When completed, this form will contain Protected Health Information
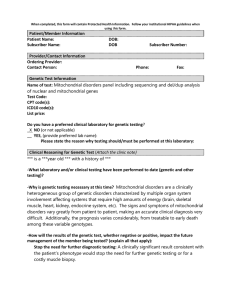
... Please state the reason why testing should/must be performed at this laboratory: Clinical Reasoning for Genetic Test (Attach the clinic note) *** is a ***year old *** with a history of *** -What laboratory and/or clinical testing have been performed to date (genetic and other testing)? -Why is genet ...
... Please state the reason why testing should/must be performed at this laboratory: Clinical Reasoning for Genetic Test (Attach the clinic note) *** is a ***year old *** with a history of *** -What laboratory and/or clinical testing have been performed to date (genetic and other testing)? -Why is genet ...
Siena Borsani - Unisi.it - Università degli Studi di Siena
... the equivalent of more than two human genomes every 24 hours ...
... the equivalent of more than two human genomes every 24 hours ...
American Journal of Medical Genetics
... 1983 by Klein, who renamed this type Klein-Waardenburg syndrome. ...
... 1983 by Klein, who renamed this type Klein-Waardenburg syndrome. ...
Medical Genomics Promise, peril and price
... • At age 5 he was re-examined. • No changes in history or exam. Development progressing but still delayed. Autistic behaviors continue. The parents were interested in having more children and were seeking recurrence risk information. • Gene Panel for Autism (61 Genes). – Normal ...
... • At age 5 he was re-examined. • No changes in history or exam. Development progressing but still delayed. Autistic behaviors continue. The parents were interested in having more children and were seeking recurrence risk information. • Gene Panel for Autism (61 Genes). – Normal ...
Pedigree Drawing
... • affects either sex but more females than males • females often more mildly affected than males • child of an affected female at 50% chance of being affected • for an affected male, all his daughters but none of his sons affected • Quite rare, examples include an inherited form of rickets (mutation ...
... • affects either sex but more females than males • females often more mildly affected than males • child of an affected female at 50% chance of being affected • for an affected male, all his daughters but none of his sons affected • Quite rare, examples include an inherited form of rickets (mutation ...
Francis Crick - WordPress.com
... Mutations, researchers realized, change the spelling of the cookbook. A single base pair may change, or a set of genes may be duplicated. Those mutations that confer a selective advantage to an individual become more common over time, and ultimately these mutant genes may drive the older versions ou ...
... Mutations, researchers realized, change the spelling of the cookbook. A single base pair may change, or a set of genes may be duplicated. Those mutations that confer a selective advantage to an individual become more common over time, and ultimately these mutant genes may drive the older versions ou ...
Get Notes - Mindset Learn
... Only those finches that were best suited to obtain food in their specific environment survived And underwent natural selection independently resulting in each island having species that are very different from each other/ they differ genotypically and phenotypically These differences prevented them ...
... Only those finches that were best suited to obtain food in their specific environment survived And underwent natural selection independently resulting in each island having species that are very different from each other/ they differ genotypically and phenotypically These differences prevented them ...
Lecture 5
... The ENCODE consortium generated more than 200 datasets and analyzed more than 600 million data points. The ENCODE consortium's major findings include : 1) the majority of DNA in the human genome is transcribed into functional molecules RNA, and that these transcripts extensively overlap one another. ...
... The ENCODE consortium generated more than 200 datasets and analyzed more than 600 million data points. The ENCODE consortium's major findings include : 1) the majority of DNA in the human genome is transcribed into functional molecules RNA, and that these transcripts extensively overlap one another. ...
Lecture 8
... networks with crossover appears limited in general, and better results should be expected with reproduction heuristics that respect the uniqueness of the distributed representations.” • Random initial networks • Fixed-sized genomes • Structural mutations • Tested with “Inducing Languages” and “Ant P ...
... networks with crossover appears limited in general, and better results should be expected with reproduction heuristics that respect the uniqueness of the distributed representations.” • Random initial networks • Fixed-sized genomes • Structural mutations • Tested with “Inducing Languages” and “Ant P ...
23.4 a closer look at natural selection
... 1. Because Darwin did not know about the work of Gregor Mendel, he could not explain how organisms pass heritable traits to their offspring. In looking at genetic variation, what are: discrete characters - ...
... 1. Because Darwin did not know about the work of Gregor Mendel, he could not explain how organisms pass heritable traits to their offspring. In looking at genetic variation, what are: discrete characters - ...
Nicole`s teacher asked her to make a diagram of a good chain for a
... A population of mice, some with light-colored fur and some with dark-colored fur, is introduced into a field with dark soil. A few generations later, the majority of the mice have dark-colored fur. Which of the following best explains this change? ...
... A population of mice, some with light-colored fur and some with dark-colored fur, is introduced into a field with dark soil. A few generations later, the majority of the mice have dark-colored fur. Which of the following best explains this change? ...
Cystic Fibrosis Carrier Screening Brochure
... CF is a serious and potentially lethal lifelong illness characterized by chronic lung infections and difficulties digesting fat requiring most individuals to take pills with every meal to assist digestion. Daily respiratory therapy, frequent antibiotics, and pills for digestion of food constitute th ...
... CF is a serious and potentially lethal lifelong illness characterized by chronic lung infections and difficulties digesting fat requiring most individuals to take pills with every meal to assist digestion. Daily respiratory therapy, frequent antibiotics, and pills for digestion of food constitute th ...
BioSc 231 2001 Exam4
... _____ A female Drosophila supposedly heterozygous for two recessive mutations cn and lz that are on the same arm of the X chromosome (cn lz/+ +) surprisingly expresses both these genes. The male progeny of the female will be A. all wild type B. all cn lz C. 1/2 cn lz and 1/2 wild type D. cn + E. + l ...
... _____ A female Drosophila supposedly heterozygous for two recessive mutations cn and lz that are on the same arm of the X chromosome (cn lz/+ +) surprisingly expresses both these genes. The male progeny of the female will be A. all wild type B. all cn lz C. 1/2 cn lz and 1/2 wild type D. cn + E. + l ...
Chapter 11
... 6. Describe Mendel’s principle of segregation. The Role of Variation in Evolution, p. 507 1. The ultimate source of all new genetic information in evolution is ____ and they increase _____. 2. What are the major sources of genetic variation? 3. Describe nondisjunction. 4. How do evolutionary changes ...
... 6. Describe Mendel’s principle of segregation. The Role of Variation in Evolution, p. 507 1. The ultimate source of all new genetic information in evolution is ____ and they increase _____. 2. What are the major sources of genetic variation? 3. Describe nondisjunction. 4. How do evolutionary changes ...
31 March 2011
... • Diagram the structure of an animal cell membrane, including the phospholipid bilayer, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates • Explain the functions of the cell membrane, including passive and active transport and communication/information processing 3. Understand the physical nature of genetic ...
... • Diagram the structure of an animal cell membrane, including the phospholipid bilayer, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates • Explain the functions of the cell membrane, including passive and active transport and communication/information processing 3. Understand the physical nature of genetic ...
GENETIC DISORDER RESEARCH PACKET
... feel sick, right? Some of the medications such as cough syrup are treatments. In other words, they treat the symptoms of coughing even though you still have the flu. Other medications such as vaccines are cures which end the illness – you no longer have the flu nor will you ever get it again. Curren ...
... feel sick, right? Some of the medications such as cough syrup are treatments. In other words, they treat the symptoms of coughing even though you still have the flu. Other medications such as vaccines are cures which end the illness – you no longer have the flu nor will you ever get it again. Curren ...
Population genetics theory (lectures 7
... from the nonfunctional class to the functional class are rarer than forward mutations. 16. The objection has been raised that natural selection cannot work because only an extremely tiny fraction of sequences at a locus will even be marginally functional. So mutants will almost always be totally non ...
... from the nonfunctional class to the functional class are rarer than forward mutations. 16. The objection has been raised that natural selection cannot work because only an extremely tiny fraction of sequences at a locus will even be marginally functional. So mutants will almost always be totally non ...
XomeDx - GeneDx
... What type of test results can I expect? There are four possible types of results we can find while analyzing your exome. Analyzing all of an individual’s genetic information is complicated, and the results can be complex. Your test results may contain a table with one or more of the types of changes ...
... What type of test results can I expect? There are four possible types of results we can find while analyzing your exome. Analyzing all of an individual’s genetic information is complicated, and the results can be complex. Your test results may contain a table with one or more of the types of changes ...
Genes
... is the regulatory element closest to the first exon. Regulator sites distant from the first exon are called enhancers. Some of these sequences may be as far as 50,000 bp upstream. General TF: many are not specific to a given gene, but function as regulatory proteins for multiple genes Specific TF: r ...
... is the regulatory element closest to the first exon. Regulator sites distant from the first exon are called enhancers. Some of these sequences may be as far as 50,000 bp upstream. General TF: many are not specific to a given gene, but function as regulatory proteins for multiple genes Specific TF: r ...
Review: Genetics
... • For example, large volumes of medicines, such as insulin, can be produced or plants resistant to diseases can be developed. ...
... • For example, large volumes of medicines, such as insulin, can be produced or plants resistant to diseases can be developed. ...
Genome-wide association (GWAS) methods for demographers
... – Do you have multilevel data sources – Do you have complex sampling designs ...
... – Do you have multilevel data sources – Do you have complex sampling designs ...
BY 123 SI Session #9 Chapter 15 Siby123.yolasite.com Terms to
... a. The genes are on the same chromosome, but they are more than 50 map units (50%) apart. b. The genes assort independently even though the chromosomes they are on travel to the metaphase plate together c. Their alleles segregate in anaphase I, and each gamete receives a single allele for all of the ...
... a. The genes are on the same chromosome, but they are more than 50 map units (50%) apart. b. The genes assort independently even though the chromosomes they are on travel to the metaphase plate together c. Their alleles segregate in anaphase I, and each gamete receives a single allele for all of the ...
Key - Madison County Schools
... duplicates its DNA then splits in two, each new organism gets one copy of DNA. Budding is when an organism fully grows and develops then splits into two organisms. e) What is a mutation and how do they occur? Are they always harmful? A mutation structure change in gene. No, mutations are not always ...
... duplicates its DNA then splits in two, each new organism gets one copy of DNA. Budding is when an organism fully grows and develops then splits into two organisms. e) What is a mutation and how do they occur? Are they always harmful? A mutation structure change in gene. No, mutations are not always ...
Gregor Mendel (1822-1844) & the Foundations of Genetics
... • Humans: 46 chromosomes - 22 pairs of autosomes plus 2 sex chromosomes (X and Y) ...
... • Humans: 46 chromosomes - 22 pairs of autosomes plus 2 sex chromosomes (X and Y) ...
a mm017e
... The Working Group shall elect its Chairperson and one or more Vice-Chairpersons from among the representatives of Members of the Working Group at the beginning of each session. These officers shall remain in office until the next session of the Working Group and shall be eligible for reelection. ...
... The Working Group shall elect its Chairperson and one or more Vice-Chairpersons from among the representatives of Members of the Working Group at the beginning of each session. These officers shall remain in office until the next session of the Working Group and shall be eligible for reelection. ...
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology. It is therefore a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA may be inserted in the host genome by first isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using molecular cloning methods to generate a DNA sequence, or by synthesizing the DNA, and then inserting this construct into the host organism. Genes may be removed, or ""knocked out"", using a nuclease. Gene targeting is a different technique that uses homologous recombination to change an endogenous gene, and can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene, or introduce point mutations.An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be a genetically modified organism (GMO). The first GMOs were bacteria generated in 1973 and GM mice in 1974. Insulin-producing bacteria were commercialized in 1982 and genetically modified food has been sold since 1994. Glofish, the first GMO designed as a pet, was first sold in the United States December in 2003.Genetic engineering techniques have been applied in numerous fields including research, agriculture, industrial biotechnology, and medicine. Enzymes used in laundry detergent and medicines such as insulin and human growth hormone are now manufactured in GM cells, experimental GM cell lines and GM animals such as mice or zebrafish are being used for research purposes, and genetically modified crops have been commercialized.























