Specifications
... 6.- Experiments of Partial Discharge and Corona. 7.- Experiments on PD and Gliding Discharges. 8.- Power frequency and impulse voltage tests on power transformer. 9.- Break down of Gases. ...
... 6.- Experiments of Partial Discharge and Corona. 7.- Experiments on PD and Gliding Discharges. 8.- Power frequency and impulse voltage tests on power transformer. 9.- Break down of Gases. ...
TRANSIENTS AND RC TIME CONSTANTS The capacitor has a
... voltage waveforms that are repetitive. The oscilloscope can continuously display some portion of a periodic input waveform. A transient waveform, however, occurs only once, and is therefore not repetitive. It can be displayed conveniently only on an oscilloscope with memory. For the oscilloscopes in ...
... voltage waveforms that are repetitive. The oscilloscope can continuously display some portion of a periodic input waveform. A transient waveform, however, occurs only once, and is therefore not repetitive. It can be displayed conveniently only on an oscilloscope with memory. For the oscilloscopes in ...
i(t)
... Source-free response: The response is due to the initial energy stored and the physical characteristics of the circuit and not due to some external sources. ...
... Source-free response: The response is due to the initial energy stored and the physical characteristics of the circuit and not due to some external sources. ...
1. Pre-Lab Introduction
... biases. Making the same assumptions, the hybrid- π and h-parameter models are equivalent at midband frequencies. For a transistor to operate as an amplifier, it must have a stable bias in the active region. To bias a transistor, a constant DC current must be established in the collector and emitter. ...
... biases. Making the same assumptions, the hybrid- π and h-parameter models are equivalent at midband frequencies. For a transistor to operate as an amplifier, it must have a stable bias in the active region. To bias a transistor, a constant DC current must be established in the collector and emitter. ...
PT2399 - The Valve Wizard
... 1kΩ is not recommended, due to excessive current demand. With a 100Ω delay resistor a delay time of 25ms is achieved with most samples. A zero-ohm delay resistor (dead short) gives almost no further decrease in delay time, and is not recommended. Latch up: If the delay resistance is less than 1kΩ th ...
... 1kΩ is not recommended, due to excessive current demand. With a 100Ω delay resistor a delay time of 25ms is achieved with most samples. A zero-ohm delay resistor (dead short) gives almost no further decrease in delay time, and is not recommended. Latch up: If the delay resistance is less than 1kΩ th ...
INF5490 RF MEMS
... C can be tuned by changing the area, C = ε A / g + No theoretical limit for TR + Pull-in effect avoided ÷ Photolithography determines precision of ...
... C can be tuned by changing the area, C = ε A / g + No theoretical limit for TR + Pull-in effect avoided ÷ Photolithography determines precision of ...
Chapter 22 notes
... resonance: a peaking of the current amplitude at a certain frequency in a constant voltage circuit. resonance angular frequency : the angular frequency ω0 at which the resonance peak occurs. The inductive and capacitive reactance are equal at the resonance angular frequency so ...
... resonance: a peaking of the current amplitude at a certain frequency in a constant voltage circuit. resonance angular frequency : the angular frequency ω0 at which the resonance peak occurs. The inductive and capacitive reactance are equal at the resonance angular frequency so ...
8.3.3 series and parallel circuits
... Connected in series/parallel to prevent significant changes in current and voltage in the circuit Voltmeter is attached in parallel and have high resistance o When voltage is constant, V=IR – a high resistance will reduce current passing through o Current divides between paths – low current reduces ...
... Connected in series/parallel to prevent significant changes in current and voltage in the circuit Voltmeter is attached in parallel and have high resistance o When voltage is constant, V=IR – a high resistance will reduce current passing through o Current divides between paths – low current reduces ...
AN9601: Using the HI7190 with Single +5V Supply
... and S4 are open during this half cycle.) During the second half cycle of operation, switches S2 and S4 are closed, with S1 and S3 open, thereby shifting capacitor C1 to C2 such that the voltage on C2 is exactly V+, assuming ideal switches and no load on C2. The ICL7660S approaches this ideal situati ...
... and S4 are open during this half cycle.) During the second half cycle of operation, switches S2 and S4 are closed, with S1 and S3 open, thereby shifting capacitor C1 to C2 such that the voltage on C2 is exactly V+, assuming ideal switches and no load on C2. The ICL7660S approaches this ideal situati ...
Some basic electronics for radio
... charged object with a conductive pathway (a path through which electrons can travel, such as a wire, salt water, or a metal doorknob), we get what we call electric current when the electrons travel from one object to another to balance the charges. By changing the characteristics of this electric cu ...
... charged object with a conductive pathway (a path through which electrons can travel, such as a wire, salt water, or a metal doorknob), we get what we call electric current when the electrons travel from one object to another to balance the charges. By changing the characteristics of this electric cu ...
WAM Chapter 5: Measuring Rotation
... variable resistor or potentiometer. They are used in dials, joysticks, and many other devices which need to produce an output in reference to a position. Potentiometers can be packaged many different ways. ...
... variable resistor or potentiometer. They are used in dials, joysticks, and many other devices which need to produce an output in reference to a position. Potentiometers can be packaged many different ways. ...
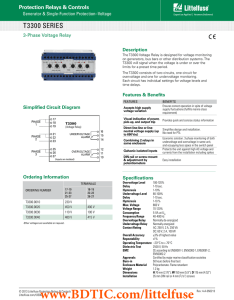
Download T3300 Datasheet
... The T3300 Voltage Relay is designed for voltage monitoring on generators, bus bars or other distribution systems. The T3300 will signal when the voltage is under or over the limits for a preset time period. The T3300 consists of two circuits, one circuit for overvoltage and one for undervoltage moni ...
... The T3300 Voltage Relay is designed for voltage monitoring on generators, bus bars or other distribution systems. The T3300 will signal when the voltage is under or over the limits for a preset time period. The T3300 consists of two circuits, one circuit for overvoltage and one for undervoltage moni ...
PPT
... Lecture 4 – capacitance Lecture 5 – resistance Lecture 6 – Kirchhoff’s rules Lecture 7 – RC circuits Lecture 12 & 13 – AC circuits ...
... Lecture 4 – capacitance Lecture 5 – resistance Lecture 6 – Kirchhoff’s rules Lecture 7 – RC circuits Lecture 12 & 13 – AC circuits ...
capacitors for rfi suppression of the ac line
... The most common class of X capacitor as it covers applications using line voltages from 150 to 250VAC (nominal) which are plugged into ordinary wall outlets. In Europe this covers a lot of ground: Computers, hair dryers, fax machines, hand power tools and so on. These capacitors are impulse tested w ...
... The most common class of X capacitor as it covers applications using line voltages from 150 to 250VAC (nominal) which are plugged into ordinary wall outlets. In Europe this covers a lot of ground: Computers, hair dryers, fax machines, hand power tools and so on. These capacitors are impulse tested w ...
CA230009EN
... Faulted capacitors are quickly removed from circuits with busmounted fuses furnished on factory-assembled capacitor blocks. A noncurrent-carrying, stainless steel flipper ejects the fuse leader from its tube when the link melts. Voltage stress across the fuse tube is eliminated by the resulting air ...
... Faulted capacitors are quickly removed from circuits with busmounted fuses furnished on factory-assembled capacitor blocks. A noncurrent-carrying, stainless steel flipper ejects the fuse leader from its tube when the link melts. Voltage stress across the fuse tube is eliminated by the resulting air ...
Capacitor
.jpg?width=300)
A capacitor (originally known as a condenser) is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store electrical energy temporarily in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors (plates) separated by a dielectric (i.e. an insulator that can store energy by becoming polarized). The conductors can be thin films, foils or sintered beads of metal or conductive electrolyte, etc. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's charge capacity. A dielectric can be glass, ceramic, plastic film, air, vacuum, paper, mica, oxide layer etc. Capacitors are widely used as parts of electrical circuits in many common electrical devices. Unlike a resistor, an ideal capacitor does not dissipate energy. Instead, a capacitor stores energy in the form of an electrostatic field between its plates.When there is a potential difference across the conductors (e.g., when a capacitor is attached across a battery), an electric field develops across the dielectric, causing positive charge +Q to collect on one plate and negative charge −Q to collect on the other plate. If a battery has been attached to a capacitor for a sufficient amount of time, no current can flow through the capacitor. However, if a time-varying voltage is applied across the leads of the capacitor, a displacement current can flow.An ideal capacitor is characterized by a single constant value, its capacitance. Capacitance is defined as the ratio of the electric charge Q on each conductor to the potential difference V between them. The SI unit of capacitance is the farad (F), which is equal to one coulomb per volt (1 C/V). Typical capacitance values range from about 1 pF (10−12 F) to about 1 mF (10−3 F).The larger the surface area of the ""plates"" (conductors) and the narrower the gap between them, the greater the capacitance is. In practice, the dielectric between the plates passes a small amount of leakage current and also has an electric field strength limit, known as the breakdown voltage. The conductors and leads introduce an undesired inductance and resistance.Capacitors are widely used in electronic circuits for blocking direct current while allowing alternating current to pass. In analog filter networks, they smooth the output of power supplies. In resonant circuits they tune radios to particular frequencies. In electric power transmission systems, they stabilize voltage and power flow.