Ch_15
... • Selection of candidate genes for further analysis is often based on mutations in diseased individuals • not all observed mutations are associated with deleterious effects: (1) no effect at all - silent mutations (2) some is deleterious with respect to normal function (3) weakly beneficial • strong ...
... • Selection of candidate genes for further analysis is often based on mutations in diseased individuals • not all observed mutations are associated with deleterious effects: (1) no effect at all - silent mutations (2) some is deleterious with respect to normal function (3) weakly beneficial • strong ...
chapter17_Sections 1-5 - (per 3) and wed 4/24 (per 2,6)
... • Evolution starts with mutations in individuals, which introduces new alleles into a population • Sexual reproduction can quickly spread a mutation through a population • population • A group of organisms of the same species who live in a specific location and breed with one another more often than ...
... • Evolution starts with mutations in individuals, which introduces new alleles into a population • Sexual reproduction can quickly spread a mutation through a population • population • A group of organisms of the same species who live in a specific location and breed with one another more often than ...
Polygenic Multifactorial Inheritance
... population in a non-random manner with statistical significance • Alleles that confer only weak susceptibility to a complex disease may be more easily found through this study than linkage studies Challenges of association studies • Association of an allele with a phenotype does not prove that one ...
... population in a non-random manner with statistical significance • Alleles that confer only weak susceptibility to a complex disease may be more easily found through this study than linkage studies Challenges of association studies • Association of an allele with a phenotype does not prove that one ...
DM-Lecture-11 - WordPress.com
... An individual(Chromosome) is encoded (naturally) as a string of length l binary digits The fitness function f of a candidate solution(chromosome) to the MAXONE problem is the number of ones in its genetic code We start with a population of n random strings. Suppose that length of each chromoso ...
... An individual(Chromosome) is encoded (naturally) as a string of length l binary digits The fitness function f of a candidate solution(chromosome) to the MAXONE problem is the number of ones in its genetic code We start with a population of n random strings. Suppose that length of each chromoso ...
chapter17_Sections 1
... • Evolution starts with mutations in individuals, which introduces new alleles into a population • Sexual reproduction can quickly spread a mutation through a population • population • A group of organisms of the same species who live in a specific location and breed with one another more often than ...
... • Evolution starts with mutations in individuals, which introduces new alleles into a population • Sexual reproduction can quickly spread a mutation through a population • population • A group of organisms of the same species who live in a specific location and breed with one another more often than ...
Patterns of Inheretance and Chromosomes chapt12 and chapt13
... - each trait is controlled by a single gene - each gene has only 2 alleles - there is a clear dominant-recessive relationship between the alleles ...
... - each trait is controlled by a single gene - each gene has only 2 alleles - there is a clear dominant-recessive relationship between the alleles ...
pGLO Transformation Review Questions
... In our agar plate if the carbohydrate _______________ is present, GFP is expressed (made) giving a green glow. Without this carbohydrate, no ______ is expressed, and there ____________ (will/will not) be a green glow. 3. What is the pGLO plasmid? Circular piece of ______ that has three genes on it: ...
... In our agar plate if the carbohydrate _______________ is present, GFP is expressed (made) giving a green glow. Without this carbohydrate, no ______ is expressed, and there ____________ (will/will not) be a green glow. 3. What is the pGLO plasmid? Circular piece of ______ that has three genes on it: ...
Date - GeneDx
... members affected = yes, “His Family history is notable for sudden cardiac death”). [Patient first name]’s clinical symptoms and results of the routine diagnostic tests suggest a diagnosis of ARVC/ARVD. However, the only way to confirm this diagnosis is to perform genetic testing on this patient. Res ...
... members affected = yes, “His Family history is notable for sudden cardiac death”). [Patient first name]’s clinical symptoms and results of the routine diagnostic tests suggest a diagnosis of ARVC/ARVD. However, the only way to confirm this diagnosis is to perform genetic testing on this patient. Res ...
Mapping genes for complex traits in founder populations
... from a limited number of founders there may be multiple loci contributing to susceptibility to a disease as common as asthma. Traditional parametric approaches are problematic for complex disorders in general [reviewed in 4], and have additional complications for inbred genealogies. For example, in ...
... from a limited number of founders there may be multiple loci contributing to susceptibility to a disease as common as asthma. Traditional parametric approaches are problematic for complex disorders in general [reviewed in 4], and have additional complications for inbred genealogies. For example, in ...
Probability and Heredity
... appearance or visible traits. • Genotype -is its genetic make up or allele combinations. • Homozygous- has two identical alleles for a trait. • Heterozygous- has two different alleles for a trait. ...
... appearance or visible traits. • Genotype -is its genetic make up or allele combinations. • Homozygous- has two identical alleles for a trait. • Heterozygous- has two different alleles for a trait. ...
CGRFA/WG-FGR-3/14/5 - Rev.1 - Genetic Diversity and Climate Change
... agriculture for coping with climate change and the need for raising awareness of their potential roles. At the same Session, the Commission adopted its Programme of Work on Climate Change and Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture1. ...
... agriculture for coping with climate change and the need for raising awareness of their potential roles. At the same Session, the Commission adopted its Programme of Work on Climate Change and Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture1. ...
statgen2
... inside each sperm. •Blending theories of inheritance supplanted the spermists and ovists during the 19th century. The mixture of sperm and egg resulted in progeny that were a "blend" of two parents' characteristics. Sex cells are known collectively as gametes (gamos, Greek, meaning marriage). ...
... inside each sperm. •Blending theories of inheritance supplanted the spermists and ovists during the 19th century. The mixture of sperm and egg resulted in progeny that were a "blend" of two parents' characteristics. Sex cells are known collectively as gametes (gamos, Greek, meaning marriage). ...
File
... Heart Disease - Genetics, diet, alcohol, and smoking are all factors that contribute to the development. Diabetes - Genetic, diet, and race are all factors that contribute to the development of the disease. Cancer - Genetics, life style habits in general are all factors that contribute to developmen ...
... Heart Disease - Genetics, diet, alcohol, and smoking are all factors that contribute to the development. Diabetes - Genetic, diet, and race are all factors that contribute to the development of the disease. Cancer - Genetics, life style habits in general are all factors that contribute to developmen ...
alleles
... Dominant and Recessive Alleles Phenotype is predominantly determined by genotype, but may also be influenced or modified due to interaction with the environment. For example the final height of a human adult depends on a combination of that person’s genotype as well as their nutrition—if they are u ...
... Dominant and Recessive Alleles Phenotype is predominantly determined by genotype, but may also be influenced or modified due to interaction with the environment. For example the final height of a human adult depends on a combination of that person’s genotype as well as their nutrition—if they are u ...
Fact Sheet 55|HUNTINGTON DISEASE In summary Huntington
... the huntingtin protein also becomes longer and this appears to interfere with its function, therefore a copy of the HTT gene with an expanded CAG repeat length can be considered faulty. The number of CAG repeats can increase when the HTT gene is passed from a parent to a child, this is known as anti ...
... the huntingtin protein also becomes longer and this appears to interfere with its function, therefore a copy of the HTT gene with an expanded CAG repeat length can be considered faulty. The number of CAG repeats can increase when the HTT gene is passed from a parent to a child, this is known as anti ...
Linkage analysis - Scheid Signalling Lab @ York University
... • IBS: if parental alleles are not know, then we can only say sibs are identical by state ...
... • IBS: if parental alleles are not know, then we can only say sibs are identical by state ...
Genetic Disorders
... disorders are inherited due to problems with the entire chromosome (which may contain hundreds of genes!) • Thus, an individual with even one chromosomal defect will most likely express the disorder. ...
... disorders are inherited due to problems with the entire chromosome (which may contain hundreds of genes!) • Thus, an individual with even one chromosomal defect will most likely express the disorder. ...
Chp 23 Evolution of Populations
... 9. Explain how genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, nonrandom mating and natural selection can cause microevolution. 10. Explain the role of population size in genetic drift. 11. Distinguish between the bottleneck effect and the founder effect. 12. Explain why mutation has little quantitative effect ...
... 9. Explain how genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, nonrandom mating and natural selection can cause microevolution. 10. Explain the role of population size in genetic drift. 11. Distinguish between the bottleneck effect and the founder effect. 12. Explain why mutation has little quantitative effect ...
Genome Analysis
... Genes (or at least their coding regions) comprise only a tiny fraction of human DNA, but they represent the major biological function of the genome and the main focus of interest by biologists Human genes tend to have small exons (encoding an average of only 50 codons) separated by long introns (s ...
... Genes (or at least their coding regions) comprise only a tiny fraction of human DNA, but they represent the major biological function of the genome and the main focus of interest by biologists Human genes tend to have small exons (encoding an average of only 50 codons) separated by long introns (s ...
Pedigree Analysis
... Each human cell contains a copy of all the genes needed to produce a human being. Cloning is the production of cells/organisms with identical genes. Identical twins are natural clones. A clone made from a living organism will be genetically identical to that organism, but will be younger. The enviro ...
... Each human cell contains a copy of all the genes needed to produce a human being. Cloning is the production of cells/organisms with identical genes. Identical twins are natural clones. A clone made from a living organism will be genetically identical to that organism, but will be younger. The enviro ...
Penelitian biologi molekular
... To detect the presence of the G71R mutation in the UGTA1A gene, a sequencing analysis has to be applied since the simple detection method, such as restriction enzyme digestion is not applicable. It results in expensive and time-consuming practice. Does DHPLC technique have good accuracy in detectin ...
... To detect the presence of the G71R mutation in the UGTA1A gene, a sequencing analysis has to be applied since the simple detection method, such as restriction enzyme digestion is not applicable. It results in expensive and time-consuming practice. Does DHPLC technique have good accuracy in detectin ...
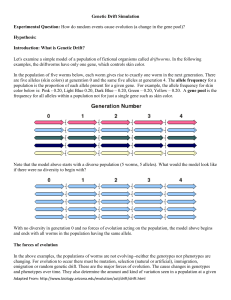
Genetic Drift Simulation Experimental Question: How do random
... None of the above events has anything to do with the dead organism's genotype or phenotype--these events occurred purely by chance. Fixation of an allele In a population model with genetic drift, alleles will eventually become "fixed". When an allele is fixed, all members of the population have that ...
... None of the above events has anything to do with the dead organism's genotype or phenotype--these events occurred purely by chance. Fixation of an allele In a population model with genetic drift, alleles will eventually become "fixed". When an allele is fixed, all members of the population have that ...
Ubiquitous Internal Gene Duplication in Eukaryotes and Intron
... The studies on molecular population genetics typically rely on assays of moderate numbers of individuals at a small numbers of loci, companied with high sampling variance. The high-throughput genomic sequencing methods yield unprecedented power for reliably estimating important parameters in populat ...
... The studies on molecular population genetics typically rely on assays of moderate numbers of individuals at a small numbers of loci, companied with high sampling variance. The high-throughput genomic sequencing methods yield unprecedented power for reliably estimating important parameters in populat ...
Population genetics
... importance of populations as units of evolution populations evolve, individuals do not evolution as changes in gene frequencies within populations ...
... importance of populations as units of evolution populations evolve, individuals do not evolution as changes in gene frequencies within populations ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.