Quantitative Genetics
... Experiments test the source or origin of variation. One way to assess genetic influence is to use inbred or genetically similar groups of animals or plants, and rear them under a range of environmental conditions. Variation between different strains reared under similar conditions can be assigned to ...
... Experiments test the source or origin of variation. One way to assess genetic influence is to use inbred or genetically similar groups of animals or plants, and rear them under a range of environmental conditions. Variation between different strains reared under similar conditions can be assigned to ...
Unit 3 - kehsscience.org
... 5. Proteins are your traits/characteristics. What is a characteristic of DNA that determines what protein is made? Sections of the DNA molecule which “code” for specific proteins are called genes. Genes have a specific starting point and ending point so the gene produces the exact same RNA every tim ...
... 5. Proteins are your traits/characteristics. What is a characteristic of DNA that determines what protein is made? Sections of the DNA molecule which “code” for specific proteins are called genes. Genes have a specific starting point and ending point so the gene produces the exact same RNA every tim ...
The Effects of Plasmid on Genotype and Phenotype
... proteins that can break down antibiotics that would otherwise prevent the bacterial cell from growing. One such protein is an enzyme called beta-lactamase which can break down penicillin and certain modified penicillins such as ampicillin. If a bacterial cell contains a plasmid carrying this gene, t ...
... proteins that can break down antibiotics that would otherwise prevent the bacterial cell from growing. One such protein is an enzyme called beta-lactamase which can break down penicillin and certain modified penicillins such as ampicillin. If a bacterial cell contains a plasmid carrying this gene, t ...
slides - Ehud Lamm
... At this point I wish to state that while I have used the term "band" in all of my papers, I was very careful to state in my article in Science that these cross striations "appear to run around an achromatic matrix." As to the ultimate nature of these "bands," I have not been, nor am I now, willing t ...
... At this point I wish to state that while I have used the term "band" in all of my papers, I was very careful to state in my article in Science that these cross striations "appear to run around an achromatic matrix." As to the ultimate nature of these "bands," I have not been, nor am I now, willing t ...
genetic control of pigment differentiation in somatic cells
... analysis is left unused. One facet of this problem which might be particularly susceptible to analysis by use of genetic techniques is implicit in the title of this paper: the genetic control of pigment differentiation. By the term "genetic control" it is meant to imply that not only is the process ...
... analysis is left unused. One facet of this problem which might be particularly susceptible to analysis by use of genetic techniques is implicit in the title of this paper: the genetic control of pigment differentiation. By the term "genetic control" it is meant to imply that not only is the process ...
The ADAMTS1 Gene Is Associated with Familial Mandibular
... skeletal class I jaw relationship and results in a normal bite and aesthetic facial appearance. Mandibular prognathism (MP; OMIM:176700; Online Mendelian Inheritance of Man, http:// omim.org/entry/176700) is a dentofacial deformity, which is characterized by overgrowth of the lower jaw with or witho ...
... skeletal class I jaw relationship and results in a normal bite and aesthetic facial appearance. Mandibular prognathism (MP; OMIM:176700; Online Mendelian Inheritance of Man, http:// omim.org/entry/176700) is a dentofacial deformity, which is characterized by overgrowth of the lower jaw with or witho ...
Fact Sheet 14 | EPIGENETICS This fact sheet describes epigenetics
... that these women would not show any symptoms since there would be enough cells with the working copy of the gene to produce the necessary protein. Rarely, some women have more cells in which the X chromosome carrying the mutation is active so that they show some of the symptoms of the condition. In ...
... that these women would not show any symptoms since there would be enough cells with the working copy of the gene to produce the necessary protein. Rarely, some women have more cells in which the X chromosome carrying the mutation is active so that they show some of the symptoms of the condition. In ...
Document
... • Biological Process = biological goal or objective – broad biological goals, such as mitosis or purine metabolism, that are accomplished by ordered assemblies of molecular functions ...
... • Biological Process = biological goal or objective – broad biological goals, such as mitosis or purine metabolism, that are accomplished by ordered assemblies of molecular functions ...
Mendel`s First Law of Genetics (Law of Segregation)
... What is seen in the F1 generation? We always see only one of the two parental phenotypes in this generation. But the F1 possesses the information needed to produce both parental phenotypes in the following generation. The F2 generation always produced a 3:1 ratio where the dominant trait is present ...
... What is seen in the F1 generation? We always see only one of the two parental phenotypes in this generation. But the F1 possesses the information needed to produce both parental phenotypes in the following generation. The F2 generation always produced a 3:1 ratio where the dominant trait is present ...
Exercise - GEP Community Server
... A large number of dark to light green boxes are now seen in the window…these are the predicted genes. Augustus and FGenesH are better at finding intron/exon boundaries while SNAP tends to report genes as single exons. Are there any tRNAs in this region? The 100 kpb view is a bit overwhelming; to red ...
... A large number of dark to light green boxes are now seen in the window…these are the predicted genes. Augustus and FGenesH are better at finding intron/exon boundaries while SNAP tends to report genes as single exons. Are there any tRNAs in this region? The 100 kpb view is a bit overwhelming; to red ...
Prezentacja programu PowerPoint
... Another mapping function (Kosambi’s) widely used in estimation of genetic distance in mammals, especially with reference to ”Interference” during meiotic recombination. ...
... Another mapping function (Kosambi’s) widely used in estimation of genetic distance in mammals, especially with reference to ”Interference” during meiotic recombination. ...
Chapter 12 Microbial Evolution and Systematics
... as judged by DNA hybridization experiments. A biovars: variant procaryotic strains characterized by biochemical or physiological differences. Morphovars: differ morphologically Serovars: have distinctive antigenic properties Type strain: it is usually one of the first strains studied and often is mo ...
... as judged by DNA hybridization experiments. A biovars: variant procaryotic strains characterized by biochemical or physiological differences. Morphovars: differ morphologically Serovars: have distinctive antigenic properties Type strain: it is usually one of the first strains studied and often is mo ...
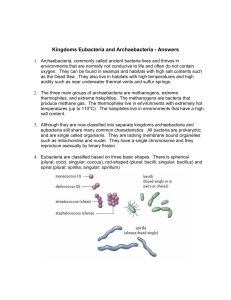
Kingdoms Eubacteria and Archaebacteria
... materials (glucose). Chemosynthetic bacteria perform the same conversion but it is driven by energy that is trapped during the breakdown of chemicals. 13. Binary fission is asexual reproduction in bacteria. The single strand of bacterial DNA replicates (copies) and the result is a copy for each new ...
... materials (glucose). Chemosynthetic bacteria perform the same conversion but it is driven by energy that is trapped during the breakdown of chemicals. 13. Binary fission is asexual reproduction in bacteria. The single strand of bacterial DNA replicates (copies) and the result is a copy for each new ...
lecture_10(LP)
... What reads the normal TYR codons, UAC? • Yeast has 8 tRNA-TYR genes • Only one of them has the suppressor mutation. What about genes that normally end in UAG? • Not all ORFs end with UAG. • For those that do, there’s still a competition between the suppressor tRNA and termination factor. Even so, a ...
... What reads the normal TYR codons, UAC? • Yeast has 8 tRNA-TYR genes • Only one of them has the suppressor mutation. What about genes that normally end in UAG? • Not all ORFs end with UAG. • For those that do, there’s still a competition between the suppressor tRNA and termination factor. Even so, a ...
Journal of Bacteriology
... operons encode transport systems that extrude the toxic metalloids, thus lowering the intracellular concentration and producing resistance (2, 8, 13). Arsenate is accumulated by both the Pit and Pst phosphate transport systems, although the Pit system may be responsible for the majority of uptake (1 ...
... operons encode transport systems that extrude the toxic metalloids, thus lowering the intracellular concentration and producing resistance (2, 8, 13). Arsenate is accumulated by both the Pit and Pst phosphate transport systems, although the Pit system may be responsible for the majority of uptake (1 ...
18- virusbacteria
... (b) Transposons contain one or more genes in addition to the transposase gene. In the transposon shown here, a gene for resistance to an antibiotic is located between twin insertion sequences. The gene for antibiotic resistance is carried along as part of the transposon when the transposon is insert ...
... (b) Transposons contain one or more genes in addition to the transposase gene. In the transposon shown here, a gene for resistance to an antibiotic is located between twin insertion sequences. The gene for antibiotic resistance is carried along as part of the transposon when the transposon is insert ...
2011 Exam
... Gorillas show an inherited recessive condition called albinism. This results in white fur. The pedigree chart below shows the inheritance of albinism in a family of gorillas. Normal fur is the dominant allele (N), while albino fur is recessive (n). ...
... Gorillas show an inherited recessive condition called albinism. This results in white fur. The pedigree chart below shows the inheritance of albinism in a family of gorillas. Normal fur is the dominant allele (N), while albino fur is recessive (n). ...
Plasmid Sex Introduction .....In most bacteria there are several
... Restriction modification systems play a role in transformation as well as in conjugation. However, it is thought that since these modification systems generate both DNA ends and smaller fragments, restriction modification may actually increase the chance of recombination with incorporated fragments. ...
... Restriction modification systems play a role in transformation as well as in conjugation. However, it is thought that since these modification systems generate both DNA ends and smaller fragments, restriction modification may actually increase the chance of recombination with incorporated fragments. ...
1768-6475-2-RV
... inphenotype without a change in genotype. Epigenetic change is a regular and natural occurrence but can also be influenced by several factors including age, the environment/lifestyle, and disease state. Epigenetic modifications can manifest as commonly as the manner in which cells terminally differe ...
... inphenotype without a change in genotype. Epigenetic change is a regular and natural occurrence but can also be influenced by several factors including age, the environment/lifestyle, and disease state. Epigenetic modifications can manifest as commonly as the manner in which cells terminally differe ...
2014 Biology STAAR EOC Review
... When HIV attacks a helper T cell, it binds to the cell membrane and enters the cell. Once the virus is inside the cell, it uses the cell’s structures to make new viruses. Then the virus destroys the cell and the new viruses are released into the bloodstream. They travel throughout the blood, infecti ...
... When HIV attacks a helper T cell, it binds to the cell membrane and enters the cell. Once the virus is inside the cell, it uses the cell’s structures to make new viruses. Then the virus destroys the cell and the new viruses are released into the bloodstream. They travel throughout the blood, infecti ...
Integrating Functional Genomic Information into the Saccharomyces Genome Database.
... anticipation of increasing data from large-scale functional analysis projects and the detection of new sequence homologs, SGD is consolidating and improving the presentation of genespecific information. Specifically, SGD has entered a collaboration with FlyBase and the MGD to create the Gene Ontolog ...
... anticipation of increasing data from large-scale functional analysis projects and the detection of new sequence homologs, SGD is consolidating and improving the presentation of genespecific information. Specifically, SGD has entered a collaboration with FlyBase and the MGD to create the Gene Ontolog ...
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology. It is therefore a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA may be inserted in the host genome by first isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using molecular cloning methods to generate a DNA sequence, or by synthesizing the DNA, and then inserting this construct into the host organism. Genes may be removed, or ""knocked out"", using a nuclease. Gene targeting is a different technique that uses homologous recombination to change an endogenous gene, and can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene, or introduce point mutations.An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be a genetically modified organism (GMO). The first GMOs were bacteria generated in 1973 and GM mice in 1974. Insulin-producing bacteria were commercialized in 1982 and genetically modified food has been sold since 1994. Glofish, the first GMO designed as a pet, was first sold in the United States December in 2003.Genetic engineering techniques have been applied in numerous fields including research, agriculture, industrial biotechnology, and medicine. Enzymes used in laundry detergent and medicines such as insulin and human growth hormone are now manufactured in GM cells, experimental GM cell lines and GM animals such as mice or zebrafish are being used for research purposes, and genetically modified crops have been commercialized.