Chapter 9 Experiment 7: Electromagnetic Oscillations
... increases in the negative direction, the rate of current change also becomes more negative until it finally becomes zero once again. Now the magnetic flux is zero, but the capacitor has a substantial negative charge and voltage. This negative emf will, similarly, cause a negative current and flux to ...
... increases in the negative direction, the rate of current change also becomes more negative until it finally becomes zero once again. Now the magnetic flux is zero, but the capacitor has a substantial negative charge and voltage. This negative emf will, similarly, cause a negative current and flux to ...
75 VOLT 5 AMP MOSFET H-BRIDGE PWM MOTOR DRIVER
... direction/speed. A 0% duty cycle (continuous TTL low) will mean full voltage to the motor in one direction. A 100% duty cycle (continuous TTL high) will mean full voltage to the motor in the other direction. A 50% duty cycle will hold the motor at 0 RPM. Current sensing is done in this case by a 0.1 ...
... direction/speed. A 0% duty cycle (continuous TTL low) will mean full voltage to the motor in one direction. A 100% duty cycle (continuous TTL high) will mean full voltage to the motor in the other direction. A 50% duty cycle will hold the motor at 0 RPM. Current sensing is done in this case by a 0.1 ...
The following step-by-step procedure may be used to solve RC or
... vii) For t→∞, assume the circuit has been stable for a long time, as in (iii), and replace C's with open circuits and L's with wires. Find vC (t → ∞) or iL (t → ∞) . ...
... vii) For t→∞, assume the circuit has been stable for a long time, as in (iii), and replace C's with open circuits and L's with wires. Find vC (t → ∞) or iL (t → ∞) . ...
Electrostatic motor
... Structure: I recommend using wood as main construction material, as it is a good enough insulator, cheap and easy to work with. If you use woodscrews, make sure they don’t come closer than about two inches to the HV-carrying parts. The structure mostly consists of a stable frame on which the upper a ...
... Structure: I recommend using wood as main construction material, as it is a good enough insulator, cheap and easy to work with. If you use woodscrews, make sure they don’t come closer than about two inches to the HV-carrying parts. The structure mostly consists of a stable frame on which the upper a ...
Electrostatic Microgenerators
... devices, the electrostatic transducer provides a very attractive approach. An electrostatic transducer uses the force between charges stored on electrodes to couple the energy from the mechanical domain into the electric domain. The charge separation Q on the electrodes depends on ...
... devices, the electrostatic transducer provides a very attractive approach. An electrostatic transducer uses the force between charges stored on electrodes to couple the energy from the mechanical domain into the electric domain. The charge separation Q on the electrodes depends on ...
Ch10_PPT_Fund_Elec_Circ_5e
... • It is important to understand a limitation of this circuit. • The larger the multiplication factor, the easier it is for the inverting stage to go out of the linear range. • Thus the larger the multiplier, the smaller the allowable input voltage. • A similar op amp circuit can simulate inductance, ...
... • It is important to understand a limitation of this circuit. • The larger the multiplication factor, the easier it is for the inverting stage to go out of the linear range. • Thus the larger the multiplier, the smaller the allowable input voltage. • A similar op amp circuit can simulate inductance, ...
Lab 9 Handout
... in the prelab. The values from the prelab are the same for this circuit. You will not put a resistor in this circuit; the series resistance of the inductor will act as the resistive component (R = 0.6 Ohms). The measurements in this circuit will be different from the first two. You will be measuring ...
... in the prelab. The values from the prelab are the same for this circuit. You will not put a resistor in this circuit; the series resistance of the inductor will act as the resistive component (R = 0.6 Ohms). The measurements in this circuit will be different from the first two. You will be measuring ...
optimal location of capacitors and capacitor sizing in a
... (RDS), I. INTRODUCTION From the studies, at the distribution side 13% of the total power is exhausted as ohmic losses caused by reactive current flowing in the network. Shunt capacitors are used for the reduction of reactive currents which consequences in loss minimization, power factor improvement, ...
... (RDS), I. INTRODUCTION From the studies, at the distribution side 13% of the total power is exhausted as ohmic losses caused by reactive current flowing in the network. Shunt capacitors are used for the reduction of reactive currents which consequences in loss minimization, power factor improvement, ...
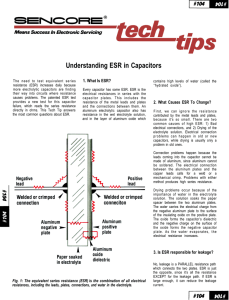
Application Note: ESR Losses In Ceramic Capacitors
... of the line. This procedure insures that the RF excitation does not load the line. See Figure 3. An RF probe located at the high impedance end of the line is connected to a millivoltmeter to measure RF voltage at resonance. From these measurements the bandwidth and Q can be established. ESR is calcu ...
... of the line. This procedure insures that the RF excitation does not load the line. See Figure 3. An RF probe located at the high impedance end of the line is connected to a millivoltmeter to measure RF voltage at resonance. From these measurements the bandwidth and Q can be established. ESR is calcu ...
• Measuring frequencies: 100kHz, 10kHz, 1kHz and 100Hz (120Hz
... Up to ±3.0VDC on generator terminal, set in 0.1V steps (internally generated) Up to ±48V DC ...
... Up to ±3.0VDC on generator terminal, set in 0.1V steps (internally generated) Up to ±48V DC ...
Heathkit CT-1 - Orange County (California) Amateur Radio Club
... shorted or intermittent condition. Capacitors above 50 µµfd (picofarads) can be checked for an open condition when shunted by a low incircuit resistance (greater than 30Ω above 350 µµfd, 400Ω between 100 and 350 µµfd and 2,000Ω between 50 and 100 µµfd). Capacitors up to 20 µfd can be checked for sho ...
... shorted or intermittent condition. Capacitors above 50 µµfd (picofarads) can be checked for an open condition when shunted by a low incircuit resistance (greater than 30Ω above 350 µµfd, 400Ω between 100 and 350 µµfd and 2,000Ω between 50 and 100 µµfd). Capacitors up to 20 µfd can be checked for sho ...
Backup Power Solutions
... Supercapacitors, which are capacitors with up to 100s of farads in value, are emerging as an alternative to batteries in applications where power delivery supercedes total energy storage. Supercapacitors have several advantages over batteries that make them a superior solution when short-term high p ...
... Supercapacitors, which are capacitors with up to 100s of farads in value, are emerging as an alternative to batteries in applications where power delivery supercedes total energy storage. Supercapacitors have several advantages over batteries that make them a superior solution when short-term high p ...
EK33821826
... too slow and unreliable for high speed use. So these ideas remained on hold for nearly two decades until the evolution of FACTS devices. Flexible AC transmission System (FACTS) controllers use thyristor switching devices to provide greater control, speed and flexibility of ac transmission systems [2 ...
... too slow and unreliable for high speed use. So these ideas remained on hold for nearly two decades until the evolution of FACTS devices. Flexible AC transmission System (FACTS) controllers use thyristor switching devices to provide greater control, speed and flexibility of ac transmission systems [2 ...
Project One – AC to DC Converter
... However, once the circuit was entered into PSpice, values could be altered for the capacitor and other resistors to ensure the best result for the output. Performance Analysis Two designs were tested during this project. The first design used a fifth diode in the filter, which proved to drop too muc ...
... However, once the circuit was entered into PSpice, values could be altered for the capacitor and other resistors to ensure the best result for the output. Performance Analysis Two designs were tested during this project. The first design used a fifth diode in the filter, which proved to drop too muc ...
STK401-020 - Audio Lab of Ga
... The radiator thermal resistance θc-a required for total substrate power dissipation Pd in the STK401-020 is determined as: Condition 1: IC substrate temperature Tc not to exceed 125°C. Pd x θc-a+Ta <125°C ······························· (1) where Ta is set assured ambient temperature. Condition 2: P ...
... The radiator thermal resistance θc-a required for total substrate power dissipation Pd in the STK401-020 is determined as: Condition 1: IC substrate temperature Tc not to exceed 125°C. Pd x θc-a+Ta <125°C ······························· (1) where Ta is set assured ambient temperature. Condition 2: P ...
Capacitor
.jpg?width=300)
A capacitor (originally known as a condenser) is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store electrical energy temporarily in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors (plates) separated by a dielectric (i.e. an insulator that can store energy by becoming polarized). The conductors can be thin films, foils or sintered beads of metal or conductive electrolyte, etc. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's charge capacity. A dielectric can be glass, ceramic, plastic film, air, vacuum, paper, mica, oxide layer etc. Capacitors are widely used as parts of electrical circuits in many common electrical devices. Unlike a resistor, an ideal capacitor does not dissipate energy. Instead, a capacitor stores energy in the form of an electrostatic field between its plates.When there is a potential difference across the conductors (e.g., when a capacitor is attached across a battery), an electric field develops across the dielectric, causing positive charge +Q to collect on one plate and negative charge −Q to collect on the other plate. If a battery has been attached to a capacitor for a sufficient amount of time, no current can flow through the capacitor. However, if a time-varying voltage is applied across the leads of the capacitor, a displacement current can flow.An ideal capacitor is characterized by a single constant value, its capacitance. Capacitance is defined as the ratio of the electric charge Q on each conductor to the potential difference V between them. The SI unit of capacitance is the farad (F), which is equal to one coulomb per volt (1 C/V). Typical capacitance values range from about 1 pF (10−12 F) to about 1 mF (10−3 F).The larger the surface area of the ""plates"" (conductors) and the narrower the gap between them, the greater the capacitance is. In practice, the dielectric between the plates passes a small amount of leakage current and also has an electric field strength limit, known as the breakdown voltage. The conductors and leads introduce an undesired inductance and resistance.Capacitors are widely used in electronic circuits for blocking direct current while allowing alternating current to pass. In analog filter networks, they smooth the output of power supplies. In resonant circuits they tune radios to particular frequencies. In electric power transmission systems, they stabilize voltage and power flow.