20070313_Questions
... 6) Does the default view that you are looking at show you all the STSs that have been mapped to this region? 7) After narrowing down the view to include just the region between STS markers D21S1869 and D21S1989, what are the chromosomal coordinates, in bp, that you are looking at? 8) The gene you ar ...
... 6) Does the default view that you are looking at show you all the STSs that have been mapped to this region? 7) After narrowing down the view to include just the region between STS markers D21S1869 and D21S1989, what are the chromosomal coordinates, in bp, that you are looking at? 8) The gene you ar ...
Prescott`s Microbiology, 9th Edition Chapter 19 –Microbial
... Figure 19.2 Would this curve be shifted to the left or the right for a microbe with an exceptionally low G + C composition? Explain your answer. Unsure student understand that melting means the hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic base stacking interactions between strands are disrupted. The covalent bond ...
... Figure 19.2 Would this curve be shifted to the left or the right for a microbe with an exceptionally low G + C composition? Explain your answer. Unsure student understand that melting means the hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic base stacking interactions between strands are disrupted. The covalent bond ...
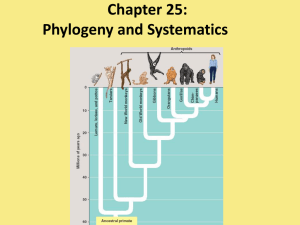
16-1 Genes and Variation
... Today, genetics, molecular biology, and evolutionary theory work together to explain how inheritable variation appears and how natural selection operates on that variation ...
... Today, genetics, molecular biology, and evolutionary theory work together to explain how inheritable variation appears and how natural selection operates on that variation ...
Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of Life
... rapid evolution; also, small changes in genes can lead to large morphological differences) • Organisms that appear similar not always closely related (convergent evolution) • Just because 2 groups share primitive characters does not mean they are closely related ...
... rapid evolution; also, small changes in genes can lead to large morphological differences) • Organisms that appear similar not always closely related (convergent evolution) • Just because 2 groups share primitive characters does not mean they are closely related ...
The corn snake genome sequenced for the first time
... similar to that of the sequenced human genome, we need to assemble chromosomes which can form chains of more than 200 millions of nucleotides”. But why the corn snake ? “This species is perfect for investigating the development and evolution of reptiles because it breeds easily, it is oviparous, an ...
... similar to that of the sequenced human genome, we need to assemble chromosomes which can form chains of more than 200 millions of nucleotides”. But why the corn snake ? “This species is perfect for investigating the development and evolution of reptiles because it breeds easily, it is oviparous, an ...
Abstract
... genetic risk scores can be calculated by integrating GWAS results with whole genome sequence data. On a broad scale, hereditary disease risks are similar for ancient hominins and modern-day humans. There is evidence that ancient pastoralists may have had healthier genomes than hunter-gatherers or fa ...
... genetic risk scores can be calculated by integrating GWAS results with whole genome sequence data. On a broad scale, hereditary disease risks are similar for ancient hominins and modern-day humans. There is evidence that ancient pastoralists may have had healthier genomes than hunter-gatherers or fa ...
2014-09 ICGI Wuhan Research Conference
... community database to further enable basic, translational and applied cotton research. ...
... community database to further enable basic, translational and applied cotton research. ...
Sunday, Oct - Okemos Public Schools
... This shockingly small number made it clear to scientists that genes alone don't dictate the differences between species; the changes, they now know, also depend on molecular switches that tell genes when and where to turn on and off. "Take the genes involved in creating the hand, the penis and the ...
... This shockingly small number made it clear to scientists that genes alone don't dictate the differences between species; the changes, they now know, also depend on molecular switches that tell genes when and where to turn on and off. "Take the genes involved in creating the hand, the penis and the ...
How We Became Human: What Makes Us Different
... molecules that cells construct according to blueprints embedded in the genes-they found that 29% of the proteins were identical (most of the proteins that aren't the same differ, on average, by only two amino-acid substitutions). The genetic differences between chimps and humans, therefore, must be ...
... molecules that cells construct according to blueprints embedded in the genes-they found that 29% of the proteins were identical (most of the proteins that aren't the same differ, on average, by only two amino-acid substitutions). The genetic differences between chimps and humans, therefore, must be ...
Human Genetics
... (GINA) act was passed in the US in 2008 Genome information is useful for developing treatment to genetic and infectious diseases ...
... (GINA) act was passed in the US in 2008 Genome information is useful for developing treatment to genetic and infectious diseases ...
Genomics
... number of tasks within the cell. The complete set of proteins in a cell can be referred to as its proteome and the study of protein structure and function and what every protein in the cell is doing is known as proteomics. The proteome is highly dynamic and it changes from time to time in response t ...
... number of tasks within the cell. The complete set of proteins in a cell can be referred to as its proteome and the study of protein structure and function and what every protein in the cell is doing is known as proteomics. The proteome is highly dynamic and it changes from time to time in response t ...
What is the most likely path of inheritance?
... the possible blood phenotypes for Bernie? Genotypes for all? ...
... the possible blood phenotypes for Bernie? Genotypes for all? ...
Threading-based Protein Structure Prediction
... – Prokaryotes (single-celled organisms with no nuclei. e.g., bacteria) – Eukaryotes (organisms with single or multiple cells. their cells have nuclei. e.g., plant & animal) ...
... – Prokaryotes (single-celled organisms with no nuclei. e.g., bacteria) – Eukaryotes (organisms with single or multiple cells. their cells have nuclei. e.g., plant & animal) ...
Evolutionary Processes ()
... • Can result from gene flow, non-random mating, genetic drift, mutation and natural selection. ...
... • Can result from gene flow, non-random mating, genetic drift, mutation and natural selection. ...
genetics - Yazscience10
... language through which the information needed to make proteins is kept ...
... language through which the information needed to make proteins is kept ...
Common Misconceptions in Genetics
... approximately 22,000 genes in the human genome. 5. All mutations are harmful Absolutely not! Most mutations that occur in our DNA sequence are changes in single nucleotides that do not cause harm to the individual. Recent research suggests that each of us inherits approximately 60 new mutations that ...
... approximately 22,000 genes in the human genome. 5. All mutations are harmful Absolutely not! Most mutations that occur in our DNA sequence are changes in single nucleotides that do not cause harm to the individual. Recent research suggests that each of us inherits approximately 60 new mutations that ...
Abstract - Anil Jegga - Cincinnati Children`s Hospital
... Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, OH-45229 The combinatorial interaction of sequence specific trans-acting factors with localized genomic cis-elements is the principal underlying mechanism for regulating tissue specific and developmental gene expression. Recent computational ...
... Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, OH-45229 The combinatorial interaction of sequence specific trans-acting factors with localized genomic cis-elements is the principal underlying mechanism for regulating tissue specific and developmental gene expression. Recent computational ...
The molecular natural history of the human genome
... Roughly a third of all human genes appear to experience alternative splicing (i.e. different ways of stitching exon sequences together). The average number of transcripts per human gene is approximately three, which contrasts with the situation in C. elegans, where the average is ~1.3. Thus, the num ...
... Roughly a third of all human genes appear to experience alternative splicing (i.e. different ways of stitching exon sequences together). The average number of transcripts per human gene is approximately three, which contrasts with the situation in C. elegans, where the average is ~1.3. Thus, the num ...
DNA and Protein Synthesis
... • Proteins are composed of amino acids. • Codons are a sequence of three bases that code for a specific amino acid. ...
... • Proteins are composed of amino acids. • Codons are a sequence of three bases that code for a specific amino acid. ...
Media:SRich072506
... – Immediate candidate gene evaluation Assumed knowledge (admission of omniscience) Gene-gene interactions Gene-environment interactions ...
... – Immediate candidate gene evaluation Assumed knowledge (admission of omniscience) Gene-gene interactions Gene-environment interactions ...
Genome evolution

Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large.