Concept Sheet
... Objectives: Students will 1. Explain what a gene pool is. 2. Identify the main sources of inheritable variation in a population. 3. State what determines how a phenotype is expressed. 4. Explain how natural selection affects single-gene and polygenic traits 5. Describe genetic drift. 6. List the fiv ...
... Objectives: Students will 1. Explain what a gene pool is. 2. Identify the main sources of inheritable variation in a population. 3. State what determines how a phenotype is expressed. 4. Explain how natural selection affects single-gene and polygenic traits 5. Describe genetic drift. 6. List the fiv ...
Identical vs. Fraternal Twins
... identical or fraternal?” The terms identical and fraternal are common words that refer to zygosity -- the characteristics of the cell union that happened at conception. Identical (monozygotic) twins form when a single fertilized egg splits into two genetically identical parts. Identical twins share ...
... identical or fraternal?” The terms identical and fraternal are common words that refer to zygosity -- the characteristics of the cell union that happened at conception. Identical (monozygotic) twins form when a single fertilized egg splits into two genetically identical parts. Identical twins share ...
B1 - Genetic Variation and Evolution Quiz
... Sexual involves fusing gametes, mixing of genetic material, two parents, results in variation, whereas asexual produces clones and only one parent is required as cells are split. ...
... Sexual involves fusing gametes, mixing of genetic material, two parents, results in variation, whereas asexual produces clones and only one parent is required as cells are split. ...
Variation in Populations
... is no input of alleles from other populations, there is no mutational change in alleles, and there is no differential survival or reproduction of different genotypes. Violation of any of these requirements can result in a distribution of genotypes other than binomial or can result in a change in the ...
... is no input of alleles from other populations, there is no mutational change in alleles, and there is no differential survival or reproduction of different genotypes. Violation of any of these requirements can result in a distribution of genotypes other than binomial or can result in a change in the ...
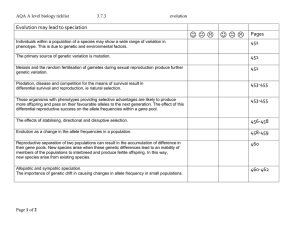
doc 3.7.3 evolution checklist
... Reproductive separation of two populations can result in the accumulation of difference in their gene pools. New species arise when these genetic differences lead to an inability of members of the populations to interbreed and produce fertile offspring. In this way, new species arise from existing s ...
... Reproductive separation of two populations can result in the accumulation of difference in their gene pools. New species arise when these genetic differences lead to an inability of members of the populations to interbreed and produce fertile offspring. In this way, new species arise from existing s ...
Genetics Slides
... Similarly, some populations have less variability in environment/experiences. Others contain individuals with dramatically different environments or experiences so “nurture” accounts for more variability of traits. ...
... Similarly, some populations have less variability in environment/experiences. Others contain individuals with dramatically different environments or experiences so “nurture” accounts for more variability of traits. ...
What is genetic engineering?
... Genetic engineering could also change the genes in the embryo – they could stop children being born with genetic defects such as cystic fibrosis. ...
... Genetic engineering could also change the genes in the embryo – they could stop children being born with genetic defects such as cystic fibrosis. ...
Evolution at multiple loci
... • Then offspring will strongly resemble parents • Suppose that differences are mostly due to environment • If offspring environment not similar to parental environment, then offspring do not closely resemble parents ...
... • Then offspring will strongly resemble parents • Suppose that differences are mostly due to environment • If offspring environment not similar to parental environment, then offspring do not closely resemble parents ...
Haploid Human Cells as Genetic Tool to Identify Genes important for
... processes. However, human lines are refractory to efficient mutagenesis-based genetics due to the diploid nature of their genome. Therefore it remains challenging to apply powerful genetic approaches that were successful in genetic model organisms such as yeast to human cells. Our group recently dev ...
... processes. However, human lines are refractory to efficient mutagenesis-based genetics due to the diploid nature of their genome. Therefore it remains challenging to apply powerful genetic approaches that were successful in genetic model organisms such as yeast to human cells. Our group recently dev ...
Study guide: Ch 4: Due Thursday (Test Friday)
... 18:What is the purpose of the Human genome project? Identify DNA sequence of each gene. 19:What is a genome? DNA in one cell 20:How do police use DNA fingerprinting to solve the crimes? Comparing suspect’s DNA with the evidence. 22:What is a Karyotype? 23:What factors can affect a person’s height? G ...
... 18:What is the purpose of the Human genome project? Identify DNA sequence of each gene. 19:What is a genome? DNA in one cell 20:How do police use DNA fingerprinting to solve the crimes? Comparing suspect’s DNA with the evidence. 22:What is a Karyotype? 23:What factors can affect a person’s height? G ...
Genes are the basic building blocks of heredity
... schizophrenia, the chances that the other twin will develop the disorder are about 50%. For fraternal twins, the chances are about 15%. * The higher rate exhibited by twins, particularly identical twins, suggests that heredity plays a crucial role in schizophrenia. ...
... schizophrenia, the chances that the other twin will develop the disorder are about 50%. For fraternal twins, the chances are about 15%. * The higher rate exhibited by twins, particularly identical twins, suggests that heredity plays a crucial role in schizophrenia. ...
Heredity
... Inherited traits-traits that are passed on from parents to offsprings. Genes-tiny message units Learned trait-a trait that is not passed on in DNA Dominant trait-a trait that will be expressed if it is inherited. Recessive trait-a trait that is not expressed if paired with a dominant trait Incomplet ...
... Inherited traits-traits that are passed on from parents to offsprings. Genes-tiny message units Learned trait-a trait that is not passed on in DNA Dominant trait-a trait that will be expressed if it is inherited. Recessive trait-a trait that is not expressed if paired with a dominant trait Incomplet ...
Quantitative Genetics
... allele or gene in a quantitative trait is small compared to qualitative genes. polygenic trait - a trait that is controlled by many genes each contributing a small affect on the phenotype. examples With a quantitative trait the gene action can be either additive, non-additive, or a combination of th ...
... allele or gene in a quantitative trait is small compared to qualitative genes. polygenic trait - a trait that is controlled by many genes each contributing a small affect on the phenotype. examples With a quantitative trait the gene action can be either additive, non-additive, or a combination of th ...
Nature vs. Nurture
... growth and social growth, and social interactions interactions • ________, _________, • ____________________ ___________, and _______________ ...
... growth and social growth, and social interactions interactions • ________, _________, • ____________________ ___________, and _______________ ...
genetic variation
... The directly method to test the genetic variation is using molecular markers, but the adaptive traits are not correlation to the results, which depend on the testing level (Hall et al., 2007). Genetic variation among tree populations is routinely studied with provenance trials (e.g. Hamann et al., 2 ...
... The directly method to test the genetic variation is using molecular markers, but the adaptive traits are not correlation to the results, which depend on the testing level (Hall et al., 2007). Genetic variation among tree populations is routinely studied with provenance trials (e.g. Hamann et al., 2 ...
advocacy vs. impartiality the problem is quite complex on one side
... zero (changes in numbers of fingers are caused by defects of development, eg thalidomide, not by heredity) * wearing earrings in 1950 had a very strong heritability (it occurred only in women, today also in men): it was related to having XX vs XY; however, it was not genetically determined ...
... zero (changes in numbers of fingers are caused by defects of development, eg thalidomide, not by heredity) * wearing earrings in 1950 had a very strong heritability (it occurred only in women, today also in men): it was related to having XX vs XY; however, it was not genetically determined ...
Quantitative Genetics
... • Variance is a useful property, because variances from different sources can be added together to get total variance. • However, the units of variance are the squares of the units used to measure the trait. Thus, if length in centimeters was measured, the variances of the length are in cm2. This is ...
... • Variance is a useful property, because variances from different sources can be added together to get total variance. • However, the units of variance are the squares of the units used to measure the trait. Thus, if length in centimeters was measured, the variances of the length are in cm2. This is ...
Quantitative Genetics - Northern Illinois University
... • In general, heavy parents gave heavy offspring and light parents gave light offspring. That is, there is a significant correlation between parent and offspring weights. • However, there is also a considerable variation among the offspring weights. This is due to variations in both genetics and env ...
... • In general, heavy parents gave heavy offspring and light parents gave light offspring. That is, there is a significant correlation between parent and offspring weights. • However, there is also a considerable variation among the offspring weights. This is due to variations in both genetics and env ...
quantitative genetics
... • In general, heavy parents gave heavy offspring and light parents gave light offspring. That is, there is a significant correlation between parent and offspring weights. • However, there is also a considerable variation among the offspring weights. This is due to variations in both genetics and env ...
... • In general, heavy parents gave heavy offspring and light parents gave light offspring. That is, there is a significant correlation between parent and offspring weights. • However, there is also a considerable variation among the offspring weights. This is due to variations in both genetics and env ...
Richard Bentall
... • Heritability is often misunderstood to be a gene/environment causation ratio, because it is defined as the percentage of the variance in a trait that is attributable to genes (which looks like a G/E ratio) = variance with genes variance with genes + variance with environment If variance in the env ...
... • Heritability is often misunderstood to be a gene/environment causation ratio, because it is defined as the percentage of the variance in a trait that is attributable to genes (which looks like a G/E ratio) = variance with genes variance with genes + variance with environment If variance in the env ...
Nervous System Development: Epigenesis
... preliminary for the next Development is four-dimensional Very early in development, most environmental events controlling gene expression are internal ...
... preliminary for the next Development is four-dimensional Very early in development, most environmental events controlling gene expression are internal ...
DEBATE HUMAN IMPACT ON THE ENVIRONMENT Points for
... Wars There are two points: positive effect & negative effect ...
... Wars There are two points: positive effect & negative effect ...