LM2937 500 mA Low Dropout Regulator
... The LM2937 is a positive voltage regulator capable of supplying up to 500 mA of load current. The use of a PNP power transistor provides a low dropout voltage characteristic. With a load current of 500 mA the minimum input to output voltage differential required for the output to remain in regulatio ...
... The LM2937 is a positive voltage regulator capable of supplying up to 500 mA of load current. The use of a PNP power transistor provides a low dropout voltage characteristic. With a load current of 500 mA the minimum input to output voltage differential required for the output to remain in regulatio ...
Abstract - PG Embedded systems
... The dc component can cause line-frequency power ripple, dc-link voltage ripple, and a further second-order harmonic in the ac current. This paper has proposed an effective solution to minimize the dc component in three-phase ac currents and developed a software-based approach to mimic the blocking c ...
... The dc component can cause line-frequency power ripple, dc-link voltage ripple, and a further second-order harmonic in the ac current. This paper has proposed an effective solution to minimize the dc component in three-phase ac currents and developed a software-based approach to mimic the blocking c ...
DC/DC Converter with Transparent Electronics for application on
... • To construct circuits on flexible substracts, such as plastic, glass: – Possible to embody in photovoltaic panels. ...
... • To construct circuits on flexible substracts, such as plastic, glass: – Possible to embody in photovoltaic panels. ...
Electrical Measurements
... Recall that voltage (or more properly potential difference) is a measurement of the electrical ‘push’ applied to an electron as it moves through a section of the circuit. It is analogous to water pressure in that the difference in the quantity determines the driving force. (No pressure difference; n ...
... Recall that voltage (or more properly potential difference) is a measurement of the electrical ‘push’ applied to an electron as it moves through a section of the circuit. It is analogous to water pressure in that the difference in the quantity determines the driving force. (No pressure difference; n ...
P6.3.1.3 - LD Didactic
... in the gas volume as UC increases, and more and more charge carriers are collected at the capacitor plates. Thus, the ionization current IC increases with the voltage UC. When UC is increased beyond a certain point, IC ultimately reaches a saturation value, as all charge carriers formed by the incid ...
... in the gas volume as UC increases, and more and more charge carriers are collected at the capacitor plates. Thus, the ionization current IC increases with the voltage UC. When UC is increased beyond a certain point, IC ultimately reaches a saturation value, as all charge carriers formed by the incid ...
Method for Static and Dynamic Resistance Measurements of HV
... that resistance is linear it is possible to simply average its value over measurement time. Using 12-bit A/D converter the accuracy of measurements on calibrated current shunts were in within accuracy limits (±0.5%) and the ripple seen in voltage as well as resistance graph is due to digitization of ...
... that resistance is linear it is possible to simply average its value over measurement time. Using 12-bit A/D converter the accuracy of measurements on calibrated current shunts were in within accuracy limits (±0.5%) and the ripple seen in voltage as well as resistance graph is due to digitization of ...
Symbols - Vishay
... IFAV Average forward current, rectified current IFRM Repetitive peak forward current IFSM Surge forward current, non-repetitive IFWM Crest working forward current ...
... IFAV Average forward current, rectified current IFRM Repetitive peak forward current IFSM Surge forward current, non-repetitive IFWM Crest working forward current ...
TPS54160 60-V, Step-Down LED Driver Design Guide Application Report ..............................................................
... The voltage on the EN pin sets the status of the device, on or off. The EN pin has an internal pullup current source, I1, of 0.9 µA that provides the default condition of the TPS54160 operating when the EN pin floats. Once the EN pin voltage exceeds 1.25 V, an additional 2.9 µA of hysteresis, Ihys, ...
... The voltage on the EN pin sets the status of the device, on or off. The EN pin has an internal pullup current source, I1, of 0.9 µA that provides the default condition of the TPS54160 operating when the EN pin floats. Once the EN pin voltage exceeds 1.25 V, an additional 2.9 µA of hysteresis, Ihys, ...
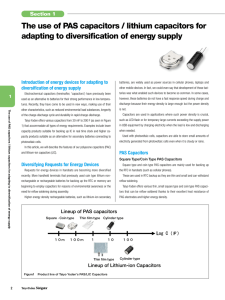
The use of PAS capacitors / lithium capacitors for adapting to
... other mobile devices. In fact, we could even say that development of those bat- ...
... other mobile devices. In fact, we could even say that development of those bat- ...
HS33 - Manual Ranging Digital Multimeter
... known temperature. A glass of stabilized ice water is very close to 32°F (0°C) and is usually very convenient but any known temperature can be used. 1. Select the 200°F range. 2. Remove back case and hold the battery in place with a rubber band so terminals are touching. 3. Stabilize a large cup of ...
... known temperature. A glass of stabilized ice water is very close to 32°F (0°C) and is usually very convenient but any known temperature can be used. 1. Select the 200°F range. 2. Remove back case and hold the battery in place with a rubber band so terminals are touching. 3. Stabilize a large cup of ...
Evaluates: MAX1856 MAX1856 Evaluation Kit SLIC Power Supply General Description
... 2) Connect a voltmeter to the VOUT1 pad. 3) Connect a +8V to +24V DC power supply to the VIN pad, with the voltage set to 0. 4) Connect the supply ground to the GND pad. 5) Turn on the power supply and gradually increase the input voltage through the +8V to +24V range. 6) Verify that VOUT1 is -72V t ...
... 2) Connect a voltmeter to the VOUT1 pad. 3) Connect a +8V to +24V DC power supply to the VIN pad, with the voltage set to 0. 4) Connect the supply ground to the GND pad. 5) Turn on the power supply and gradually increase the input voltage through the +8V to +24V range. 6) Verify that VOUT1 is -72V t ...
High Efficiency, Inductorless Step-Down DC/DC Converter
... load current. f is divided from the base clock, half for G=1/2; one-third for G=2/3; and LDO control for G=1. In other control methodology, such as PFM and PWM, d or f varies with both input voltage and load current, it can not achieve small ripple under all conditions. But when the load resistor be ...
... load current. f is divided from the base clock, half for G=1/2; one-third for G=2/3; and LDO control for G=1. In other control methodology, such as PFM and PWM, d or f varies with both input voltage and load current, it can not achieve small ripple under all conditions. But when the load resistor be ...
lab sheet - Faculty of Engineering
... 2. Adjust the sending-end voltage E1 to 300 V and keep it constant for the reminder part of the experiment. Use a three-phase resistive load and increase the load in steps making sure that the loads are balanced. Take readings of sending end and receiving end voltages and powers, E1, Q1, P1, E2, Q2, ...
... 2. Adjust the sending-end voltage E1 to 300 V and keep it constant for the reminder part of the experiment. Use a three-phase resistive load and increase the load in steps making sure that the loads are balanced. Take readings of sending end and receiving end voltages and powers, E1, Q1, P1, E2, Q2, ...
TechTopics No. 20 - Power factor correction capacitor
... the motor when the motor is switched off. At the instant that the motor is switched off, the motor and the driven load are at full speed. When the motor is switched off, the motor and load inertia will continue to drive the motor. If the magnetizing current required by the motor is available from th ...
... the motor when the motor is switched off. At the instant that the motor is switched off, the motor and the driven load are at full speed. When the motor is switched off, the motor and load inertia will continue to drive the motor. If the magnetizing current required by the motor is available from th ...
lab sheet - Faculty of Engineering
... 2. Adjust the sending-end voltage E1 to 300 V and keep it constant for the reminder part of the experiment. Use a three-phase resistive load and increase the load in steps making sure that the loads are balanced. Take readings of sending end and receiving end voltages and powers, E1, Q1, P1, E2, Q2, ...
... 2. Adjust the sending-end voltage E1 to 300 V and keep it constant for the reminder part of the experiment. Use a three-phase resistive load and increase the load in steps making sure that the loads are balanced. Take readings of sending end and receiving end voltages and powers, E1, Q1, P1, E2, Q2, ...
PTD1 - Faculty of Engineering
... 2. Adjust the sending-end voltage E1 to 300 V and keep it constant for the reminder part of the experiment. Use a three-phase resistive load and increase the load in steps making sure that the loads are balanced. Take readings of sending end and receiving end voltages and powers, E1, Q1, P1, E2, Q2, ...
... 2. Adjust the sending-end voltage E1 to 300 V and keep it constant for the reminder part of the experiment. Use a three-phase resistive load and increase the load in steps making sure that the loads are balanced. Take readings of sending end and receiving end voltages and powers, E1, Q1, P1, E2, Q2, ...
Example 1 with TAP
... ascertain the defining features of the work and their contributions to the whole. 2. Synthesis: Draw together disparate claims into a coherent whole in order to arrive at well-reasoned and well-supported inferences that can be justified as a conclusion. ...
... ascertain the defining features of the work and their contributions to the whole. 2. Synthesis: Draw together disparate claims into a coherent whole in order to arrive at well-reasoned and well-supported inferences that can be justified as a conclusion. ...
H047014954
... usually possess a varying reactive power requirement. Unregulated fixed compensation is not possible in such cases since an uneconomical undercompensation or a dangerous over-compensation can occur. One must therefore continuously adjust the capacitor power to the required reactive power requirement ...
... usually possess a varying reactive power requirement. Unregulated fixed compensation is not possible in such cases since an uneconomical undercompensation or a dangerous over-compensation can occur. One must therefore continuously adjust the capacitor power to the required reactive power requirement ...
Capacitor
.jpg?width=300)
A capacitor (originally known as a condenser) is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store electrical energy temporarily in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors (plates) separated by a dielectric (i.e. an insulator that can store energy by becoming polarized). The conductors can be thin films, foils or sintered beads of metal or conductive electrolyte, etc. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's charge capacity. A dielectric can be glass, ceramic, plastic film, air, vacuum, paper, mica, oxide layer etc. Capacitors are widely used as parts of electrical circuits in many common electrical devices. Unlike a resistor, an ideal capacitor does not dissipate energy. Instead, a capacitor stores energy in the form of an electrostatic field between its plates.When there is a potential difference across the conductors (e.g., when a capacitor is attached across a battery), an electric field develops across the dielectric, causing positive charge +Q to collect on one plate and negative charge −Q to collect on the other plate. If a battery has been attached to a capacitor for a sufficient amount of time, no current can flow through the capacitor. However, if a time-varying voltage is applied across the leads of the capacitor, a displacement current can flow.An ideal capacitor is characterized by a single constant value, its capacitance. Capacitance is defined as the ratio of the electric charge Q on each conductor to the potential difference V between them. The SI unit of capacitance is the farad (F), which is equal to one coulomb per volt (1 C/V). Typical capacitance values range from about 1 pF (10−12 F) to about 1 mF (10−3 F).The larger the surface area of the ""plates"" (conductors) and the narrower the gap between them, the greater the capacitance is. In practice, the dielectric between the plates passes a small amount of leakage current and also has an electric field strength limit, known as the breakdown voltage. The conductors and leads introduce an undesired inductance and resistance.Capacitors are widely used in electronic circuits for blocking direct current while allowing alternating current to pass. In analog filter networks, they smooth the output of power supplies. In resonant circuits they tune radios to particular frequencies. In electric power transmission systems, they stabilize voltage and power flow.