Glossary of technical terms in animal genetics for course WAP 214
... Breeding objective -- A general goal for a breeding program, a notion of what constitutes the best animal. See also Selection criterion. Breeding value -- The value of an individual as a parent. The effects of an animal's genes that can be passed on to offspring. Because one-half of an animal's gene ...
... Breeding objective -- A general goal for a breeding program, a notion of what constitutes the best animal. See also Selection criterion. Breeding value -- The value of an individual as a parent. The effects of an animal's genes that can be passed on to offspring. Because one-half of an animal's gene ...
Chapter 2 Outline
... The Influence of Heredity on Development a. Genetic influences on development b. Mitosis – genetic code carried into new cells in our bodied c. Meiosis – sperm and ova are produced this way d. Twins Monozygote, dizygote Chromosomes and Genes a. Chromosomes, genes, polygenic, DNA defined b. Discussio ...
... The Influence of Heredity on Development a. Genetic influences on development b. Mitosis – genetic code carried into new cells in our bodied c. Meiosis – sperm and ova are produced this way d. Twins Monozygote, dizygote Chromosomes and Genes a. Chromosomes, genes, polygenic, DNA defined b. Discussio ...
In heterozygote, one allele may conceal the
... 3. The Principle of Independent Assortment The alleles of different genes segregate or assort, independently of each other it can be explained by dihybrid crosses Aim of dihybrid crosses To see if the two seed trait (color and texture) are inherited independently Each trait is controled by a dif ...
... 3. The Principle of Independent Assortment The alleles of different genes segregate or assort, independently of each other it can be explained by dihybrid crosses Aim of dihybrid crosses To see if the two seed trait (color and texture) are inherited independently Each trait is controled by a dif ...
• Recognize Mendel`s contribution to the field of genetics. • Review
... Phenotype of Hydrangea flower color • Blue flowers in highly acid soil • Pink flowers in neutral or slightly acid soil ...
... Phenotype of Hydrangea flower color • Blue flowers in highly acid soil • Pink flowers in neutral or slightly acid soil ...
AP Biology Unit 5 Packet-- Classical Genetics/Heredity
... Classical Genetics (Mendelian Genetics) Gregor Mendel: The Father of Genetics What is genetics? In its simplest form, genetics is the study of heredity. It explains how certain characteristics are passed on from parents to children. Much of what we know about genetics was discovered by the monk Greg ...
... Classical Genetics (Mendelian Genetics) Gregor Mendel: The Father of Genetics What is genetics? In its simplest form, genetics is the study of heredity. It explains how certain characteristics are passed on from parents to children. Much of what we know about genetics was discovered by the monk Greg ...
One more funny wrinkle. . . Another example
... feeding, and setters which tend to stay in one place as they feed • This is governed by one gene with two alleles: forR and fors • Work by Sokolowski et al. (1997) suggests that density-dependent selection maintains these two alleles in the population—when one is most common, the other has the s ...
... feeding, and setters which tend to stay in one place as they feed • This is governed by one gene with two alleles: forR and fors • Work by Sokolowski et al. (1997) suggests that density-dependent selection maintains these two alleles in the population—when one is most common, the other has the s ...
Mendelian Inheritance - Santa Susana High School
... characteristics. • For each characteristic, an organism inherits two alleles. One from each parent. • If 2 alleles inherited differ, the dominant one is expressed • Law of Segregation - Two alleles for a heritable characteristic are separated during gametogenesis and end up indifferent gametes • Law ...
... characteristics. • For each characteristic, an organism inherits two alleles. One from each parent. • If 2 alleles inherited differ, the dominant one is expressed • Law of Segregation - Two alleles for a heritable characteristic are separated during gametogenesis and end up indifferent gametes • Law ...
The Practical Reach of Pharmacogenomics: are Custom Drugs a Possibility?
... Just two years after studies of the genome the Genome Wide Association studies launched which accounts for the skyrocketing results. Over time with better and better technology more diseases will be discovered and the strength of DTC will only increase. There are three main reasons the GWA studi ...
... Just two years after studies of the genome the Genome Wide Association studies launched which accounts for the skyrocketing results. Over time with better and better technology more diseases will be discovered and the strength of DTC will only increase. There are three main reasons the GWA studi ...
SYLABUS
... Chromosome analysis using the banding and molecular techniques. Human normal karyotype. Alignment of chromosomes in karyograms – practical exercise. International System of Cytogenetic Nomenclature (ISCN). Basics of molecular cytogenetics. Prenatal diagnosis possibilities, in utero invasive and noni ...
... Chromosome analysis using the banding and molecular techniques. Human normal karyotype. Alignment of chromosomes in karyograms – practical exercise. International System of Cytogenetic Nomenclature (ISCN). Basics of molecular cytogenetics. Prenatal diagnosis possibilities, in utero invasive and noni ...
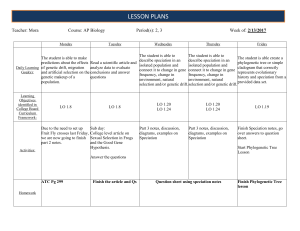
lesson Plans - Lemon Bay High School
... Due to the need to set up Fruit Fly crosses last Friday, we are now going to finish part 2 notes. Activities: ...
... Due to the need to set up Fruit Fly crosses last Friday, we are now going to finish part 2 notes. Activities: ...
Psycho-genetics and Genetic Influences on Behavior
... PSYCHOLOGY - Vol .II - Psycho-genetics and Genetic Influences on Behavior - Carlo Calzone, Mariano S. Pergola ...
... PSYCHOLOGY - Vol .II - Psycho-genetics and Genetic Influences on Behavior - Carlo Calzone, Mariano S. Pergola ...
Genetics - Faculty Web Sites
... have received the appropriate blueproducing gene from both parents If they received it from only one parent or from neither they will end up with brown eyes (dominant) ...
... have received the appropriate blueproducing gene from both parents If they received it from only one parent or from neither they will end up with brown eyes (dominant) ...
7.14ABCTestReviewKEY
... 11. Where are genes stored in the cell? On chromosomes within the nucleus of a cell 12. What is a trait? is a physical or behavioral characteristic expressed by your genes 13. What is a genotype? The organisms genetic makeup; it consist of one allele from each parent; represented by capital and low ...
... 11. Where are genes stored in the cell? On chromosomes within the nucleus of a cell 12. What is a trait? is a physical or behavioral characteristic expressed by your genes 13. What is a genotype? The organisms genetic makeup; it consist of one allele from each parent; represented by capital and low ...
No Slide Title
... • experienced an ice-age, • undergone a transition from hunter-gatherer to agricultural societies, • witnessed rapid increases in densities, • new proximity of farmers to animal pathogens. Recent statistical analyses of genetic data reveal hundreds of human genes that show signals of very strong and ...
... • experienced an ice-age, • undergone a transition from hunter-gatherer to agricultural societies, • witnessed rapid increases in densities, • new proximity of farmers to animal pathogens. Recent statistical analyses of genetic data reveal hundreds of human genes that show signals of very strong and ...
Chapter Two Theories - Dimensions Family Therapy
... Individuals with a parent, sibling, or child with a serious genetic condition known to be dominant or recessive Couples with history of early spontaneous abortions, stillbirths, or infertility Couples from the same ethnic group or ...
... Individuals with a parent, sibling, or child with a serious genetic condition known to be dominant or recessive Couples with history of early spontaneous abortions, stillbirths, or infertility Couples from the same ethnic group or ...
File
... A genotype refers to the makeup of a specific set of genes. – Your alleles that you inherited A phenotype is the physical expression of a trait. – What you see ...
... A genotype refers to the makeup of a specific set of genes. – Your alleles that you inherited A phenotype is the physical expression of a trait. – What you see ...
genes
... No allele is dominant over another Heterozygous phenotype is a blending of the 2 homozygous phenotypes For Example: Four O’Clock Flowers Red (RR) X White (WW) Results in pink flowers (RW) ...
... No allele is dominant over another Heterozygous phenotype is a blending of the 2 homozygous phenotypes For Example: Four O’Clock Flowers Red (RR) X White (WW) Results in pink flowers (RW) ...
Activists Call For A Treaty to Share the Genetic Commons
... arrangements and consultative initiatives based on the principle of selling prospecting rights to genetic information and extending intellectual property protection to life are unacceptable mechanisms for governing the gene pool." Vandana Shiva of the Research Foundation for Science, Technology and ...
... arrangements and consultative initiatives based on the principle of selling prospecting rights to genetic information and extending intellectual property protection to life are unacceptable mechanisms for governing the gene pool." Vandana Shiva of the Research Foundation for Science, Technology and ...
Genetics Unit Review 1. How are the steps of meiosis different from
... 9. In pea plants tall is dominant over short. Imagine two pea plants, both being heterozygous for the trait plant height, are crossed. Using the letter T, show the genotypes of the parents and the resulting Punnett square. What are the phenotypic and genotypic ratios? ...
... 9. In pea plants tall is dominant over short. Imagine two pea plants, both being heterozygous for the trait plant height, are crossed. Using the letter T, show the genotypes of the parents and the resulting Punnett square. What are the phenotypic and genotypic ratios? ...
Beyond Dominant and Recessive Alleles
... Both alleles contribute to the phenotype of the organism. Ex. Cattle red hair is codominant with the allele for white hair. Cattle with both alleles are roan (pinkish brown). Ex. Chickens with speckled feathers. ...
... Both alleles contribute to the phenotype of the organism. Ex. Cattle red hair is codominant with the allele for white hair. Cattle with both alleles are roan (pinkish brown). Ex. Chickens with speckled feathers. ...
Y-Linked Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Autosomal Dominant
... In some instances, affected individuals appear either to be more severely affected, or to have an earlier age of onset The heterozygote with a intermediate phenotype is consistent with a haploinsufficiency loss of-function mutation ...
... In some instances, affected individuals appear either to be more severely affected, or to have an earlier age of onset The heterozygote with a intermediate phenotype is consistent with a haploinsufficiency loss of-function mutation ...
Behavioural genetics

Behavioural genetics, also commonly referred to as behaviour genetics, is the field of study that examines the role of genetic and environmental influences on animal (including human) behaviour. Often associated with the ""nature versus nurture"" debate, behavioural genetics is highly interdisciplinary, involving contributions from biology, neuroscience, genetics, epigenetics, ethology, psychology, and statistics. Behavioural geneticists study the inheritance of behavioural traits. In humans, this information is often gathered through the use of the twin study or adoption study. In animal studies, breeding, transgenesis, and gene knockout techniques are common. Psychiatric genetics is a closely related field.