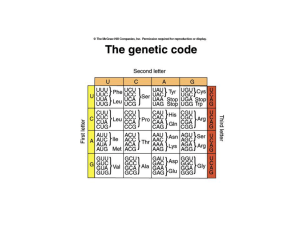
Features of the genetic code
... UGA (opal) • Degenerate • Open reading frame starting at the initiation codon (AUG) • Each codon has 5’ base and a 3’ base e.g. 5’CGU3’ • Mutations that modify the genetic code are of 3 types: frameshift (include deletions and insertions), missense (lead to an amino acid replacement) and nonsense (m ...
... UGA (opal) • Degenerate • Open reading frame starting at the initiation codon (AUG) • Each codon has 5’ base and a 3’ base e.g. 5’CGU3’ • Mutations that modify the genetic code are of 3 types: frameshift (include deletions and insertions), missense (lead to an amino acid replacement) and nonsense (m ...
DIR 145 - licence summary - Office of the Gene Technology Regulator
... Credible pathways to potential harm that were considered included: toxic and allergenic properties of the GM cottons; potential for increased weediness of the GM cotton relative to unmodified plants; and vertical transfer of material to other sexually compatible plants. The principal reasons for the ...
... Credible pathways to potential harm that were considered included: toxic and allergenic properties of the GM cottons; potential for increased weediness of the GM cotton relative to unmodified plants; and vertical transfer of material to other sexually compatible plants. The principal reasons for the ...
Introduction to Genetics PP
... • Original pair of plants = P (parental) generation • Offspring = F1 (first filial) • Offspring of crosses between parents w/ different traits = hybrids ...
... • Original pair of plants = P (parental) generation • Offspring = F1 (first filial) • Offspring of crosses between parents w/ different traits = hybrids ...
Correlation of Age, Degeneration, and Biomechanical Properties of
... Several of the genes in Tables 1 have not previously been investigated for any potential role they may play in disc pathology. The results of this study indicate that further research involving these genes could prove worthwhile in uncovering meaningful conclusions related to disc mechanics, biology ...
... Several of the genes in Tables 1 have not previously been investigated for any potential role they may play in disc pathology. The results of this study indicate that further research involving these genes could prove worthwhile in uncovering meaningful conclusions related to disc mechanics, biology ...
www.sakshieducation.com
... ¾ A large no of insects like grasshopper show XO type of sex determination ¾ It is a case of male heterogamety , where 50% of the sperms bear an X-chromosome and the other 50% of the sperms do not have the X-chromosome, but only the autosomes ; all the ova bear an X-chromosome ¾ When an ovum is fer ...
... ¾ A large no of insects like grasshopper show XO type of sex determination ¾ It is a case of male heterogamety , where 50% of the sperms bear an X-chromosome and the other 50% of the sperms do not have the X-chromosome, but only the autosomes ; all the ova bear an X-chromosome ¾ When an ovum is fer ...
Mitochondrialproteinphylogenyjoins myriapods with chelicerates
... § Abteilung fuÈr Evolutionsgenetik, Institut fuÈr Genetik, UniversitaÈt zu KoÈln, Weyertal 121, 50931 KoÈln, Germany ...
... § Abteilung fuÈr Evolutionsgenetik, Institut fuÈr Genetik, UniversitaÈt zu KoÈln, Weyertal 121, 50931 KoÈln, Germany ...
Ch 11 Standards Test Practice
... During warm temperatures of summer, the 6 arctic fox produces enzymes that cause its fur to become reddish brown. During the cold temperatures of winter, these enzymes do not function. As a result, the fox has a white coat that blends into the snowy background. What explains this change in color? A ...
... During warm temperatures of summer, the 6 arctic fox produces enzymes that cause its fur to become reddish brown. During the cold temperatures of winter, these enzymes do not function. As a result, the fox has a white coat that blends into the snowy background. What explains this change in color? A ...
Arjun Bhargava - Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
... expressions of GPI-anchored complement inhibitors leads to complement-mediated hemolysis ...
... expressions of GPI-anchored complement inhibitors leads to complement-mediated hemolysis ...
11.1 Genetic Variation Within Populations
... change can form a new allele. Mutations in reproductive cells can be passed on to offspring. This increases the genetic variation in the gene pool. Because there are many genes in each individual and many individuals in a population, new mutations form frequently in gene pools. • Recombination New a ...
... change can form a new allele. Mutations in reproductive cells can be passed on to offspring. This increases the genetic variation in the gene pool. Because there are many genes in each individual and many individuals in a population, new mutations form frequently in gene pools. • Recombination New a ...
File
... Punnet Square - A tool we use for predicting the traits of an offspring – Letters are used as symbols to designate genes – Capital letters are used for dominant genes – Lower case letters are used for recessive genes – Genes always exist in pairs – Alleles are different forms of a gene, like having ...
... Punnet Square - A tool we use for predicting the traits of an offspring – Letters are used as symbols to designate genes – Capital letters are used for dominant genes – Lower case letters are used for recessive genes – Genes always exist in pairs – Alleles are different forms of a gene, like having ...
Chapter 7: Genetics Lesson 7.3: Human Genetics and Biotechnology
... http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/gender/Y_evolution.html ...
... http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/gender/Y_evolution.html ...
Evolution of Populations
... Although Mendel and Darwin both worked in the 1800’s, they were not able to share information as scientists do today. By the 1930’s evolutionary biologists started to focus on genes as a way to understand evolutionary change. ...
... Although Mendel and Darwin both worked in the 1800’s, they were not able to share information as scientists do today. By the 1930’s evolutionary biologists started to focus on genes as a way to understand evolutionary change. ...
10.2 - Dihybrid Crosses and Gene Linkage
... During prophase I, the homologous pairs of chromosomes pair up and are in close proximity to each other. Breakages may occur along the chromatids, allowing fragments to be exchanged between the non-sister chromatids. The rejoining of non-sister chromatids forms chiasmata, which remain intact until t ...
... During prophase I, the homologous pairs of chromosomes pair up and are in close proximity to each other. Breakages may occur along the chromatids, allowing fragments to be exchanged between the non-sister chromatids. The rejoining of non-sister chromatids forms chiasmata, which remain intact until t ...
Genetics Jeopardy-0 - Montgomery County Schools
... molecules known as chromosomes. B. Genes are responsible for all the traits of an organism. C. The genes of a particular organism can never change throughout its lifetime. D. In humans, genes are passed to an offspring from two parents. ...
... molecules known as chromosomes. B. Genes are responsible for all the traits of an organism. C. The genes of a particular organism can never change throughout its lifetime. D. In humans, genes are passed to an offspring from two parents. ...
Early beliefs about Heredity and Gregory Mendel
... a. Ex: Giraffe = a cross from a camel and a leopard. B. Because the eggs are much larger than the sperm, some scientists believed that the female had a greater influence on the characteristics of the offspring than the male. Mendel’s studies Mendel’s studies were designed to examine these two assump ...
... a. Ex: Giraffe = a cross from a camel and a leopard. B. Because the eggs are much larger than the sperm, some scientists believed that the female had a greater influence on the characteristics of the offspring than the male. Mendel’s studies Mendel’s studies were designed to examine these two assump ...
File
... Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (SL) Outline the use of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to copy and amplify minute quantities of DNA. State that, in gel electrophoresis, fragments of DNA move in an electric field and are separated according to their size. State that gel electrophoresis of DNA ...
... Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (SL) Outline the use of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to copy and amplify minute quantities of DNA. State that, in gel electrophoresis, fragments of DNA move in an electric field and are separated according to their size. State that gel electrophoresis of DNA ...
Course Competencies Template – Form 112
... the basics principles of Mendelian genetics by: 1. Discussing the progression of discovery from Classical to Modern Genetics. 2. Defining basic concepts of Classical Genetics. 3. Describing Mendel’s experimental design. 4. Utilizing conventional Mendelian genetic terminology. 5. Explaining Mendel’s ...
... the basics principles of Mendelian genetics by: 1. Discussing the progression of discovery from Classical to Modern Genetics. 2. Defining basic concepts of Classical Genetics. 3. Describing Mendel’s experimental design. 4. Utilizing conventional Mendelian genetic terminology. 5. Explaining Mendel’s ...
Course Competencies Template – Form 112
... the basics principles of Mendelian genetics by: 1. Discussing the progression of discovery from Classical to Modern Genetics. 2. Defining basic concepts of Classical Genetics. 3. Describing Mendel’s experimental design. 4. Utilizing conventional Mendelian genetic terminology. 5. Explaining Mendel’s ...
... the basics principles of Mendelian genetics by: 1. Discussing the progression of discovery from Classical to Modern Genetics. 2. Defining basic concepts of Classical Genetics. 3. Describing Mendel’s experimental design. 4. Utilizing conventional Mendelian genetic terminology. 5. Explaining Mendel’s ...
Nature, Nurture, and the Disunity of Knowledge
... study of “lengths” or “widths” alone. Such an advance would require no new tools, but rather a change in the way we think about rectangles. So, too, is it with “nature” and “nurture,” for life does not emerge as a function of either. It is equally wrong-headed to assume that, oh yes, phenotype deriv ...
... study of “lengths” or “widths” alone. Such an advance would require no new tools, but rather a change in the way we think about rectangles. So, too, is it with “nature” and “nurture,” for life does not emerge as a function of either. It is equally wrong-headed to assume that, oh yes, phenotype deriv ...
• Genetic Influences: Terms and Patterns of Transmission • Genetic
... – Another woman or female relative is inseminated and carried the fetus to term until birth, usually under a contractual agreement. Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis – A new prenatal technique. Can identify genetic defects in embryos of from 4 to 8 cells, which were conceived by in vitro fertilizati ...
... – Another woman or female relative is inseminated and carried the fetus to term until birth, usually under a contractual agreement. Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis – A new prenatal technique. Can identify genetic defects in embryos of from 4 to 8 cells, which were conceived by in vitro fertilizati ...
7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype
... • In incomplete dominance, neither allele is completely dominant nor completely recessive. – Heterozygous phenotype is intermediate between the two homozygous phenotypes – Homozygous parental phenotypes not seen in F1 offspring ...
... • In incomplete dominance, neither allele is completely dominant nor completely recessive. – Heterozygous phenotype is intermediate between the two homozygous phenotypes – Homozygous parental phenotypes not seen in F1 offspring ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE
... _____ E. coli cells were spread on an agar plate, producing 1000 colonies. The colonies are replica plated on two agar plates containing the antibiotic kanamycin and one agar plate without antibiotics. All of the colonies are able to grow on the agar plate without antibiotic but only 4 colonies are ...
... _____ E. coli cells were spread on an agar plate, producing 1000 colonies. The colonies are replica plated on two agar plates containing the antibiotic kanamycin and one agar plate without antibiotics. All of the colonies are able to grow on the agar plate without antibiotic but only 4 colonies are ...
Comparative phylogenomics of symbiotic associations
... symbiosis on the plant side, a single origin and multiple losses, was the most favorable option to study. Indeed, convergent losses are detectable, assuming a reliable identification of orthogroups. Unfortunately, most other described symbiotic plant–microbe interactions followed completely differen ...
... symbiosis on the plant side, a single origin and multiple losses, was the most favorable option to study. Indeed, convergent losses are detectable, assuming a reliable identification of orthogroups. Unfortunately, most other described symbiotic plant–microbe interactions followed completely differen ...
Mutation
... Indel lengths exhibit a bimodal frequency distribution, with short indels (up to 20–30 nucleotides) being caused by errors of DNA replication, such as slipped-strand mispairing, and with long indels occurring mainly because of unequal crossing-over, sitespecific recombination, DNA transposition, or ...
... Indel lengths exhibit a bimodal frequency distribution, with short indels (up to 20–30 nucleotides) being caused by errors of DNA replication, such as slipped-strand mispairing, and with long indels occurring mainly because of unequal crossing-over, sitespecific recombination, DNA transposition, or ...
Genome evolution

Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large.