3 slides
... Categories of Natural Selection: 3) Disruptional Selection • Favors organisms with extreme values for a trait and selected against individuals with average values Allows populations to utilize different types of resources in a given habitat ...
... Categories of Natural Selection: 3) Disruptional Selection • Favors organisms with extreme values for a trait and selected against individuals with average values Allows populations to utilize different types of resources in a given habitat ...
File
... (f) What is the value of chi square at the 5% level of significance (alpha = 0.05) with the number of degrees of freedom you gave in part (e)? (g) Do the data allow you to reject Joe’s hypothesis given by the expected ratio at the 5% level of significance? How did you decide this? Answer: ...
... (f) What is the value of chi square at the 5% level of significance (alpha = 0.05) with the number of degrees of freedom you gave in part (e)? (g) Do the data allow you to reject Joe’s hypothesis given by the expected ratio at the 5% level of significance? How did you decide this? Answer: ...
5 In vivo gene cloning
... 1. Isolation – of the DNA containing the required gene 2. Insertion – of the DNA into a vector 3. Transformation – Transfer of DNA into a suitable host 4. Identification – finding those host organisms containing the vector and DNA (by use of gene markers) 5. Growth/Cloning – of the successful host c ...
... 1. Isolation – of the DNA containing the required gene 2. Insertion – of the DNA into a vector 3. Transformation – Transfer of DNA into a suitable host 4. Identification – finding those host organisms containing the vector and DNA (by use of gene markers) 5. Growth/Cloning – of the successful host c ...
Origin of the eukaryotic cell
... Another interesting phenomenon as a result of endosymbionts was the gene migration from the organelle genome to the nuclear genome, and thus the reduction of the organelle genome, since stable environment within eukaryotic cells has eliminated the unnecessary genes that used to be essential for free ...
... Another interesting phenomenon as a result of endosymbionts was the gene migration from the organelle genome to the nuclear genome, and thus the reduction of the organelle genome, since stable environment within eukaryotic cells has eliminated the unnecessary genes that used to be essential for free ...
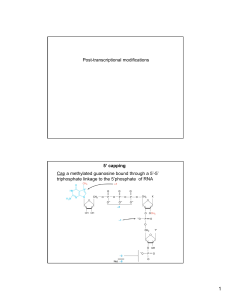
Post-transcriptional modifications Cap a
... In some cases, mobile, sequence-specific silencing signals can move from cell-to-cell or even over long distances in the plant. Several current models hold that silencing signals are “aberrant” RNAs (aRNA), that differ in some way from normal mRNAs. The most likely candidates are small antisense RNA ...
... In some cases, mobile, sequence-specific silencing signals can move from cell-to-cell or even over long distances in the plant. Several current models hold that silencing signals are “aberrant” RNAs (aRNA), that differ in some way from normal mRNAs. The most likely candidates are small antisense RNA ...
Genetics: The Information Broker
... In genetic crosses the re-current quantitative ratio of 3:1 among offspring supports the presence of ____ copy/copies of each gene in an organism of all species of eukaryotes. ...
... In genetic crosses the re-current quantitative ratio of 3:1 among offspring supports the presence of ____ copy/copies of each gene in an organism of all species of eukaryotes. ...
Linkage Analysis and Mapping
... • Recombination is caused by formation of chiasmata along the chromosome at multiple points. • If the distance between two genes is large enough, there can potentially be multiple chiasmata formation between them; – so there could be multiple crossovers. • What would happen if there were two crossov ...
... • Recombination is caused by formation of chiasmata along the chromosome at multiple points. • If the distance between two genes is large enough, there can potentially be multiple chiasmata formation between them; – so there could be multiple crossovers. • What would happen if there were two crossov ...
Analysis of Transcription Initiation in the Panolisflammea Nuclear
... These include AcMNPV (Hooft van Iddekinge et al., 1983). Bombyx mori MNPV (Iatrou et al., 1985), OpMNPV (Leisy et al., 1986a), Op single nucleocapsid NPV (Leisy et al., 1986b), Trichoplusia ni GV (Akiyoshi et al., 1985) and Pieris brassicae GV (Chakerian et al., 1985). The polyhedrin genes have a hi ...
... These include AcMNPV (Hooft van Iddekinge et al., 1983). Bombyx mori MNPV (Iatrou et al., 1985), OpMNPV (Leisy et al., 1986a), Op single nucleocapsid NPV (Leisy et al., 1986b), Trichoplusia ni GV (Akiyoshi et al., 1985) and Pieris brassicae GV (Chakerian et al., 1985). The polyhedrin genes have a hi ...
Alternative Splicing A very short introduction (in plants)
... Genome-wide analyses of alternative splicing in plants: Opportunities and challenges Genome Res. 2008. 18:1381-1392 ...
... Genome-wide analyses of alternative splicing in plants: Opportunities and challenges Genome Res. 2008. 18:1381-1392 ...
PLEIOTROPIC EFFECT OF Rht3 DWARFING GENE ON SOME
... and Rht1S are prevalentin Southern European cultivars (W ORLAND and LAW 1986). There were trials of using some other Rht dwarfing genes, but without significant success (W ORLAND et al. 1980). For now, only strong dwarfing allel Rht3 (known as 'Tom Thumb' or 'Minister dwarf' gene) shows some breedin ...
... and Rht1S are prevalentin Southern European cultivars (W ORLAND and LAW 1986). There were trials of using some other Rht dwarfing genes, but without significant success (W ORLAND et al. 1980). For now, only strong dwarfing allel Rht3 (known as 'Tom Thumb' or 'Minister dwarf' gene) shows some breedin ...
An introduction to genetic algorithms for neural networks
... employing a high mutation rate, and also through fitness scaling. This is a process that re-scales the absolute Fi with respect to the average of the population, so that the fittest chromosome is only, say, twice as likely to be chosen for cross-breeding as the average chromosome. This procedure als ...
... employing a high mutation rate, and also through fitness scaling. This is a process that re-scales the absolute Fi with respect to the average of the population, so that the fittest chromosome is only, say, twice as likely to be chosen for cross-breeding as the average chromosome. This procedure als ...
Section 2 Gene Expression in Development and Cell Division
... • A promoter is the segment of DNA that is recognized by the enzyme RNA polymerase, which then initiates transcription. • An operator is the segment of DNA that acts as a “switch” by controlling the access of RNA polymerase to the promoter. ...
... • A promoter is the segment of DNA that is recognized by the enzyme RNA polymerase, which then initiates transcription. • An operator is the segment of DNA that acts as a “switch” by controlling the access of RNA polymerase to the promoter. ...
DNA Technology
... • process utilizes negative charge of DNA to move pieces thru the gel • bigger pieces stay close to origin, smaller pieces move farther toward the positive end • result is a DNA fingerprint (bar code) of your specific DNA pieces…everyone’s DNA will chop up differently fingerprint is unique ...
... • process utilizes negative charge of DNA to move pieces thru the gel • bigger pieces stay close to origin, smaller pieces move farther toward the positive end • result is a DNA fingerprint (bar code) of your specific DNA pieces…everyone’s DNA will chop up differently fingerprint is unique ...
PDF
... [5], providing the opportunity to compare the mouse and human genomes. Comparing the human genome with the mouse genome can greatly help our understanding of both genomes. We used the BLASTN program [6] to compare the December 2001 golden path freeze of the human genome, which is also NCBI build 28, ...
... [5], providing the opportunity to compare the mouse and human genomes. Comparing the human genome with the mouse genome can greatly help our understanding of both genomes. We used the BLASTN program [6] to compare the December 2001 golden path freeze of the human genome, which is also NCBI build 28, ...
Chapter-12 PTT
... The Human Genome Project • In 1990 an international consortium of government-funded the Human Genome Project. The goal was to sequence the human genome so scientists could have roadmap for finding genes ...
... The Human Genome Project • In 1990 an international consortium of government-funded the Human Genome Project. The goal was to sequence the human genome so scientists could have roadmap for finding genes ...
Chapter 21 The Genetic Control of Animal Development
... 0.5 or less, the animal is a male.CLASSIC Definition But wrong In Drosophila, the key genes in sex determination encode proteins that regulate RNA processing. ...
... 0.5 or less, the animal is a male.CLASSIC Definition But wrong In Drosophila, the key genes in sex determination encode proteins that regulate RNA processing. ...
Chapter 11: Gene Expression PPT
... SPI 3210.4.8 Determine the relationship between mutations and human genetic disorders. • SPI 3210.4.9 Evaluate the scientific and ethical issues associated with gene technologies: genetic engineering, cloning, transgenic organism production, stem cell research, and DNA fingerprinting. ...
... SPI 3210.4.8 Determine the relationship between mutations and human genetic disorders. • SPI 3210.4.9 Evaluate the scientific and ethical issues associated with gene technologies: genetic engineering, cloning, transgenic organism production, stem cell research, and DNA fingerprinting. ...
Lecture 11 Biol302 Spring 2011
... In XX embryos, where TRA is present, dsx transcripts are processed to encode a DSX protein that represses the genes for male development. In XY embryos, where TRA is absent, dsx transcripts are processed to encode a DSX protein that represses the genes for female development. ...
... In XX embryos, where TRA is present, dsx transcripts are processed to encode a DSX protein that represses the genes for male development. In XY embryos, where TRA is absent, dsx transcripts are processed to encode a DSX protein that represses the genes for female development. ...
Recombinant DNA Activity
... Recombinant DNA technology is one of the new techniques of biotechnology. Biotechnology uses living organisms to carry out chemical processes or to produce substances, combining biology with chemistry and science with industry. Biotechnology includes the field of genetic engineering, which is the sc ...
... Recombinant DNA technology is one of the new techniques of biotechnology. Biotechnology uses living organisms to carry out chemical processes or to produce substances, combining biology with chemistry and science with industry. Biotechnology includes the field of genetic engineering, which is the sc ...
Heredity Notes
... • “Females” produce sex cells called eggs – Half of the “mother’s” DNA is in this egg ...
... • “Females” produce sex cells called eggs – Half of the “mother’s” DNA is in this egg ...
Genetics Since Mendel
... produce a trait. The effects of many alleles produces a wide variety of phenotypes. For this reason, it may be hard to classify all the different shades of eye color. Your height and the color of your eyes and skin are just some of the many human traits controlled by polygenic inheritance. It is est ...
... produce a trait. The effects of many alleles produces a wide variety of phenotypes. For this reason, it may be hard to classify all the different shades of eye color. Your height and the color of your eyes and skin are just some of the many human traits controlled by polygenic inheritance. It is est ...
p AB - UCL
... populations. Humans: disequilibria significant between marker loci (e.g. microsatellites, SNPs) and between markers and genetic disease loci ~ 1Mb apart, due to drift ...
... populations. Humans: disequilibria significant between marker loci (e.g. microsatellites, SNPs) and between markers and genetic disease loci ~ 1Mb apart, due to drift ...
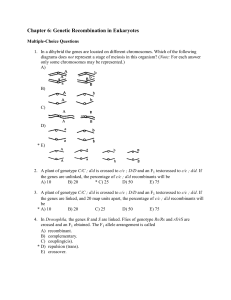
7.03 Problem Set 1 Solutions 1. 2.
... be in the same complementation group and therefore in the same gene. Based on noncomplementation of the recessive mutations, we can conclude that mutants 1 and 3 form one complementation group and are mutations in the same gene (gene A). Likewise, we can conclude that mutations 2 and 5 form a second ...
... be in the same complementation group and therefore in the same gene. Based on noncomplementation of the recessive mutations, we can conclude that mutants 1 and 3 form one complementation group and are mutations in the same gene (gene A). Likewise, we can conclude that mutations 2 and 5 form a second ...
Genome evolution

Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large.