Camelid Geneticists Chart Course for Future Research
... and llamas suffer no apparent ill-effects of this hyperglycemia. It might be important for researchers investigating human diabetes to know how camelids remain healthy while maintaining such high levels and why? Genetic technology is helping to solve these kinds of problems in other species and ther ...
... and llamas suffer no apparent ill-effects of this hyperglycemia. It might be important for researchers investigating human diabetes to know how camelids remain healthy while maintaining such high levels and why? Genetic technology is helping to solve these kinds of problems in other species and ther ...
Linkage, Recombination, and Crossing Over
... • The frequency of recombination measures the intensity of linkage. In the absence of linkage, this frequency is 50 percent; for very tight linkage, it is close to zero. ...
... • The frequency of recombination measures the intensity of linkage. In the absence of linkage, this frequency is 50 percent; for very tight linkage, it is close to zero. ...
File
... Investigate the transmission of characteristics from parents to offspring, and identify examples of characteristics in offspring that are: The same as the characteristics of both parents The same as the characteristics of one parent Intermediate between parent characteristics Different fro ...
... Investigate the transmission of characteristics from parents to offspring, and identify examples of characteristics in offspring that are: The same as the characteristics of both parents The same as the characteristics of one parent Intermediate between parent characteristics Different fro ...
Chapter 8 - Lamar County School District
... (Remember, haploid or half plus haploid or half gives diploid or whole?) ...
... (Remember, haploid or half plus haploid or half gives diploid or whole?) ...
Chapter 11 Learning Goals
... 1. Contrast the number of chromosomes in body cells and in gametes. (Compare diploid (2n) and haploid (n) cells.) 2. Describe homologous chromosomes. 3. Define gamete, sperm, egg and zygote. 4. Explain sexual reproduction, and why it has an evolutionary advantage. 5. Compare and contrast the process ...
... 1. Contrast the number of chromosomes in body cells and in gametes. (Compare diploid (2n) and haploid (n) cells.) 2. Describe homologous chromosomes. 3. Define gamete, sperm, egg and zygote. 4. Explain sexual reproduction, and why it has an evolutionary advantage. 5. Compare and contrast the process ...
Chapter 3 Mendelian Genetics
... hybridization was performed with pollen and ovum for all crosses to prove that pollen or ovum didn’t play a role in expression of the trait. ...
... hybridization was performed with pollen and ovum for all crosses to prove that pollen or ovum didn’t play a role in expression of the trait. ...
Genetics
... tell the difference between the two) • Wild Type is the typical form of the organism, strain, or gene • Pure traits are those with identical genes (homozygous). • Hybrids have mixed genes for the same trait (heterozygous). • Gametes only carry one allele for each trait (they are haploid) ...
... tell the difference between the two) • Wild Type is the typical form of the organism, strain, or gene • Pure traits are those with identical genes (homozygous). • Hybrids have mixed genes for the same trait (heterozygous). • Gametes only carry one allele for each trait (they are haploid) ...
PopStratGEMS2012 - Division of Statistical Genomics
... What is Population Stratification (PS) ? In narrow sense PS is the presence of a systematic difference in allele frequencies between subpopulations in a population, possibly due to different ancestry or origins, especially in the context of genetic association studies. Population stratification is ...
... What is Population Stratification (PS) ? In narrow sense PS is the presence of a systematic difference in allele frequencies between subpopulations in a population, possibly due to different ancestry or origins, especially in the context of genetic association studies. Population stratification is ...
Genetic Testing
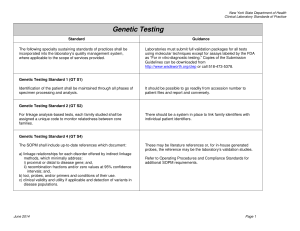
... For linkage analysis-based tests, each family studied shall be assigned a unique code to monitor relatedness between core ...
... For linkage analysis-based tests, each family studied shall be assigned a unique code to monitor relatedness between core ...
Human Genetic Disorders - Effingham County Schools
... • Trisomy disorders are considered major chromosomal abnormalities that involve the addition of an extra chromosome or part of a chromosome. Most individuals will only have two copies of a single chromosome one that was received from Mom and one received from Dad. • These disorders are caused by a n ...
... • Trisomy disorders are considered major chromosomal abnormalities that involve the addition of an extra chromosome or part of a chromosome. Most individuals will only have two copies of a single chromosome one that was received from Mom and one received from Dad. • These disorders are caused by a n ...
Punnett Squares
... PUNNETT SQUARES A punnett square is a diagram used to predict the outcome of a breeding experiment. ...
... PUNNETT SQUARES A punnett square is a diagram used to predict the outcome of a breeding experiment. ...
DRAGON GENETICS LAB
... Your instructor does not care which partner worked the hardest. This is a no divorce classroom. The lab must be completed on time. 2. Each partner must pick up five Popsicle sticks -- one of each color of autosome, and one sex chromosome stick. Each side of a stick represents a chromosome, and the t ...
... Your instructor does not care which partner worked the hardest. This is a no divorce classroom. The lab must be completed on time. 2. Each partner must pick up five Popsicle sticks -- one of each color of autosome, and one sex chromosome stick. Each side of a stick represents a chromosome, and the t ...
DRAGON GENETICS LAB
... Your instructor does not care which partner worked the hardest. This is a no divorce classroom. The lab must be completed on time. 2. Each partner must pick up five Popsicle sticks -- one of each color of autosome, and one sex chromosome stick. Each side of a stick represents a chromosome, and the t ...
... Your instructor does not care which partner worked the hardest. This is a no divorce classroom. The lab must be completed on time. 2. Each partner must pick up five Popsicle sticks -- one of each color of autosome, and one sex chromosome stick. Each side of a stick represents a chromosome, and the t ...
DRAGON GENETICS LAB -- Principles of Mendelian Genetics
... Your instructor does not care which partner worked the hardest. This is a no divorce classroom. The lab must be completed on time. 2. Each partner must pick up five Popsicle sticks -- one of each color of autosome, and one sex chromosome stick. Each side of a stick represents a chromosome, and the t ...
... Your instructor does not care which partner worked the hardest. This is a no divorce classroom. The lab must be completed on time. 2. Each partner must pick up five Popsicle sticks -- one of each color of autosome, and one sex chromosome stick. Each side of a stick represents a chromosome, and the t ...
Dragon Genetics2 - Biology Junction
... Your instructor does not care which partner worked the hardest. This is a no divorce classroom. The lab must be completed on time. 2. Each partner must pick up five Popsicle sticks -- one of each color of autosome, and one sex chromosome stick. Each side of a stick represents a chromosome, and the t ...
... Your instructor does not care which partner worked the hardest. This is a no divorce classroom. The lab must be completed on time. 2. Each partner must pick up five Popsicle sticks -- one of each color of autosome, and one sex chromosome stick. Each side of a stick represents a chromosome, and the t ...
Heredity and Health-Related Fitness
... Both approaches are very useful in delineating how important genes are for a give phenotype. However, they differ considerably in the type of information they can provide. The first approach is asking whether individual differences for a given phenotype are caused by DNA sequence variation, gene -en ...
... Both approaches are very useful in delineating how important genes are for a give phenotype. However, they differ considerably in the type of information they can provide. The first approach is asking whether individual differences for a given phenotype are caused by DNA sequence variation, gene -en ...
Basic Assumptions to Make When Solving Genetics Problems
... on autosomes and are not sex-linked. (Note: “Sex-linked” historically has been used to describe genes “on the X chromosome”. Genes carried on the Y chromosome are now recognized but tend to be described as “Y-linked” rather than sex-linked.) 3. Is there a lethal allele? If a gene is lethal, then you ...
... on autosomes and are not sex-linked. (Note: “Sex-linked” historically has been used to describe genes “on the X chromosome”. Genes carried on the Y chromosome are now recognized but tend to be described as “Y-linked” rather than sex-linked.) 3. Is there a lethal allele? If a gene is lethal, then you ...
The Science of Inheritance
... The work of Gregor Mendel Earlier Notions of Inheritance – Blending – Spermists – Ovists ...
... The work of Gregor Mendel Earlier Notions of Inheritance – Blending – Spermists – Ovists ...
Genetics - Humble ISD
... monosaccharides into starch and form smooth seeds when they dry. Mendel’s Law of Heredity (#2) • Law of Independent Assortment o Each pair of alleles — for each trait — segregates into gametes independently = independent assortment. o 4 classes of gametes — YR, Yr, yR, yr — are produced in equal amo ...
... monosaccharides into starch and form smooth seeds when they dry. Mendel’s Law of Heredity (#2) • Law of Independent Assortment o Each pair of alleles — for each trait — segregates into gametes independently = independent assortment. o 4 classes of gametes — YR, Yr, yR, yr — are produced in equal amo ...
Basic Genetics and Genomics: A Primer for Nurses
... The completion of the Human Genome Project...is leading to a new type of medicine, called personalized medicine.The Human Genome Project (HGP) was an international research effort to read and map all of the genes in the human body, which together are known as the human genome. The HGP, completed in ...
... The completion of the Human Genome Project...is leading to a new type of medicine, called personalized medicine.The Human Genome Project (HGP) was an international research effort to read and map all of the genes in the human body, which together are known as the human genome. The HGP, completed in ...
Modes of Inheritance
... to black (n) and brown eyes (B) are dominant to blue (b). The alpha male is black with blue eyes and the alpha female is heterozygous for normal colored coat and for brown eyes. What are their genotypes? ...
... to black (n) and brown eyes (B) are dominant to blue (b). The alpha male is black with blue eyes and the alpha female is heterozygous for normal colored coat and for brown eyes. What are their genotypes? ...
dragon genetics lab - Aurora Public Schools
... Your instructor does not care which partner worked the hardest. This is a no divorce classroom. The lab must be completed on time. 2. Each partner must pick up five Popsicle sticks -- one of each color of autosome, and one sex chromosome stick. Each side of a stick represents a chromosome, and the t ...
... Your instructor does not care which partner worked the hardest. This is a no divorce classroom. The lab must be completed on time. 2. Each partner must pick up five Popsicle sticks -- one of each color of autosome, and one sex chromosome stick. Each side of a stick represents a chromosome, and the t ...
Behavioural genetics

Behavioural genetics, also commonly referred to as behaviour genetics, is the field of study that examines the role of genetic and environmental influences on animal (including human) behaviour. Often associated with the ""nature versus nurture"" debate, behavioural genetics is highly interdisciplinary, involving contributions from biology, neuroscience, genetics, epigenetics, ethology, psychology, and statistics. Behavioural geneticists study the inheritance of behavioural traits. In humans, this information is often gathered through the use of the twin study or adoption study. In animal studies, breeding, transgenesis, and gene knockout techniques are common. Psychiatric genetics is a closely related field.