GENETIC CONTROL MECHANISMS AND …
... __________________ : arises when a change in the base sequence of DNA alters a codon, leading to a ______________ amino acid being placed in the protein sequence. Nonsense mutation: converts a codon specifying an amino acid to a _______ codon. Nonsense mutations are often lethal to the cell as prote ...
... __________________ : arises when a change in the base sequence of DNA alters a codon, leading to a ______________ amino acid being placed in the protein sequence. Nonsense mutation: converts a codon specifying an amino acid to a _______ codon. Nonsense mutations are often lethal to the cell as prote ...
Mass spectrometry and stable isotope labeling for
... modified RNAs has expanded and increasing numbers of modified sites continue to be found in catalytic, non-coding and messenger RNAs across the species. Still, their biological implications remain elusive, in part, because of the lack of experimental methods that would enable quantitative assessment ...
... modified RNAs has expanded and increasing numbers of modified sites continue to be found in catalytic, non-coding and messenger RNAs across the species. Still, their biological implications remain elusive, in part, because of the lack of experimental methods that would enable quantitative assessment ...
Misconceptions, misunderstandings and questions students
... In my experience and in discussions with colleagues, there is a consensus that students do not have an understanding of how traits are inherited and expressed. The topics of meiosis and protein synthesis are extremely challenging to teach for a variety of reasons. They are often taught in isolation, ...
... In my experience and in discussions with colleagues, there is a consensus that students do not have an understanding of how traits are inherited and expressed. The topics of meiosis and protein synthesis are extremely challenging to teach for a variety of reasons. They are often taught in isolation, ...
How Do Heritable Changes in Genes Occur?
... transcription and replication of the genes in which they are present, these lesions are fatal if they go uncorrected. Not surprisingly, therefore, organisms (including ourselves) have a number of different DNA repair systems for eliminating such damage from DNA. But it is the very act of attempting ...
... transcription and replication of the genes in which they are present, these lesions are fatal if they go uncorrected. Not surprisingly, therefore, organisms (including ourselves) have a number of different DNA repair systems for eliminating such damage from DNA. But it is the very act of attempting ...
Quiz 4 Thursday 4
... 2. The recurrence risk of heart disease in the monozygotic twin of a proband is 38%; in a dizygotic twin it is 16%; and in a full sibling it is 7%. a) Why is the recurrence risk less for a dizygotic twin then it is for a monozygotic twin? Because heart disease has a genetic component, and monozygoti ...
... 2. The recurrence risk of heart disease in the monozygotic twin of a proband is 38%; in a dizygotic twin it is 16%; and in a full sibling it is 7%. a) Why is the recurrence risk less for a dizygotic twin then it is for a monozygotic twin? Because heart disease has a genetic component, and monozygoti ...
BACKGROUNDER – About Fragile X – EMBARGOED JULY 26 2011
... the remainder have either normal intelligence or learning disabilities. Around 40 per cent of older male gene carriers may have tremors, poor balance and memory loss (often misdiagnosed as Alzheimer’s disease, senile dementia or Parkinson’s disease). Up to 25 per cent of female carriers experien ...
... the remainder have either normal intelligence or learning disabilities. Around 40 per cent of older male gene carriers may have tremors, poor balance and memory loss (often misdiagnosed as Alzheimer’s disease, senile dementia or Parkinson’s disease). Up to 25 per cent of female carriers experien ...
The cytoplasm helps maintain cell shape, much like the human
... The Correct Answer is… When a scientist named Pavlov fed his dogs he rang a bell each and every time. His dogs came to associate the sound of a bell with food. Anytime they heard a noise resembling a bell they started to salivate (drool). This kind of learning, where two unrelated things are associa ...
... The Correct Answer is… When a scientist named Pavlov fed his dogs he rang a bell each and every time. His dogs came to associate the sound of a bell with food. Anytime they heard a noise resembling a bell they started to salivate (drool). This kind of learning, where two unrelated things are associa ...
Finding the Fault in Nick`s Genome – sp2015
... What questions and concerns would Nic's parents have? ...
... What questions and concerns would Nic's parents have? ...
Lecture 23
... Indeed, it has been suggested that when these 3 conditions are met, then evolution must occur. Daniel Dennett has referred to the process of involving these 3 steps as the evolutionary algorithm. Genes clearly satisfy the first two requirements, and there is plenty of evidence that many environmenta ...
... Indeed, it has been suggested that when these 3 conditions are met, then evolution must occur. Daniel Dennett has referred to the process of involving these 3 steps as the evolutionary algorithm. Genes clearly satisfy the first two requirements, and there is plenty of evidence that many environmenta ...
Course Outline - Athol Murray College of Notre Dame
... 2. Explain how the processes of diffusion, active transport, photosynthesis, and respiration are accomplished in a cell. 2.1 Identify the factors which influence the rate and direction of diffusion. 2.2 Examine the mechanisms of active transport by identifying and explaining the two processes. (Proc ...
... 2. Explain how the processes of diffusion, active transport, photosynthesis, and respiration are accomplished in a cell. 2.1 Identify the factors which influence the rate and direction of diffusion. 2.2 Examine the mechanisms of active transport by identifying and explaining the two processes. (Proc ...
GFP plasmid - Kiwi.mendelu.cz
... Plasmids are fragments of doublestranded DNA that can replicate independently of chromosomal DNA, and carry genes Their size is between 1,000-20,000 base pairs and they are stable ...
... Plasmids are fragments of doublestranded DNA that can replicate independently of chromosomal DNA, and carry genes Their size is between 1,000-20,000 base pairs and they are stable ...
Septic Arthritis and Osteomyelitis
... 2-Select the correct ABX 3-Deliver the ABX to the organism 4-Stop tissue destruction ...
... 2-Select the correct ABX 3-Deliver the ABX to the organism 4-Stop tissue destruction ...
Pelagia Research Library Exogenous gene transfer in Assam tea
... competence for transformation as well as regeneration [3]. Foreign genes have been introduced into cells of several woody crops by using the Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid [4]. Genetic transformation is a way to develop plants with lengthy generation and breeding cycles, such as tea. Conservat ...
... competence for transformation as well as regeneration [3]. Foreign genes have been introduced into cells of several woody crops by using the Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid [4]. Genetic transformation is a way to develop plants with lengthy generation and breeding cycles, such as tea. Conservat ...
sets of metaphors in multilevel cognitive models
... Genetic systems are both directly invisible and regulated at various levels. Therefore, as a rule, they're firstly represented by means of diverse MTs and MRs, and only after that become indirectly seen to verify or to falsify them. To analyze these metaphors, the method logically similar to linguis ...
... Genetic systems are both directly invisible and regulated at various levels. Therefore, as a rule, they're firstly represented by means of diverse MTs and MRs, and only after that become indirectly seen to verify or to falsify them. To analyze these metaphors, the method logically similar to linguis ...
Mutational analysis of the connexin 36 gene (CX36)
... encoding a putative cation channel is associated with catatonic schizophrenia in a large pedigree. Mol. Psychiatry 6, 302 – 306. Meyer, J., Ortega, G., Schraut, K., Nürnberg, G., Rüschendorf, F., Saar, K., Mössner, R., Wienker, T.F., Reis, A., Stöber, G., Lesch, K.P., 2002. Exclusion of the neur ...
... encoding a putative cation channel is associated with catatonic schizophrenia in a large pedigree. Mol. Psychiatry 6, 302 – 306. Meyer, J., Ortega, G., Schraut, K., Nürnberg, G., Rüschendorf, F., Saar, K., Mössner, R., Wienker, T.F., Reis, A., Stöber, G., Lesch, K.P., 2002. Exclusion of the neur ...
Foundations of Biology.pptx
... carrying information as codons (packages of information encoding the protein). • Adapter hypothesis—an adapter molecule exists in the cell that can bind amino acids, and recognize a nucleotide sequence, or these “codons.” These adapter molecules must contain anticodons complementary to these codons ...
... carrying information as codons (packages of information encoding the protein). • Adapter hypothesis—an adapter molecule exists in the cell that can bind amino acids, and recognize a nucleotide sequence, or these “codons.” These adapter molecules must contain anticodons complementary to these codons ...
Introduction to Genetics using Punnett Squares
... flowers his pea plants were either violet or white, Mendel began to study the segregation of heritable traits. ...
... flowers his pea plants were either violet or white, Mendel began to study the segregation of heritable traits. ...
Author`s personal copy
... The aim of this model is to investigate the minimal conditions that allow for complex evolutionary relationships to emerge between the genotype–phenotype map and genome structure. Modelling precisely a particular gene network or specific biochemical reactions is, therefore, not the purpose. Here, the ...
... The aim of this model is to investigate the minimal conditions that allow for complex evolutionary relationships to emerge between the genotype–phenotype map and genome structure. Modelling precisely a particular gene network or specific biochemical reactions is, therefore, not the purpose. Here, the ...
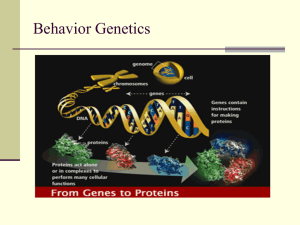
Behavior Genetics
... influences are typically far more important than shared environmental influences. Notice that the unshared environment idea is linked to the active child concept (Why?) and is used to explain the fact that adoptive siblings and even biologically related siblings are typically not very similar. A ...
... influences are typically far more important than shared environmental influences. Notice that the unshared environment idea is linked to the active child concept (Why?) and is used to explain the fact that adoptive siblings and even biologically related siblings are typically not very similar. A ...
Introduction to Genetics using Punnett Squares
... flowers his pea plants were either violet or white, Mendel began to study the segregation of heritable traits. ...
... flowers his pea plants were either violet or white, Mendel began to study the segregation of heritable traits. ...
Rearrangements of the Blood Group RhD Gene
... This is explained by assuming that the D antigen is a "mosaic" structure and that the RBCs from some D variant individuals may lackpart of this mosaic and become immunized to the D epitopes that they do not possess. Rh-positive individuals that make anti-D have been classified into six main differen ...
... This is explained by assuming that the D antigen is a "mosaic" structure and that the RBCs from some D variant individuals may lackpart of this mosaic and become immunized to the D epitopes that they do not possess. Rh-positive individuals that make anti-D have been classified into six main differen ...
Hand out - WebLearn
... The transcription factor proteins encoded by the gap and pair rule genes divide the embryo in consecutively smaller units (segments/parasegments), ending with stripes of expression of the segment polarity genes in each segment. Up until now transcription factors were able to interact with each other ...
... The transcription factor proteins encoded by the gap and pair rule genes divide the embryo in consecutively smaller units (segments/parasegments), ending with stripes of expression of the segment polarity genes in each segment. Up until now transcription factors were able to interact with each other ...
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology. It is therefore a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA may be inserted in the host genome by first isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using molecular cloning methods to generate a DNA sequence, or by synthesizing the DNA, and then inserting this construct into the host organism. Genes may be removed, or ""knocked out"", using a nuclease. Gene targeting is a different technique that uses homologous recombination to change an endogenous gene, and can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene, or introduce point mutations.An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be a genetically modified organism (GMO). The first GMOs were bacteria generated in 1973 and GM mice in 1974. Insulin-producing bacteria were commercialized in 1982 and genetically modified food has been sold since 1994. Glofish, the first GMO designed as a pet, was first sold in the United States December in 2003.Genetic engineering techniques have been applied in numerous fields including research, agriculture, industrial biotechnology, and medicine. Enzymes used in laundry detergent and medicines such as insulin and human growth hormone are now manufactured in GM cells, experimental GM cell lines and GM animals such as mice or zebrafish are being used for research purposes, and genetically modified crops have been commercialized.