Epigenetics - HudsonAlpha Institute for Biotechnology
... yellow twin is not a change in the DNA sequence of the agouti gene. Instead, the difference stems from a tiny molecular tag made of carbon and hydrogen. In the healthy mice, this tag, called a methyl group, binds to the agouti gene, silencing it during the majority of development (figure 1). No meth ...
... yellow twin is not a change in the DNA sequence of the agouti gene. Instead, the difference stems from a tiny molecular tag made of carbon and hydrogen. In the healthy mice, this tag, called a methyl group, binds to the agouti gene, silencing it during the majority of development (figure 1). No meth ...
6.4 Traits, Genes, and Alleles
... • An a______ is any alternative form of a gene occurring at a specific locus on a chromosome. – Each parent donates one allele for every gene. – H___________s describes two alleles that are the same at a specific locus. – H___________s describes two alleles that are different at a specific locus. ...
... • An a______ is any alternative form of a gene occurring at a specific locus on a chromosome. – Each parent donates one allele for every gene. – H___________s describes two alleles that are the same at a specific locus. – H___________s describes two alleles that are different at a specific locus. ...
Genetics webquest - Sciencelearn Hub
... STUDENT ACTIVITY: Genetics webquest Activity idea In this activity, students carry out a genetics webquest using resources from the Science Learning Hub or a genetics animation from the Learn Genetics website. By ...
... STUDENT ACTIVITY: Genetics webquest Activity idea In this activity, students carry out a genetics webquest using resources from the Science Learning Hub or a genetics animation from the Learn Genetics website. By ...
Natural Selection
... favors one end of a range over another. • Disruptive selection: disfavors the midrange. • Stabilizing selection: favors the mid-range. ...
... favors one end of a range over another. • Disruptive selection: disfavors the midrange. • Stabilizing selection: favors the mid-range. ...
that evolution would not occur
... population was large, say 10, 000, you would expect 200 frogs to carry the allele. If severe weather conditions caused 50% of them to die, then you would expect 100 of 500 surviving frogs to carry the allele. But in this case the species is endangered and there are only 100 frogs. In this case only ...
... population was large, say 10, 000, you would expect 200 frogs to carry the allele. If severe weather conditions caused 50% of them to die, then you would expect 100 of 500 surviving frogs to carry the allele. But in this case the species is endangered and there are only 100 frogs. In this case only ...
Slide 1
... population was large, say 10, 000, you would expect 200 frogs to carry the allele. If severe weather conditions caused 50% of them to die, then you would expect 100 of 500 surviving frogs to carry the allele. But in this case the species is endangered and there are only 100 frogs. In this case only ...
... population was large, say 10, 000, you would expect 200 frogs to carry the allele. If severe weather conditions caused 50% of them to die, then you would expect 100 of 500 surviving frogs to carry the allele. But in this case the species is endangered and there are only 100 frogs. In this case only ...
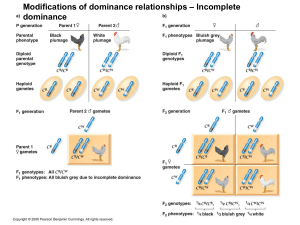
Modifications of dominance relationships – Incomplete dominance
... In some plants a red pigment, cyanidin, is synthesized from colorless precursor. The addition of a hydroxyl group (OH) to cyanidin molecules causes it to become purple. In a cros between two randomly selected purple plants the following ...
... In some plants a red pigment, cyanidin, is synthesized from colorless precursor. The addition of a hydroxyl group (OH) to cyanidin molecules causes it to become purple. In a cros between two randomly selected purple plants the following ...
Case Study: Genetic Control of Reward System
... “While the sample size in this study was fairly substantial for an imaging study, it is rather small for a genetics study. The reviewer appreciates the logistical problems and cost of a very large scale imaging x genetics study, and their sample size certainly falls within the scope of others of thi ...
... “While the sample size in this study was fairly substantial for an imaging study, it is rather small for a genetics study. The reviewer appreciates the logistical problems and cost of a very large scale imaging x genetics study, and their sample size certainly falls within the scope of others of thi ...
Ch. 16 The Evolution of Populations and Speciation
... variation of a trait are more fit than individuals w/ the average form of the trait. D. Sexual Selection- females choosing male mates based upon certain traits. – Genes of successful reproducers not of those that merely survive are amplified through natural selection. ...
... variation of a trait are more fit than individuals w/ the average form of the trait. D. Sexual Selection- females choosing male mates based upon certain traits. – Genes of successful reproducers not of those that merely survive are amplified through natural selection. ...
Essential Standard: 1.1 Understanding the relationship between
... Crossing over Fertilization Independent assortment Meiosis Nondisjunction Random assortment Sexual reproduction ...
... Crossing over Fertilization Independent assortment Meiosis Nondisjunction Random assortment Sexual reproduction ...
Chapter 11
... •Sexual reproduction creates unique combination of genes. Any human couple can produce a child with one of about 70 trillion different combinations –independent assortment of chromosomes in meiosis –random fertilization of gametes –Crossing-over (exchange of chromosome segments between homologous ch ...
... •Sexual reproduction creates unique combination of genes. Any human couple can produce a child with one of about 70 trillion different combinations –independent assortment of chromosomes in meiosis –random fertilization of gametes –Crossing-over (exchange of chromosome segments between homologous ch ...
evolution of populations
... result of radiation of chemicals in the environment. Mutations do not always affect an organism’s phenotype. o Some can affect an organism’s fitness, or its ability to survive and reproduce in its environment. Other mutations may have no effect on fitness ...
... result of radiation of chemicals in the environment. Mutations do not always affect an organism’s phenotype. o Some can affect an organism’s fitness, or its ability to survive and reproduce in its environment. Other mutations may have no effect on fitness ...
03HeredityEnvironment2
... After an egg is fertilized, it is called what? The 23rd. Pair of chromosomes in women are: The 23rd. Pair of chromosomes in men are: What is the monozygotic and dizygotic twins? ...
... After an egg is fertilized, it is called what? The 23rd. Pair of chromosomes in women are: The 23rd. Pair of chromosomes in men are: What is the monozygotic and dizygotic twins? ...
BSC 350 Classical and Molecular Genetics Master Syllabus
... 3. Analyze genetic data to determine the modes of inheritance and predict outcomes in future generations. 4. Calculate genetics predictions using Hardy-Weinberg equations, Punnett-squares, estimate responses to selection using quantitative genetic analysis, two and three point test-crosses, variance ...
... 3. Analyze genetic data to determine the modes of inheritance and predict outcomes in future generations. 4. Calculate genetics predictions using Hardy-Weinberg equations, Punnett-squares, estimate responses to selection using quantitative genetic analysis, two and three point test-crosses, variance ...
Heredity and Genetics Vocabulary (Part 2) 1. Traits: A
... Inheritance: receiving genetic qualities that are passed from parent to offspring. Genetics: The scientific study of heredity. Allele: A form of a gene for a specific trait. Offspring: The new organisms produced by one or two parent organisms. Punnett square: A chart used to show all the ways genes ...
... Inheritance: receiving genetic qualities that are passed from parent to offspring. Genetics: The scientific study of heredity. Allele: A form of a gene for a specific trait. Offspring: The new organisms produced by one or two parent organisms. Punnett square: A chart used to show all the ways genes ...
who, icidh, 1980 - EMGO Institute for Health and Care Research
... Epilepsy, dementia, depression? ...
... Epilepsy, dementia, depression? ...
Chapter 12 Review & Wrap-up
... 10. In this type of inheritance, the phenotype of the heterozygote is intermediate to those of the two homozygotes. ...
... 10. In this type of inheritance, the phenotype of the heterozygote is intermediate to those of the two homozygotes. ...
Mendel and The Gene Idea
... • Phenotype – an organism's traits or physical appearance (purple or white ...
... • Phenotype – an organism's traits or physical appearance (purple or white ...
Science-Dragon Genetics - Florida Department of Education
... Direct Link: http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/exchange/waldron/dragongenetics1 This is a lab/activity that uses dragons as "research subjects" for genetics research. It highlights independent assortment as well as gene linkage. Students will do the first part of the activity using independent assortment ...
... Direct Link: http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/exchange/waldron/dragongenetics1 This is a lab/activity that uses dragons as "research subjects" for genetics research. It highlights independent assortment as well as gene linkage. Students will do the first part of the activity using independent assortment ...
Basic genetic evaluation in obstetrics
... preceding five generations, the likelihood of their inheriting an identical allele ( from their common ancestor) and passing it to their child is high • Sharing of Genes • Mating between third degree relatives who share 1/16 of genes EX mating between first cousin, a half uncle or aunt, a half niece ...
... preceding five generations, the likelihood of their inheriting an identical allele ( from their common ancestor) and passing it to their child is high • Sharing of Genes • Mating between third degree relatives who share 1/16 of genes EX mating between first cousin, a half uncle or aunt, a half niece ...
Genetics and Heredity
... • Chromosomes are made up of many genes joined together like beads on a string. • The chromosomes in a pair may have different alleles for some genes and the same allele for others. ...
... • Chromosomes are made up of many genes joined together like beads on a string. • The chromosomes in a pair may have different alleles for some genes and the same allele for others. ...
GENETICS Anno accademico 2016/17 CdS BIOLOGICAL
... hemoglobin: complete dominance, co-dominance, incomplete dominance depending on the analyzed phenotype. Interactions between allelic series in single locus, as Clover. lethal alleles. Examples of the rat "yellow", the dwarfism achondroplastic and the Isle of Man cat. segregation ratios 2: 1 which ar ...
... hemoglobin: complete dominance, co-dominance, incomplete dominance depending on the analyzed phenotype. Interactions between allelic series in single locus, as Clover. lethal alleles. Examples of the rat "yellow", the dwarfism achondroplastic and the Isle of Man cat. segregation ratios 2: 1 which ar ...
Behavioural genetics

Behavioural genetics, also commonly referred to as behaviour genetics, is the field of study that examines the role of genetic and environmental influences on animal (including human) behaviour. Often associated with the ""nature versus nurture"" debate, behavioural genetics is highly interdisciplinary, involving contributions from biology, neuroscience, genetics, epigenetics, ethology, psychology, and statistics. Behavioural geneticists study the inheritance of behavioural traits. In humans, this information is often gathered through the use of the twin study or adoption study. In animal studies, breeding, transgenesis, and gene knockout techniques are common. Psychiatric genetics is a closely related field.