! Genetic Variation Within Populations
... A phenotype is a trait produced by one or more genes. In a population, there may be a wide range of phenotypes. For example, some penguins may be short and rounded. Others could be tall and slim. Natural selection acts on different phenotypes in a population. The expression of different phenotypes ...
... A phenotype is a trait produced by one or more genes. In a population, there may be a wide range of phenotypes. For example, some penguins may be short and rounded. Others could be tall and slim. Natural selection acts on different phenotypes in a population. The expression of different phenotypes ...
EQUATIONS USED IN 40-300 POPULATION GENETICS
... We can use OBSERVED values of FST to calculate the parameter Nem from the above equation. This estimate can be thought of as the combination of gene flow and drift that would result in the observed value of FST at equilibrium. When Nem = 1, subpopulations are exchanging one migrant per generation, o ...
... We can use OBSERVED values of FST to calculate the parameter Nem from the above equation. This estimate can be thought of as the combination of gene flow and drift that would result in the observed value of FST at equilibrium. When Nem = 1, subpopulations are exchanging one migrant per generation, o ...
history
... • Y-DNA (Hammer et al. Molecular Biology and Evolution 15, 427-441, 1998) • 11 X-Linked Regions (Balciuniene et al. 2001; Garrigan et al. 2005; Hammer et al. 2004; Harris. & Hey, 1999, 2001; Kaessmann et al. 1999; Nachman et al. 2004; Saunders et al. 2002; Verrelli et al. 2002; Yu et al. 2002) ...
... • Y-DNA (Hammer et al. Molecular Biology and Evolution 15, 427-441, 1998) • 11 X-Linked Regions (Balciuniene et al. 2001; Garrigan et al. 2005; Hammer et al. 2004; Harris. & Hey, 1999, 2001; Kaessmann et al. 1999; Nachman et al. 2004; Saunders et al. 2002; Verrelli et al. 2002; Yu et al. 2002) ...
Populations Close Notes Booklet - Morinville Community High School
... Obviously, the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium cannot exist in real life. Some or all of these types of forces all act on living populations at various times and evolution at some level occurs in all living organisms. The Hardy-Weinberg formulas allow us to detect some allele frequencies that change from ...
... Obviously, the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium cannot exist in real life. Some or all of these types of forces all act on living populations at various times and evolution at some level occurs in all living organisms. The Hardy-Weinberg formulas allow us to detect some allele frequencies that change from ...
Document
... Law of segregation: the two factors for each trait segregate - _________________ from each other – during _______________ when gametes form. Law of independent assortment: the factors for one trait separate _____________________ of how factors for other traits separate. Modern Definitions of Men ...
... Law of segregation: the two factors for each trait segregate - _________________ from each other – during _______________ when gametes form. Law of independent assortment: the factors for one trait separate _____________________ of how factors for other traits separate. Modern Definitions of Men ...
Mendelian Genetics
... Each gamete has a single allele for each trait b. Allele present is one of four possible parental alleles ...
... Each gamete has a single allele for each trait b. Allele present is one of four possible parental alleles ...
Playing God? The Ethics of Genetic Manipulation
... appropriate for God than human beings Unnatural The “giftedness” argument (Sandel) ...
... appropriate for God than human beings Unnatural The “giftedness” argument (Sandel) ...
GENETIC PRINCIPLES
... Imprinting: DNA methylation marks preserved across generations. Templating: DNA methylation and histone marks preserved across cell division. ...
... Imprinting: DNA methylation marks preserved across generations. Templating: DNA methylation and histone marks preserved across cell division. ...
H-W - ap biology
... "Rhesus factor" - aka Rh - on the surface of their red blood cells. The presence of Rh reflects a dominant allele. In a study of human blood groups, it was found that among a population of 400 individuals, 230 had the Rh protein (Rh+) and 170 did not (Rh-). For this population, calculate both allele ...
... "Rhesus factor" - aka Rh - on the surface of their red blood cells. The presence of Rh reflects a dominant allele. In a study of human blood groups, it was found that among a population of 400 individuals, 230 had the Rh protein (Rh+) and 170 did not (Rh-). For this population, calculate both allele ...
Department of Health funded exon skipping
... ii. Developing the chemistry of the antisense oligonucleotides (AO’s). ...
... ii. Developing the chemistry of the antisense oligonucleotides (AO’s). ...
Biological Basis of Behaviour – Genetics, Evolutionary Psychology
... Although identical twins have the same genes, they don’t always have he same number of copies of those genes. Explains why one twin only can get a disease. Most identical twins share 1 placenta during development. 1 in 3 cases has 2 placentas, 1 for each twin. Explains some differences in identical ...
... Although identical twins have the same genes, they don’t always have he same number of copies of those genes. Explains why one twin only can get a disease. Most identical twins share 1 placenta during development. 1 in 3 cases has 2 placentas, 1 for each twin. Explains some differences in identical ...
Administrative Office St. Joseph`s Hospital Site, L301
... test are expected to be 6 – 8 weeks if no mutation is found. Positive results will take about 2 weeks longer, because any positive result must be confirmed by an independent second test. The laboratory protocols will be modified regularly as new information about the genes and new technologies becom ...
... test are expected to be 6 – 8 weeks if no mutation is found. Positive results will take about 2 weeks longer, because any positive result must be confirmed by an independent second test. The laboratory protocols will be modified regularly as new information about the genes and new technologies becom ...
Wrestling with Behavioral Genetics.
... But forensic scientists and geneticists contacted by Nature question whether the scientific evidence supports the conclusions reached in the psychiatric report presented to Judge Reinotti. "We don't know how the whole genome functions and the [possible] protective effects of other genes," says Giuse ...
... But forensic scientists and geneticists contacted by Nature question whether the scientific evidence supports the conclusions reached in the psychiatric report presented to Judge Reinotti. "We don't know how the whole genome functions and the [possible] protective effects of other genes," says Giuse ...
16-2 Evolution as Genetic Change
... Evolution Versus Genetic Equilibrium The Hardy-Weinberg principle states that allele frequencies in a population will remain constant unless one or more factors cause those frequencies to change. When allele frequencies remain constant it is called genetic equilibrium. ...
... Evolution Versus Genetic Equilibrium The Hardy-Weinberg principle states that allele frequencies in a population will remain constant unless one or more factors cause those frequencies to change. When allele frequencies remain constant it is called genetic equilibrium. ...
Developing a New View of Evolution
... "biogenetic law," summed up in the popular phrase "ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny." He and his followers thought that evolution simply adds new stages of development to an embryo, so that mammalian development, for example, added extra steps to that of fishes or reptiles. In this view, watching an ...
... "biogenetic law," summed up in the popular phrase "ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny." He and his followers thought that evolution simply adds new stages of development to an embryo, so that mammalian development, for example, added extra steps to that of fishes or reptiles. In this view, watching an ...
Population Genetics - Drift
... ¾ What is the probability that the d allele will become fixed in the population? ¾ If fixation occurs, how long will it take? ¾ How will the growth of the population, from generation to generation, affect the answers to parts a and b? ...
... ¾ What is the probability that the d allele will become fixed in the population? ¾ If fixation occurs, how long will it take? ¾ How will the growth of the population, from generation to generation, affect the answers to parts a and b? ...
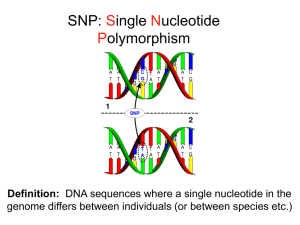
SNP presentation
... T allele- nonsense SNP. People with two T alleles have no functional alpha-actin-3 (TT are endurance athletes) A study of olympic weightlifters everyone of them has at least one copy of C Would you change your behavior if you knew your genotype? ...
... T allele- nonsense SNP. People with two T alleles have no functional alpha-actin-3 (TT are endurance athletes) A study of olympic weightlifters everyone of them has at least one copy of C Would you change your behavior if you knew your genotype? ...
Document
... If the population size is too large, the processing time is high and the GA tends to take longer to converge upon a solution (because less fit members have to be selected to make up the required population) If the population size is too small, the GA is in danger of premature convergence upon a sub- ...
... If the population size is too large, the processing time is high and the GA tends to take longer to converge upon a solution (because less fit members have to be selected to make up the required population) If the population size is too small, the GA is in danger of premature convergence upon a sub- ...
Ch 14 Lecture
... The ratio between purple and white flowers in the F2 generation were 3:1. Mendel reasoned that though the F1 generation had no white flowers, they must have carried the heritable trait for white flower color. Mendel said that the purple color gene was “dominant” and the white color gene was “rece ...
... The ratio between purple and white flowers in the F2 generation were 3:1. Mendel reasoned that though the F1 generation had no white flowers, they must have carried the heritable trait for white flower color. Mendel said that the purple color gene was “dominant” and the white color gene was “rece ...
Genetic Diversity in an Andean Population from Peru and Regional
... haplogroups A–D in Peruvians is more similar to the Andean Amerindians than to the Amazon Amerindians, and the geographic distribution of A–D haplogroups may be interpreted as the consequence of at least two migratory routes within the continent. The Y chromosome haplotypes were similar to those obs ...
... haplogroups A–D in Peruvians is more similar to the Andean Amerindians than to the Amazon Amerindians, and the geographic distribution of A–D haplogroups may be interpreted as the consequence of at least two migratory routes within the continent. The Y chromosome haplotypes were similar to those obs ...
Understanding genetic counseling and testing
... your personal risk, and discussing your genetic testing options. These services should be provided by a counselor who is board-certified by the American Board of Genetic Counseling. Genetic tests of blood and other tissue are used to identify genetic disorders and can help determine a more precise e ...
... your personal risk, and discussing your genetic testing options. These services should be provided by a counselor who is board-certified by the American Board of Genetic Counseling. Genetic tests of blood and other tissue are used to identify genetic disorders and can help determine a more precise e ...
Why Terminator technology won`t prevent GM
... trigger the switch in every case. The effect may be sufficient to make saving seed an unreliable exercise for farmers, but not enough for complete gene containment. • There may be gene silencing or instability of one component leading to failure of the system. Depending on which gene was affected, t ...
... trigger the switch in every case. The effect may be sufficient to make saving seed an unreliable exercise for farmers, but not enough for complete gene containment. • There may be gene silencing or instability of one component leading to failure of the system. Depending on which gene was affected, t ...
Sequencing a genome
... Most genome sequences are not complete (not finished). Whole Genome Shotguns are referred to as having an X-fold coverage. Low coverage (2x) is sufficient for gene discovery and some regulatory element identification. High coverage (6x) is good for gene annotation. There will still be some missing g ...
... Most genome sequences are not complete (not finished). Whole Genome Shotguns are referred to as having an X-fold coverage. Low coverage (2x) is sufficient for gene discovery and some regulatory element identification. High coverage (6x) is good for gene annotation. There will still be some missing g ...
Chapter 12: Patterns of Inheritance
... Mendel’s Laws Mendel’s First Law of Heredity: Segregation 1. The two alleles for a gene segregate during gamete formation and are rejoined at random during fertilization ! disjunction of homologs in Anaphase I ...
... Mendel’s Laws Mendel’s First Law of Heredity: Segregation 1. The two alleles for a gene segregate during gamete formation and are rejoined at random during fertilization ! disjunction of homologs in Anaphase I ...
CLOUSTON SYNDROME: FIRST CASE IN RUSSIA
... of structural defects in the examined sample. The patient was worried about the risk of having an affected child. During genetic counseling, Clouston syndrome was hypothesized and the woman was sent for molecular genetic screening of mutations in the GJB6 gene. We performed whole gene sequencing usi ...
... of structural defects in the examined sample. The patient was worried about the risk of having an affected child. During genetic counseling, Clouston syndrome was hypothesized and the woman was sent for molecular genetic screening of mutations in the GJB6 gene. We performed whole gene sequencing usi ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.