where all the genes of an organisms are held. • Other forms: chromosomes, chromosomal ...
... order: the human species has 23 pairs, designated 1 to 22 in order of decreasing size and X and Y for the female and male sex chromosomes respectively. • Our definition: The place where all the genes of an organisms are held. • Other forms: chromosomes, chromosomal ...
Silencing The
... technology, known as the HELP assay, can detect epigenetic changes at key regions in every gene. Mr. and Mrs. Hershaft’s gift will support the work of Dr. John Greally, Assistant Professor of Medicine (hematology) and of Molecular Genetics, and Dr. Ari Melnick, Assistant Professor of Medicine (oncol ...
... technology, known as the HELP assay, can detect epigenetic changes at key regions in every gene. Mr. and Mrs. Hershaft’s gift will support the work of Dr. John Greally, Assistant Professor of Medicine (hematology) and of Molecular Genetics, and Dr. Ari Melnick, Assistant Professor of Medicine (oncol ...
4th Exam is Thursday, December 9
... Because the number of possible genotypes is so large, at any given time, a population will only represent a small fraction of the possible genotypes. Mendelian assortment and recombination produce new allele combinations, but do not produce new alleles. ...
... Because the number of possible genotypes is so large, at any given time, a population will only represent a small fraction of the possible genotypes. Mendelian assortment and recombination produce new allele combinations, but do not produce new alleles. ...
Framework for Teachable Unit
... 2. Compare and contrast the impact of acetylation and methylation on gene expression 3. Evaluate an experiment that demonstrates epigenetic silencing 4. Discuss consequences of epigenetics on human health ...
... 2. Compare and contrast the impact of acetylation and methylation on gene expression 3. Evaluate an experiment that demonstrates epigenetic silencing 4. Discuss consequences of epigenetics on human health ...
ch 18 reading guide
... The overview for Chapter 18 introduces the idea that while all cells of an organism have all genes in the genome, not all genes are expressed in every cell. What regulates gene expression? Gene expression in prokaryotic cells differs from that in eukaryotic cells. How do disruptions in gene regulati ...
... The overview for Chapter 18 introduces the idea that while all cells of an organism have all genes in the genome, not all genes are expressed in every cell. What regulates gene expression? Gene expression in prokaryotic cells differs from that in eukaryotic cells. How do disruptions in gene regulati ...
Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives)
... Nucleotide sequences in the 3’ untranslated (3’-UTR) trailer region 4. RNA interference (micro RNA) ...
... Nucleotide sequences in the 3’ untranslated (3’-UTR) trailer region 4. RNA interference (micro RNA) ...
the channel capacity of selective breeding
... Very briefly, we regard selective breeding as a communication channel in which the “message sent” is the rule for selecting which organisms in each generation to breed from, and the “message received” is a single organism sampled once mutation-selection equilibrium is reached. The information transm ...
... Very briefly, we regard selective breeding as a communication channel in which the “message sent” is the rule for selecting which organisms in each generation to breed from, and the “message received” is a single organism sampled once mutation-selection equilibrium is reached. The information transm ...
Male Female vg + b + pr + vg b + pr + vg + b pr + vg b pr + vg + b + pr
... Allele C is always found in affected individuals with one exception Marker G8 is linked to Huntingtons disease at a distance of 2 cM With a LOD score of 12.1 ...
... Allele C is always found in affected individuals with one exception Marker G8 is linked to Huntingtons disease at a distance of 2 cM With a LOD score of 12.1 ...
Genome evolution

Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large.