Natural Selection - Teacher **DRAFT
... evolutionary change include gene flow (“migration” of genes from one population to another, i.e., the genetic exchange between populations), genetic drift (change in a population’s gene pool due to chance), mutation (change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene), and natural selection (detailed below ...
... evolutionary change include gene flow (“migration” of genes from one population to another, i.e., the genetic exchange between populations), genetic drift (change in a population’s gene pool due to chance), mutation (change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene), and natural selection (detailed below ...
Genetic Engineering
... GMO Wheat May Help Solve Food Crisis, Australian Scientist Says Aya Takada July 4, 2008 Wheat genetically modified to tolerate drought would boost crop yields and may help the world resolve a food crisis, an Australian state researcher said. ...
... GMO Wheat May Help Solve Food Crisis, Australian Scientist Says Aya Takada July 4, 2008 Wheat genetically modified to tolerate drought would boost crop yields and may help the world resolve a food crisis, an Australian state researcher said. ...
Slide 1
... Increase in Genetic Information • High throughput technologies have increased ability to generate genotypes • Lead to increase in “collections” of data: – Independent lab studies – Consortium studies: HapMap – “Open source” – Forensic ...
... Increase in Genetic Information • High throughput technologies have increased ability to generate genotypes • Lead to increase in “collections” of data: – Independent lab studies – Consortium studies: HapMap – “Open source” – Forensic ...
Chapter 8 Population genetics and natural selection
... even though in a different environment. Example: Turesson’s planting experiment. Plants from nine different areas planted in the same garden show different morphology. Fig.8.8 Another example: Fig.8.10. ...
... even though in a different environment. Example: Turesson’s planting experiment. Plants from nine different areas planted in the same garden show different morphology. Fig.8.8 Another example: Fig.8.10. ...
Human Genetic Disorders
... • A genetic counselor can prepare a family pedigree or record that shows inheritance patterns over several generations. This can help determine the chance of being a carrier for that disorder. • We also have genetic testing now and we can test for the presence of specific genes known to cause geneti ...
... • A genetic counselor can prepare a family pedigree or record that shows inheritance patterns over several generations. This can help determine the chance of being a carrier for that disorder. • We also have genetic testing now and we can test for the presence of specific genes known to cause geneti ...
Genes and genomes
... code for a particular amino acid, much as letters join together to form words. ...
... code for a particular amino acid, much as letters join together to form words. ...
Cell 103 Heredity and Society
... - Describe genes and relate them to protein synthesis leading to genetic traits - Explain the rules governing gene transmission to offspring and prediction of inherited traits - Understand gene mutation and relate it to inherited and non-inherited diseases such sickle cell anemia and cancer - Unders ...
... - Describe genes and relate them to protein synthesis leading to genetic traits - Explain the rules governing gene transmission to offspring and prediction of inherited traits - Understand gene mutation and relate it to inherited and non-inherited diseases such sickle cell anemia and cancer - Unders ...
Human Genome Project, Gene Therapy, and Cloning
... 2. Infect a target cell, usually the one with the illness, such as a liver or lung. 3. The virus uses the normal sequence to produce the missing protein and the cell returns to normal. ...
... 2. Infect a target cell, usually the one with the illness, such as a liver or lung. 3. The virus uses the normal sequence to produce the missing protein and the cell returns to normal. ...
Which statement best states the effect of this movement of the brown
... bottom of the Pacific Ocean, while other crab species are unable to survive there. D. Some members of a garter snake species are resistant to a toxin produced by one of its food sources and will successfully reproduce and pass the resistant trait on to their offspring. School Board of Broward County ...
... bottom of the Pacific Ocean, while other crab species are unable to survive there. D. Some members of a garter snake species are resistant to a toxin produced by one of its food sources and will successfully reproduce and pass the resistant trait on to their offspring. School Board of Broward County ...
Mechanisms of Evolution
... but rather natural selection acts on the range of phenotypes in a population. Evolution occurs as a populations genes and their frequencies change over time. Gene Pool- All the alleles of a populations genes. Allelic Frequency- the percentage of any specific allele in a gene pool. Genetic Equilibriu ...
... but rather natural selection acts on the range of phenotypes in a population. Evolution occurs as a populations genes and their frequencies change over time. Gene Pool- All the alleles of a populations genes. Allelic Frequency- the percentage of any specific allele in a gene pool. Genetic Equilibriu ...
Biodiversity - kingscollege.net
... submission of man’s intellect and will. 2415- The seventh commandment enjoins respect for the integrity of creation…Man’s dominion over inanimate and other living beings granted by the Creator is not absolute; it is limited by concern for the quality of life of his neighbour, including generations ...
... submission of man’s intellect and will. 2415- The seventh commandment enjoins respect for the integrity of creation…Man’s dominion over inanimate and other living beings granted by the Creator is not absolute; it is limited by concern for the quality of life of his neighbour, including generations ...
Evolution Terms and Pictures
... the middle range confer greater survival/reproduction, while phenotypes at both extremes lead to decreased fitness • Directional selection: phenotypes at one end of the spectrum lead to greater survival/reproduction • Disruptive selection: phenotypes at both ends of the spectrum lead to greater surv ...
... the middle range confer greater survival/reproduction, while phenotypes at both extremes lead to decreased fitness • Directional selection: phenotypes at one end of the spectrum lead to greater survival/reproduction • Disruptive selection: phenotypes at both ends of the spectrum lead to greater surv ...
DISRUPTING GENETIC EQUILIBRIUM
... Gene Pool = the total genetic material available in a population Adapting to new selection factors can only use existing genes found in the population Allele Frequency = the number of a certain allele in the population / the total number of all alleles The phenotype frequencies can change between ge ...
... Gene Pool = the total genetic material available in a population Adapting to new selection factors can only use existing genes found in the population Allele Frequency = the number of a certain allele in the population / the total number of all alleles The phenotype frequencies can change between ge ...
Agents of Evolutionary Change
... of evolutionary change in a population, by comparing it to an ideal, never evolving population ...
... of evolutionary change in a population, by comparing it to an ideal, never evolving population ...
Hardy Weinberg Principle (equilibrium)
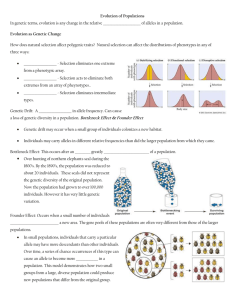
... Genetic drift – the alteration of allele frequencies by chance events. Gene flow – transport of genes into or out of a population by migrating individuals. Genetic drift, gene flow, and mutations can greatly affect small populations. Natural selection is usually the most significant cause of changes ...
... Genetic drift – the alteration of allele frequencies by chance events. Gene flow – transport of genes into or out of a population by migrating individuals. Genetic drift, gene flow, and mutations can greatly affect small populations. Natural selection is usually the most significant cause of changes ...
Larsen Chapter Guide 5
... 1. How do humans functionally adapt to hot climates? What genetic adaptations have occurred in people living for generations in hot climates? 2. How do humans functionally adapt to cold climates? What genetic adaptations have occurred in people living for generations in cold climates? 3. How do huma ...
... 1. How do humans functionally adapt to hot climates? What genetic adaptations have occurred in people living for generations in hot climates? 2. How do humans functionally adapt to cold climates? What genetic adaptations have occurred in people living for generations in cold climates? 3. How do huma ...
11.3 Other Mechanisms of Evolution
... dying), poor sperm quality, and greater susceptibility to disease. Inbred animals suffer from a lack of genetic diversity. ...
... dying), poor sperm quality, and greater susceptibility to disease. Inbred animals suffer from a lack of genetic diversity. ...
3chap23guidedreadingVideo
... a. Genetic drift b. Bottleneck effect c. Founder effect d. Gene flow 12. Why would we discuss adaptive evolution and what role does natural selection play? ...
... a. Genetic drift b. Bottleneck effect c. Founder effect d. Gene flow 12. Why would we discuss adaptive evolution and what role does natural selection play? ...
INTERVIEW WITH RICHARD LEWONTIN edited transcript Richard
... Peoples who have occupied major geographical areas for much of the recent evolution of humans look different from one another. Sub-Saharan Africans have dark skin and people who live in East Asia tend to have a light tan skin and an eye color and eye shape and hair that is different than Europeans. ...
... Peoples who have occupied major geographical areas for much of the recent evolution of humans look different from one another. Sub-Saharan Africans have dark skin and people who live in East Asia tend to have a light tan skin and an eye color and eye shape and hair that is different than Europeans. ...
Practice Exam 4, Biology 211, Fall 2007
... b. The evolutionary record considered over long periods of time. c. The creation of reproductive barriers between related populations. d. Slow, but steady, changes in the genetic makeup of populations over time. e. The appearance in the evolutionary record of novel forms and structures. 20. Which of ...
... b. The evolutionary record considered over long periods of time. c. The creation of reproductive barriers between related populations. d. Slow, but steady, changes in the genetic makeup of populations over time. e. The appearance in the evolutionary record of novel forms and structures. 20. Which of ...
Topic 18 revision notes - Mr Cartlidge`s Saigon Science Blog
... Describe evolution as the change in adaptive features of a population over time as the result of natural selection Define the process of adaptation - the process, resulting from natural selection, by which populations become more suited to their environment over many generations Describe the develop ...
... Describe evolution as the change in adaptive features of a population over time as the result of natural selection Define the process of adaptation - the process, resulting from natural selection, by which populations become more suited to their environment over many generations Describe the develop ...
File - Hanna Biology
... Isolating Mechanism: What factors are involved in the formation of new species? The gene pools of two populations must become separated for them to become new species. As new species evolve, populations become ____________________ isolated from each other. When the members of two populations cannot ...
... Isolating Mechanism: What factors are involved in the formation of new species? The gene pools of two populations must become separated for them to become new species. As new species evolve, populations become ____________________ isolated from each other. When the members of two populations cannot ...
Lecture 10
... • RFLP (or Restriction fragment length polymorphism) – RFLP was an important tool in genome mapping, localization of genes for genetic disorders, determination of risk for disease, and paternity testing. ...
... • RFLP (or Restriction fragment length polymorphism) – RFLP was an important tool in genome mapping, localization of genes for genetic disorders, determination of risk for disease, and paternity testing. ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.