Correction: Characterization of the Structure and Immunostimulatory
... residue of the outer core oligosaccharide. However, it was confirmed that the strain contained the gene intact. Therefore, we believe that dLOS contains the whole core OS structure. We corrected the predicted structure of dLOS in Figure 1D and also revised the text and figure legend accordingly.’’ T ...
... residue of the outer core oligosaccharide. However, it was confirmed that the strain contained the gene intact. Therefore, we believe that dLOS contains the whole core OS structure. We corrected the predicted structure of dLOS in Figure 1D and also revised the text and figure legend accordingly.’’ T ...
an agricultural and environmental biotechnology - Moodle
... Diploid cell. A cell which contains two copies of each chromosome. See Haploid cell. Directional cloning. DNA insert and vector molecules are digested with two different restriction enzymes to create noncomplementary sticky ends at either end of each restriction fragment. This allows the insert to b ...
... Diploid cell. A cell which contains two copies of each chromosome. See Haploid cell. Directional cloning. DNA insert and vector molecules are digested with two different restriction enzymes to create noncomplementary sticky ends at either end of each restriction fragment. This allows the insert to b ...
599 KB - CSIRO Publishing
... to characterise the DNA of the human Y and find the active gene. This was tough because the Y is largely composed of repetitive sequence. Since the discovery of non-coding RNAs with functions in gene regulation we are more careful about dismissing such repetitive sequences as ‘junk DNA’, but most of ...
... to characterise the DNA of the human Y and find the active gene. This was tough because the Y is largely composed of repetitive sequence. Since the discovery of non-coding RNAs with functions in gene regulation we are more careful about dismissing such repetitive sequences as ‘junk DNA’, but most of ...
Evolution of antifreeze glycoprotein gene from a trypsinogen gene in
... and amplification events did not need to occur in the order given. Indeed, an AFGPytrypsinogen hybrid protein coding region formed by some amount of duplication of the 9-nt Thr-Ala-Ala coding element before bulk deletion of trypsinogen sequence might in fact be a more stable structure for the evolvi ...
... and amplification events did not need to occur in the order given. Indeed, an AFGPytrypsinogen hybrid protein coding region formed by some amount of duplication of the 9-nt Thr-Ala-Ala coding element before bulk deletion of trypsinogen sequence might in fact be a more stable structure for the evolvi ...
CHAPTER 5: THE INHERITANCE OF SINGLE
... 2. Crosses using diploid organisms in which products of meiosis are pooled individual 1 ...
... 2. Crosses using diploid organisms in which products of meiosis are pooled individual 1 ...
AP Biology Chapter 15 Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Guided
... The Chromosomal Basis of Sex • In humans and other mammals, there are two varieties of sex chromosomes: a larger ____ chromosome and a smaller __ chromosome • Only the ________________________ have regions that are homologous with corresponding regions of the X chromosome • The ________________ on ...
... The Chromosomal Basis of Sex • In humans and other mammals, there are two varieties of sex chromosomes: a larger ____ chromosome and a smaller __ chromosome • Only the ________________________ have regions that are homologous with corresponding regions of the X chromosome • The ________________ on ...
DNA Sequencing
... Only a cell that took up a plasmid, which has the ampR gene, will reproduce and form a colony. Colonies with nonrecombinant plasmids will be blue, because they can hydrolyze X-gal. Colonies with recombinant plasmids, in which lacZ is disrupted, will be white, because they cannot hydrolyze X-gal. By ...
... Only a cell that took up a plasmid, which has the ampR gene, will reproduce and form a colony. Colonies with nonrecombinant plasmids will be blue, because they can hydrolyze X-gal. Colonies with recombinant plasmids, in which lacZ is disrupted, will be white, because they cannot hydrolyze X-gal. By ...
The Comparison of Transcriptomes Undergoing Waterlogging at the
... facilitation (51.7%), universal stress related (73.2%), and unknown function (55.2%). A total of 1438 of the regulated genes were specifically regulated in ZS9, with 612 being up-regulated and 826 genes down-regulated in this tolerant variety (Appendix E). The GO term analysis (Table 3) showed that ...
... facilitation (51.7%), universal stress related (73.2%), and unknown function (55.2%). A total of 1438 of the regulated genes were specifically regulated in ZS9, with 612 being up-regulated and 826 genes down-regulated in this tolerant variety (Appendix E). The GO term analysis (Table 3) showed that ...
economic perspectives
... iotechnology is the most recent step in humankind’s long endeavor to use nature’s own processes to advance the human condition. The word itself joins knowledge to practice, science to technology. We might have used it to describe the emergence of agriculture, or of pharmacology, or even the training ...
... iotechnology is the most recent step in humankind’s long endeavor to use nature’s own processes to advance the human condition. The word itself joins knowledge to practice, science to technology. We might have used it to describe the emergence of agriculture, or of pharmacology, or even the training ...
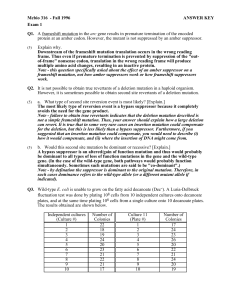
Mcbio 316 - Fall 1996 ANSWER KEY Exam 1 Q1. A frameshift
... Note - some people answered screen because some of the cells were plated on non-selective media. Note that in addition to being non-selective, the LB and MM+Met media didn't provide a screen or enrichment for mutants either. d. Why are there no colonies growing close to the mutagen in the figure? [E ...
... Note - some people answered screen because some of the cells were plated on non-selective media. Note that in addition to being non-selective, the LB and MM+Met media didn't provide a screen or enrichment for mutants either. d. Why are there no colonies growing close to the mutagen in the figure? [E ...
The Making of the Fittest: Evolving Switches, Evolving Bodies
... development raises chicken-or-egg questions. Although the development of a complex animal from a single cell is not fully understood, great progress has been made in recent decades to understand how different sets of genes move the development of an embryo through different stages to maturity. These ...
... development raises chicken-or-egg questions. Although the development of a complex animal from a single cell is not fully understood, great progress has been made in recent decades to understand how different sets of genes move the development of an embryo through different stages to maturity. These ...
Accepted Manuscript
... death and the clinical history” [14]. Our case is in concordance with this definition. The genetic analysis in our index case identified 7 genetic variations in 6 different genes that could explain his death. Of them, 2 variants were previously associated with pathologies. Thus, p.R83H_KCNE3 has bee ...
... death and the clinical history” [14]. Our case is in concordance with this definition. The genetic analysis in our index case identified 7 genetic variations in 6 different genes that could explain his death. Of them, 2 variants were previously associated with pathologies. Thus, p.R83H_KCNE3 has bee ...
No Slide Title
... In theory: same sequence could code for 2 or 3 different polypeptides Most DNA sequences: one reading frame; one protein product ...
... In theory: same sequence could code for 2 or 3 different polypeptides Most DNA sequences: one reading frame; one protein product ...
Name______KEY Genetics C3032 - Examination #2
... DNA transposons excise and then insert into other regions of the DNA; retroposons make an RNA intermediate. d. Conversion vs. recombination using Hfr and F- strains. Conversion from an F- to F+ is rare because the F factor enters the F- cell late; recombination occurs much more frequently because th ...
... DNA transposons excise and then insert into other regions of the DNA; retroposons make an RNA intermediate. d. Conversion vs. recombination using Hfr and F- strains. Conversion from an F- to F+ is rare because the F factor enters the F- cell late; recombination occurs much more frequently because th ...
Complex Trait Genetics
... especially inadequate protein, is known to contribute to stunted growth. Within one genera‐ on of the end of the World War II, the average height of the Japanese popula on increased almost 5 cm. This was not the result of changes in the popula on's gene cs but in the quality of their diet. Because ...
... especially inadequate protein, is known to contribute to stunted growth. Within one genera‐ on of the end of the World War II, the average height of the Japanese popula on increased almost 5 cm. This was not the result of changes in the popula on's gene cs but in the quality of their diet. Because ...
Copy Number and Gene Expression Integration in Partek
... will produce more interesting results as differentially expressed genes will be merged with aberrant regions shared across many samples. The resulting table will be named genes merged with CN.txt, by default. Under standing the Number of Rows in the “Genes Mer ged with CN” Table The resulting table ...
... will produce more interesting results as differentially expressed genes will be merged with aberrant regions shared across many samples. The resulting table will be named genes merged with CN.txt, by default. Under standing the Number of Rows in the “Genes Mer ged with CN” Table The resulting table ...
Supplementary Information
... CpG dinucleotide, along with its relative distance to the transcription start site and the oligomer DNA sequences are provided. Finally, the CpG island status of the genomic locus containing each CpG dinucleotide is measured using a relaxed version of the Takai and Jones CpG Island criteria – althou ...
... CpG dinucleotide, along with its relative distance to the transcription start site and the oligomer DNA sequences are provided. Finally, the CpG island status of the genomic locus containing each CpG dinucleotide is measured using a relaxed version of the Takai and Jones CpG Island criteria – althou ...
Gestation
... ends when the zygote implants into the wall of the mother's uterus. from two to eight weeks following conception the major organs and bodily systems form ...
... ends when the zygote implants into the wall of the mother's uterus. from two to eight weeks following conception the major organs and bodily systems form ...
Gene families and evolution of trehalose
... optimal tree – maximum parsimony, minimum distance or maximum likelihood. In streptophyte plants (Streptophyta), this fundamental dichotomy is supported by clear differences in gene structure, with the class I genes containing at least 16 exons within the coding region, whereas the class II genes ar ...
... optimal tree – maximum parsimony, minimum distance or maximum likelihood. In streptophyte plants (Streptophyta), this fundamental dichotomy is supported by clear differences in gene structure, with the class I genes containing at least 16 exons within the coding region, whereas the class II genes ar ...
Determining the cause of patchwork HBA1 and HBA2 genes
... respectively. A further two out of 120 Iranian samples screened were positive for the α212 allele (0.83% allele ...
... respectively. A further two out of 120 Iranian samples screened were positive for the α212 allele (0.83% allele ...
GNET/BIOL 621 Fall 2016 - UNC Department of Biology
... third of the course, plus 50 points from each of the first and second thirds of the course, and will be 25% of the final grade. Exams will consist of questions similar to those on problem sets, and are meant to emphasize conceptual understanding of genetics. No makeup exams will be given; this inclu ...
... third of the course, plus 50 points from each of the first and second thirds of the course, and will be 25% of the final grade. Exams will consist of questions similar to those on problem sets, and are meant to emphasize conceptual understanding of genetics. No makeup exams will be given; this inclu ...
Genome evolution

Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large.