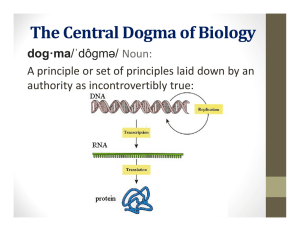
Study Guide: Lecture 1 1. What does “GMO” stand for and what does
... c. What ploidy level is a plant with this formula? 3. Explain the meaning of “genome size”, and the units sizes used to describe genome sizes. 4. Is a 758 Mb genome size a huge, average, or small genome size for a diploid plant? 5. What is “gene flow” and does it only occur with transgenic plants? 6 ...
... c. What ploidy level is a plant with this formula? 3. Explain the meaning of “genome size”, and the units sizes used to describe genome sizes. 4. Is a 758 Mb genome size a huge, average, or small genome size for a diploid plant? 5. What is “gene flow” and does it only occur with transgenic plants? 6 ...
1406 final exam guide.doc
... The chromosomal basis of sex varies with the organism (human, grasshopper, chicken and bees) ex. XY, XO, ZW Sex linked genes are more likely to be inherited by males or females What is Duchenne muscular dystrophy What is a linked gene What is Nondisjunction, at what stage of meiosis does this occurs ...
... The chromosomal basis of sex varies with the organism (human, grasshopper, chicken and bees) ex. XY, XO, ZW Sex linked genes are more likely to be inherited by males or females What is Duchenne muscular dystrophy What is a linked gene What is Nondisjunction, at what stage of meiosis does this occurs ...
Genetic and Genomics: An Introduction
... traits occurred via units (which would later be described as genes). In 1944, scientists at the Rockefeller Institute in New York reported that the genetic material was “DNA” or deoxyribonucleic ...
... traits occurred via units (which would later be described as genes). In 1944, scientists at the Rockefeller Institute in New York reported that the genetic material was “DNA” or deoxyribonucleic ...
13.3- The Human Genome
... make up the human genome.They were able to learn that all genes do not have one specific role, as was previously believed, but can actually make up to three proteins” (Discovery Channel). ...
... make up the human genome.They were able to learn that all genes do not have one specific role, as was previously believed, but can actually make up to three proteins” (Discovery Channel). ...
Cracking the code of life
... 10. Would you be willing to take a test to tell you if your children would be at risk for certain disorders and diseases? Why or why not? ...
... 10. Would you be willing to take a test to tell you if your children would be at risk for certain disorders and diseases? Why or why not? ...
Alkaline Lysis Mini
... The genome of any organism is an amazing piece of biology. It is a highly efficient and adaptive information storage, delivery and retrieval mechanism capable of propagating, modifying and repairing itself. Understanding how genomes function is central to a broad range of disciplines including genet ...
... The genome of any organism is an amazing piece of biology. It is a highly efficient and adaptive information storage, delivery and retrieval mechanism capable of propagating, modifying and repairing itself. Understanding how genomes function is central to a broad range of disciplines including genet ...
Biology 325: Genetics
... Prokaryotic Gene Regulation: To enable bacteria to respond to their environments, transcription initiation is turned on and off mainly by trans-acting proteins; gene expression is also regulated after initiation by cis- or transacting RNAs, or trans-acting proteins. Eukaryotic Gene Regulation: Multi ...
... Prokaryotic Gene Regulation: To enable bacteria to respond to their environments, transcription initiation is turned on and off mainly by trans-acting proteins; gene expression is also regulated after initiation by cis- or transacting RNAs, or trans-acting proteins. Eukaryotic Gene Regulation: Multi ...
PAG XXIV San Diego 2016 Duckweeds, the smallest flowering
... Wang et al. (2014) Nat Commun. 5:3311 ...
... Wang et al. (2014) Nat Commun. 5:3311 ...
The Human Genome https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_genome
... contained in germ cells (the egg and spermgamete cells created in the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction before fertilization creates a zygote) consist of three billion DNAbase pairs, while diploid genomes (found in somatic cells) have twice the DNA content. While there are significant differences ...
... contained in germ cells (the egg and spermgamete cells created in the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction before fertilization creates a zygote) consist of three billion DNAbase pairs, while diploid genomes (found in somatic cells) have twice the DNA content. While there are significant differences ...
Comparative Genomics Course
... of most vertebrates, then use UCSC or Ensembl. As you noticed, I have emphasized the UCSC Genome Browser because of its versatility, near-ubiquity in analyses of vertebrate genomes, and its organization around genome assemblies. However, if you are studying other types of organisms (microbes, flies, ...
... of most vertebrates, then use UCSC or Ensembl. As you noticed, I have emphasized the UCSC Genome Browser because of its versatility, near-ubiquity in analyses of vertebrate genomes, and its organization around genome assemblies. However, if you are studying other types of organisms (microbes, flies, ...
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Det matematisk
... 1. Briefly describe the types of sequences found in the human genome (or a sequenced genome of your choice). 2. How does the length of exons compare to the length of introns in different organisms ranging from prokaryotes to vertebrates? 3. Discuss the evidence that supports both the “introns early” ...
... 1. Briefly describe the types of sequences found in the human genome (or a sequenced genome of your choice). 2. How does the length of exons compare to the length of introns in different organisms ranging from prokaryotes to vertebrates? 3. Discuss the evidence that supports both the “introns early” ...
Study Questions – Chapter 1
... 3. Evidence from caves in the Middle East shows that about 80,000 years ago modern humans and Neanderthals lived in the same region. What does whole genome sequencing tell us about the relationship between these two groups and how does such a study help point to recently evolved genes? As you consid ...
... 3. Evidence from caves in the Middle East shows that about 80,000 years ago modern humans and Neanderthals lived in the same region. What does whole genome sequencing tell us about the relationship between these two groups and how does such a study help point to recently evolved genes? As you consid ...
Molecular_Evolution
... The Genome: smaller than we once thought • The collection of all the DNA in the cell is referred to as the genome. • We now know that most of the DNA does not code for amino acid sequences • Non-coding segments guide translation and are called introns • Coding segments are called exons ...
... The Genome: smaller than we once thought • The collection of all the DNA in the cell is referred to as the genome. • We now know that most of the DNA does not code for amino acid sequences • Non-coding segments guide translation and are called introns • Coding segments are called exons ...
TRANSPONSONS or TRANSPOSABLE ELEMENTS
... These are some notes taken whilst view the PowerPoint presentation and some may be of assistance in filling the gaps. Barbara McLintock (1940s) was the founder of “jumping genes” which led to the discovery of transposable elements (TE). She suggested that genes could change loci and produce phenotyp ...
... These are some notes taken whilst view the PowerPoint presentation and some may be of assistance in filling the gaps. Barbara McLintock (1940s) was the founder of “jumping genes” which led to the discovery of transposable elements (TE). She suggested that genes could change loci and produce phenotyp ...
The Genome of Theobroma Cacao
... The genome, consisting of long strings of chemicals called DNA sequence, includes all the genes of a given organism, but also DNA that is not part of a gene, or noncoding DNA sequence. Each gene contains instructions for assembly of proteins, which consist of strands of amino acids that fold into an ...
... The genome, consisting of long strings of chemicals called DNA sequence, includes all the genes of a given organism, but also DNA that is not part of a gene, or noncoding DNA sequence. Each gene contains instructions for assembly of proteins, which consist of strands of amino acids that fold into an ...
Nature Reviews Genetics, 10
... reconstruction is being used as the ‘gold standard’ against which to test computational methods. The authors compared genome data from the Yeast Gene Order Browser (YGOB) of five post-WGD yeast species (descended from the ancestor that underwent WGD) and six non-WGD yeast species. They visually comp ...
... reconstruction is being used as the ‘gold standard’ against which to test computational methods. The authors compared genome data from the Yeast Gene Order Browser (YGOB) of five post-WGD yeast species (descended from the ancestor that underwent WGD) and six non-WGD yeast species. They visually comp ...
Slide 1
... Archibald Garrod, observes that the disease alkaptonuria has a genetic cause and is inherited as a recessive condition. ...
... Archibald Garrod, observes that the disease alkaptonuria has a genetic cause and is inherited as a recessive condition. ...
Lec. 26 - Genomics
... • The sizes of many gene families has increased in some organisms more than others • Accounts at least partially for the relatively high genetic complexity of plants. ...
... • The sizes of many gene families has increased in some organisms more than others • Accounts at least partially for the relatively high genetic complexity of plants. ...
Human genome study reveals certain genes are less essential than
... “When we analysed the genomes of 2,500 people we were surprised to see over 200 genes that are missing entirely in some people,” said Jan Korbel of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, who led one of the genome project’s studies. The finding has astonished resear ...
... “When we analysed the genomes of 2,500 people we were surprised to see over 200 genes that are missing entirely in some people,” said Jan Korbel of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg, Germany, who led one of the genome project’s studies. The finding has astonished resear ...
Lecture 32 Slides
... if functional domain is duplicated --> functional enhancement -complete gene gene dosage enhanced New function can evolve due to relaxed selection on one copy ...
... if functional domain is duplicated --> functional enhancement -complete gene gene dosage enhanced New function can evolve due to relaxed selection on one copy ...
High throughput gene sequencing to identify new genes that cause
... molecular basis for 50% of these pathologies. However, the causative mutations in half of patients are still unknown. This is mainly due to genetic heterogeneity (mutation in several genes causing the same or very similar disease) and to the lack of large families and large panels of patients. To da ...
... molecular basis for 50% of these pathologies. However, the causative mutations in half of patients are still unknown. This is mainly due to genetic heterogeneity (mutation in several genes causing the same or very similar disease) and to the lack of large families and large panels of patients. To da ...
Genome evolution

Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large.