Sexual reproduction and evolution
... Sex, however, requires a partner. Each individual produces specialised sex cells, called gametes, which usually carry half of their genetic material - one copy of each chromosome (packaged DNA) rather than two. Sexual reproduction involves a male gamete successfully fusing with a female gamete. Whil ...
... Sex, however, requires a partner. Each individual produces specialised sex cells, called gametes, which usually carry half of their genetic material - one copy of each chromosome (packaged DNA) rather than two. Sexual reproduction involves a male gamete successfully fusing with a female gamete. Whil ...
Chp 12 Notes
... A. Inheritance of Traits 1. Pedigrees: a diagram that shows how a trait is inherited over several generations a. Explain Key on Example on page 241 2. Patterns of Inheritance: the expression of genes over generations a. Carriers: an individual that has one copy of a recessive allele 1. don't show tr ...
... A. Inheritance of Traits 1. Pedigrees: a diagram that shows how a trait is inherited over several generations a. Explain Key on Example on page 241 2. Patterns of Inheritance: the expression of genes over generations a. Carriers: an individual that has one copy of a recessive allele 1. don't show tr ...
File
... controls melanin. Individuals with this trait do not produce melanin, which can effect vision in addition to skin/hair color. ...
... controls melanin. Individuals with this trait do not produce melanin, which can effect vision in addition to skin/hair color. ...
Designed to inhabit the earth
... changes that affect the shape of bones do not necessarily require simultaneous genetic changes affecting nerves, muscles, and vessels because of the design in how these structures develop. So bones may lengthen or shorten, fuse or divide, and the supporting structures would still be available to the ...
... changes that affect the shape of bones do not necessarily require simultaneous genetic changes affecting nerves, muscles, and vessels because of the design in how these structures develop. So bones may lengthen or shorten, fuse or divide, and the supporting structures would still be available to the ...
Goodman, et al. Chapter 7 Why Human Variation is NOT Racial
... Remember phenotype (how we look) and genotype (our genetic make-up at the gene level) are associated. • But not all genes are on the same chromosomes, even for skin color and so forth. • Also, most phenotypic traits are influenced by many genes. All that said, some traits TEND to group together. Why ...
... Remember phenotype (how we look) and genotype (our genetic make-up at the gene level) are associated. • But not all genes are on the same chromosomes, even for skin color and so forth. • Also, most phenotypic traits are influenced by many genes. All that said, some traits TEND to group together. Why ...
Statistical Power for Computational Mapping
... null consists of within-group variance and between-group variance. For a power analysis using one-way ANOVA, one standard way to define the effect size is (17): In our case, the groups are defined by haplotypes, and 2 is the genetic effect of the haplotypes on the trait value. Let n be the total sa ...
... null consists of within-group variance and between-group variance. For a power analysis using one-way ANOVA, one standard way to define the effect size is (17): In our case, the groups are defined by haplotypes, and 2 is the genetic effect of the haplotypes on the trait value. Let n be the total sa ...
a, -c, +i, +e, -o,
... We need to define mutation, crossover, and selection methods to aid in evolving a solution from this population ...
... We need to define mutation, crossover, and selection methods to aid in evolving a solution from this population ...
The Bio tech Century - The CS Lewis Study Group
... product because oxygen, helium and gold are products of nature. Genes are never invented de nova, they are products of nature, they are Gods creation. The Human Genome project will, within the next 8 years, identify and catalog all sixty-thousand genes that make up the blueprint of human-life. Whoev ...
... product because oxygen, helium and gold are products of nature. Genes are never invented de nova, they are products of nature, they are Gods creation. The Human Genome project will, within the next 8 years, identify and catalog all sixty-thousand genes that make up the blueprint of human-life. Whoev ...
Chapter 14 Study Qs
... seeds (R) are dominant to wrinkled seeds (r). A plant that is heterozygous for both traits is crossed with a plant that is heterozygous for flower color and has wrinkled seeds. Draw a Punnett Square illustrating this cross and list the genotype and phenotype ratios expected in the offspring. ...
... seeds (R) are dominant to wrinkled seeds (r). A plant that is heterozygous for both traits is crossed with a plant that is heterozygous for flower color and has wrinkled seeds. Draw a Punnett Square illustrating this cross and list the genotype and phenotype ratios expected in the offspring. ...
C303, Teaching Building 2015/09 Genetic Susceptibility(易感性)
... creates association within families, but not between unrelated people. ...
... creates association within families, but not between unrelated people. ...
Genetics Review
... How many sex cells are produced during meiosis? What is a mutation? Are all mutations harmful? How many pairs of chromosomes do humans have? How is asexual reproduction different than sexual reproduction? What are the male sex chromosomes? What are the female sex chromosomes? Who were the scientists ...
... How many sex cells are produced during meiosis? What is a mutation? Are all mutations harmful? How many pairs of chromosomes do humans have? How is asexual reproduction different than sexual reproduction? What are the male sex chromosomes? What are the female sex chromosomes? Who were the scientists ...
Press Release
... Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology, Hyderabad, India The worst luck in the world? The heart disease mutation carried by 60 million people Heart disease is the number one killer in the world. It is estimated that the highest death rates in India are associated with problems of the heart and bl ...
... Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology, Hyderabad, India The worst luck in the world? The heart disease mutation carried by 60 million people Heart disease is the number one killer in the world. It is estimated that the highest death rates in India are associated with problems of the heart and bl ...
B2.7_Cell_division_a..
... •No one knew about chromosomes or genes at the time •Mendel was not a well respected scientist and his work was not published in respected journals What did Mendel use for his experiments? Pea plants Distinguish between the terms genotype and phenotype using an example for each. •Genotype: combinati ...
... •No one knew about chromosomes or genes at the time •Mendel was not a well respected scientist and his work was not published in respected journals What did Mendel use for his experiments? Pea plants Distinguish between the terms genotype and phenotype using an example for each. •Genotype: combinati ...
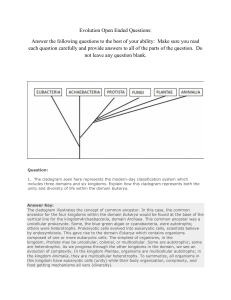
Evolution Open Ended Questions: Answer the following
... because of widespread pollution during the Industrial Revolution in England, the dark colored moths became much more common. 2. What specifically caused the shift in phenotype of the moths? Please explain in detail. Answer Key: The light colored peppered moths were well camouflaged on the trees whic ...
... because of widespread pollution during the Industrial Revolution in England, the dark colored moths became much more common. 2. What specifically caused the shift in phenotype of the moths? Please explain in detail. Answer Key: The light colored peppered moths were well camouflaged on the trees whic ...
class03.pps - CS Technion
... significant, authors would not include many other tests they would have done with non-significant results and thus would not apply Bonferroni to same extent they should. Also for tests published in other papers on the same set of patients or tests done subsequently would need to be corrected taking ...
... significant, authors would not include many other tests they would have done with non-significant results and thus would not apply Bonferroni to same extent they should. Also for tests published in other papers on the same set of patients or tests done subsequently would need to be corrected taking ...
Genetics
... Greater variation within the species makes a population better suited to adaptation to changes in the environment. ...
... Greater variation within the species makes a population better suited to adaptation to changes in the environment. ...
new03
... significant, authors would not include many other tests they would have done with non-significant results and thus would not apply Bonferroni to same extent they should. Also for tests published in other papers on the same set of patients or tests done subsequently would need to be corrected taking ...
... significant, authors would not include many other tests they would have done with non-significant results and thus would not apply Bonferroni to same extent they should. Also for tests published in other papers on the same set of patients or tests done subsequently would need to be corrected taking ...
Human fertility gene found - Carole Ober
... Many genes have been identified that cause infertility in humans, but finding genes that enhance fertility is tougher because people often choose to limit their family size for various cultural, social, and economic reasons. The Hutterites, however, do the opposite. This isolated group of Anabaptist ...
... Many genes have been identified that cause infertility in humans, but finding genes that enhance fertility is tougher because people often choose to limit their family size for various cultural, social, and economic reasons. The Hutterites, however, do the opposite. This isolated group of Anabaptist ...
HGT
... transfer of genetic material between organisms other than through vertical gene that studies vertical transfer of What is the science genes? transfer • They are “alien” regions in the genome (chromosome or plasmids) ...
... transfer of genetic material between organisms other than through vertical gene that studies vertical transfer of What is the science genes? transfer • They are “alien” regions in the genome (chromosome or plasmids) ...
Cellular Control Unit 1 Communication, Homeostasis and Energy
... A farmer crossed a true-breeding, red-coated cow with a true-breeding white-coated bull. The calf produced had roan coat colouring (made up of an equal number of red and white hairs). Explain the result and draw a genetic diagram to predict the outcome of crossing two roan coloured ...
... A farmer crossed a true-breeding, red-coated cow with a true-breeding white-coated bull. The calf produced had roan coat colouring (made up of an equal number of red and white hairs). Explain the result and draw a genetic diagram to predict the outcome of crossing two roan coloured ...
Communication - Miss Hanson's Biology Resources
... A farmer crossed a true-breeding, red-coated cow with a true-breeding white-coated bull. The calf produced had roan coat colouring (made up of an equal number of red and white hairs). Explain the result and draw a genetic diagram to predict the outcome of crossing two roan coloured ...
... A farmer crossed a true-breeding, red-coated cow with a true-breeding white-coated bull. The calf produced had roan coat colouring (made up of an equal number of red and white hairs). Explain the result and draw a genetic diagram to predict the outcome of crossing two roan coloured ...
outline21590
... c. HGP began 1990 d. Joint effort by DOE and NIH e. Estimated completion 15 years f. Working draft announced June 2000 2. HGP - Working Draft a. 16 Sequencing centers b. 22.1 billion bases of raw data c. 30% high quality finished sequence d. Map of 90% of genes on every chromosome e. 3164.7 million ...
... c. HGP began 1990 d. Joint effort by DOE and NIH e. Estimated completion 15 years f. Working draft announced June 2000 2. HGP - Working Draft a. 16 Sequencing centers b. 22.1 billion bases of raw data c. 30% high quality finished sequence d. Map of 90% of genes on every chromosome e. 3164.7 million ...
Media:SRich072506
... – Immediate candidate gene evaluation Assumed knowledge (admission of omniscience) Gene-gene interactions Gene-environment interactions ...
... – Immediate candidate gene evaluation Assumed knowledge (admission of omniscience) Gene-gene interactions Gene-environment interactions ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.