Transcription and Translation
... http://www.pbslearningmedia.org/resource/lsps07.sci.life.gen.rnai/rnai-discovered/ ...
... http://www.pbslearningmedia.org/resource/lsps07.sci.life.gen.rnai/rnai-discovered/ ...
PPT File
... rearrangement, and mutation of DNA contribute to genome evolution • The basis of change at the genomic level is mutation, which underlies much of genome evolution • The earliest forms of life likely had a minimal number of genes, including only those necessary for survival and reproduction • The siz ...
... rearrangement, and mutation of DNA contribute to genome evolution • The basis of change at the genomic level is mutation, which underlies much of genome evolution • The earliest forms of life likely had a minimal number of genes, including only those necessary for survival and reproduction • The siz ...
Document
... Not uncommon to assemble trillions of sequence reads. Some things to consider: If error rates are high (454, Illumina) 30-50x genome sequencing is required. If error rates are low (SOLiD, Ion Torrent) 4-5x coverage is ...
... Not uncommon to assemble trillions of sequence reads. Some things to consider: If error rates are high (454, Illumina) 30-50x genome sequencing is required. If error rates are low (SOLiD, Ion Torrent) 4-5x coverage is ...
TOC - G3: Genes | Genomes | Genetics
... A Versatile Two-Step CRISPR- and RMCE-Based Strategy for Efficient Genome Engineering in Drosophila Xu Zhang, Wouter H. Koolhaas, and Frank Schnorrer The development of CRISPR/Cas technologies promises a quantum leap in genome engineering. However, an efficient standard protocol has not yet emerged. Z ...
... A Versatile Two-Step CRISPR- and RMCE-Based Strategy for Efficient Genome Engineering in Drosophila Xu Zhang, Wouter H. Koolhaas, and Frank Schnorrer The development of CRISPR/Cas technologies promises a quantum leap in genome engineering. However, an efficient standard protocol has not yet emerged. Z ...
Document
... human gene that causes disease. For example, after the mutation causing cystic fibrosis was identified, the analogous gene was mutated in the mouse. Mice with mutations in this gene have symptoms similar to the human symptoms (though not identical). These mice can be used to study the disease and to ...
... human gene that causes disease. For example, after the mutation causing cystic fibrosis was identified, the analogous gene was mutated in the mouse. Mice with mutations in this gene have symptoms similar to the human symptoms (though not identical). These mice can be used to study the disease and to ...
Ingenious Genes Curriculum Links for AQA GCSE Combined
... All the genes present in an individual organism interact with the environment in which the organism grows and develops its observable appearance and character. These characteristics are its phenotype. The variation in the characteristics of individuals of the same kind may be due to differences in: ...
... All the genes present in an individual organism interact with the environment in which the organism grows and develops its observable appearance and character. These characteristics are its phenotype. The variation in the characteristics of individuals of the same kind may be due to differences in: ...
Lecture 17 POWERPOINT here
... Selectively Neutral Mutations - no effect and is kept - also known as Silent Mutations Deleterious - harmful and result in the death of the cell or individual, normally prior to reproduction ...
... Selectively Neutral Mutations - no effect and is kept - also known as Silent Mutations Deleterious - harmful and result in the death of the cell or individual, normally prior to reproduction ...
CONFOUNDING PHYLOGENETIC TREES
... machinery hasn’t had a chance to alter the base composition to that normally present in the chromosome (-different species often differ in mutations present in the replication and repair machinery, especially pathogenic species) -non-pathogenic bacteria also have islands that confer antibiotic resi ...
... machinery hasn’t had a chance to alter the base composition to that normally present in the chromosome (-different species often differ in mutations present in the replication and repair machinery, especially pathogenic species) -non-pathogenic bacteria also have islands that confer antibiotic resi ...
Special Topics gene expression
... C. Denaturing of proteins leads to loss of function i. Ways to denature protiens D. Genes code for proteins i. Genome vs. gene ii. Polymer of monomers (nucleic acid vs. nucleotide) III. Transcription – DNA to RNA A. Where does this occur? IV. Translation –RNA to protein A. Where does this occur? VI. ...
... C. Denaturing of proteins leads to loss of function i. Ways to denature protiens D. Genes code for proteins i. Genome vs. gene ii. Polymer of monomers (nucleic acid vs. nucleotide) III. Transcription – DNA to RNA A. Where does this occur? IV. Translation –RNA to protein A. Where does this occur? VI. ...
Lars Steinmetz, Wolfgang Huber, Richard Bourgon and
... the exchange of DNA is reciprocal and hence, the effects larger. But non-crossovers can also break up gene blocks, through one-way transfer of genetic material. As Lars puts it, “Noncrossover hotspots create holes in linkage maps.” That means that conventional linkage maps may miss the essential det ...
... the exchange of DNA is reciprocal and hence, the effects larger. But non-crossovers can also break up gene blocks, through one-way transfer of genetic material. As Lars puts it, “Noncrossover hotspots create holes in linkage maps.” That means that conventional linkage maps may miss the essential det ...
Lecture 1: Overview of bioinformatics
... genomes of Eukaryotes, among them two yeasts, the roundworm C. elegans, the fruitfly Drosophila melanogaster, the mosquito A. gambiae, the malaria parasite P. falciparum, and the plant Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress). There are also drafts of 11 other genomes of eukaryotes, most notably of the hu ...
... genomes of Eukaryotes, among them two yeasts, the roundworm C. elegans, the fruitfly Drosophila melanogaster, the mosquito A. gambiae, the malaria parasite P. falciparum, and the plant Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress). There are also drafts of 11 other genomes of eukaryotes, most notably of the hu ...
The Human Genome Project: Science At Its Best
... Opponents pointed out that the huge government research investment (many billions of dollars over at least ten years) would mean that hundreds of other worthwhile scientific projects could not be supported. Furthermore it can be argued that much of that money will be used to determine the sequence i ...
... Opponents pointed out that the huge government research investment (many billions of dollars over at least ten years) would mean that hundreds of other worthwhile scientific projects could not be supported. Furthermore it can be argued that much of that money will be used to determine the sequence i ...
document
... Elements, following a similar study of 1% of the human genome. It was done for both D. melanogaster and C. elegans. An exhaustive study of chromatin structures, plus epigenetics and histone modifications, DNA replication, and RNA transcription. It succeeded in tripling the number of nucleotides in t ...
... Elements, following a similar study of 1% of the human genome. It was done for both D. melanogaster and C. elegans. An exhaustive study of chromatin structures, plus epigenetics and histone modifications, DNA replication, and RNA transcription. It succeeded in tripling the number of nucleotides in t ...
genetic modification
... biotechnology techniques to change the genes of an organism (animal or plant). It is used to change an organism to have more favorable traits. GM includes using genes form one organism and inserting them into another but this is not necessary to create a GMO. GMO can mean that an organism’s ow ...
... biotechnology techniques to change the genes of an organism (animal or plant). It is used to change an organism to have more favorable traits. GM includes using genes form one organism and inserting them into another but this is not necessary to create a GMO. GMO can mean that an organism’s ow ...
Genome Transplantation in Bacteria: Changing One Species to
... • Is the similarity of the donor and recipient organisms a limitation? • Can this technique be used to successfully transplant a synthetic genome? ...
... • Is the similarity of the donor and recipient organisms a limitation? • Can this technique be used to successfully transplant a synthetic genome? ...
Disease Identification
... 3. Chromosomal Disease: Caused by alterations in chromosome structure or number. i. Mosaicism ii. Chromosomal Disorder 4. Complex Diseases: Most diseases are the result of multiple genetic changes as well as environmental influences ...
... 3. Chromosomal Disease: Caused by alterations in chromosome structure or number. i. Mosaicism ii. Chromosomal Disorder 4. Complex Diseases: Most diseases are the result of multiple genetic changes as well as environmental influences ...
Grade 9 Science Ch 4 - Answers to Comprehensive Questions
... 4. Why is the nucleus sometimes called "the control center of the cell"? Because the nucleus is responsible for controlling the functions of the cell. The info contained in the nucleus instructs your cells to produce or import all the materials they need to survive. 5. Why is DNA required in every c ...
... 4. Why is the nucleus sometimes called "the control center of the cell"? Because the nucleus is responsible for controlling the functions of the cell. The info contained in the nucleus instructs your cells to produce or import all the materials they need to survive. 5. Why is DNA required in every c ...
Applied Genetics
... • Genes are now known to control more than one trait • By altering/changing a single gene, multiple traits may be changed in ways we can’t predict • Human genes are only a small percentage of the information contained in DNA (5% or less)…we don’t know what most of the rest does ...
... • Genes are now known to control more than one trait • By altering/changing a single gene, multiple traits may be changed in ways we can’t predict • Human genes are only a small percentage of the information contained in DNA (5% or less)…we don’t know what most of the rest does ...
Lecture 25 student powerpoint
... 1. Genome sequencing provides a map to genes but does not reveal their function. Comparative genome analysis: a. Compares genes with low evolutionary rate and high functional significance. b. Pseudogenes, which are free to mutate, are used to calculate expected mutation rates. c. Regions of high seq ...
... 1. Genome sequencing provides a map to genes but does not reveal their function. Comparative genome analysis: a. Compares genes with low evolutionary rate and high functional significance. b. Pseudogenes, which are free to mutate, are used to calculate expected mutation rates. c. Regions of high seq ...
Mutations I
... Gene Effects • Regulatory mutations: some genes “switch on” or “switch off” other genes—mutations in the control genes may have huge effects • Mutations in genes for DNA repair enzymes can cause the overall mutation rate for the entire genome to increase or decrease ...
... Gene Effects • Regulatory mutations: some genes “switch on” or “switch off” other genes—mutations in the control genes may have huge effects • Mutations in genes for DNA repair enzymes can cause the overall mutation rate for the entire genome to increase or decrease ...
The Yale Center for Genome Analysis
... human genomes a month, yielding a tremendous volume of information that drives research not only in human biology and medicine, but in every area of the life sciences. This is indeed the age of genomics. The marriage of high-throughput screening technologies and bioinformatics has created a powerful ...
... human genomes a month, yielding a tremendous volume of information that drives research not only in human biology and medicine, but in every area of the life sciences. This is indeed the age of genomics. The marriage of high-throughput screening technologies and bioinformatics has created a powerful ...
FUNCTIONAL CHARACTERIZATION OF - SBBq
... pathogenicity island PAPI-1 that contains several virulence-related genes of unknown function. Between two copies of direct repeat sequences in PAPI-1, there are two pairs of two-component regulatory systems, pvrSR and rcsCB and a putative fimbrial chaperone-usher gene cluster named cupD. In an atte ...
... pathogenicity island PAPI-1 that contains several virulence-related genes of unknown function. Between two copies of direct repeat sequences in PAPI-1, there are two pairs of two-component regulatory systems, pvrSR and rcsCB and a putative fimbrial chaperone-usher gene cluster named cupD. In an atte ...
Siena Borsani - Unisi.it - Università degli Studi di Siena
... - Lifetime risk of developing Alzheimer's disease is three times higher for carriers of one APOE epsilon4 allele - Approximately 1 in 7 people carry the epsilon4 variant of APOE ...
... - Lifetime risk of developing Alzheimer's disease is three times higher for carriers of one APOE epsilon4 allele - Approximately 1 in 7 people carry the epsilon4 variant of APOE ...
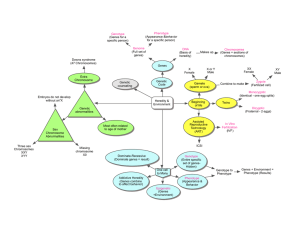
Genome evolution

Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large.