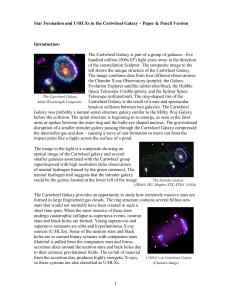
4P38.pdf
... Vidal-Madjar et al. (2003). This effect may partly explain the paucity of exoplanets detected at close orbital distances (<0.05 AU). ...
... Vidal-Madjar et al. (2003). This effect may partly explain the paucity of exoplanets detected at close orbital distances (<0.05 AU). ...
Astronomy Astrophysics − Astrophysical parameters of the peculiar X-ray transient
... Context. The current generation of X-ray satellites has discovered many new X-ray sources that are difficult to classify within the well-described subclasses. The hard X-ray source IGR J11215−5952 is a peculiar transient, displaying very short X-ray outbursts every 165 days. Aims. To characterise the ...
... Context. The current generation of X-ray satellites has discovered many new X-ray sources that are difficult to classify within the well-described subclasses. The hard X-ray source IGR J11215−5952 is a peculiar transient, displaying very short X-ray outbursts every 165 days. Aims. To characterise the ...
Results from the search for tidal disruption flares in the GALEX Deep
... • They are an unambiguous probe for supermassive black holes lurking in the nuclei of normal galaxies. • The luminosity, temperature, and decay of the flare is dependent on the mass and spin of the black hole. • They may contribute to black hole growth over cosmic times, and the faint end of the AGN ...
... • They are an unambiguous probe for supermassive black holes lurking in the nuclei of normal galaxies. • The luminosity, temperature, and decay of the flare is dependent on the mass and spin of the black hole. • They may contribute to black hole growth over cosmic times, and the faint end of the AGN ...
A neutron star with a carbon atmosphere in the Cassiopeia A
... (4 km and 5 km, respectively) are much smaller than the theoretical size of a neutron star RNS (∼ 10 km; ref. 14). This would suggest the emission region is a hot spot on the neutron star surface, which would probably result in X-ray pulsations as the hot spot rotated with the star. However, these p ...
... (4 km and 5 km, respectively) are much smaller than the theoretical size of a neutron star RNS (∼ 10 km; ref. 14). This would suggest the emission region is a hot spot on the neutron star surface, which would probably result in X-ray pulsations as the hot spot rotated with the star. However, these p ...
Into the darkness peering
... Simpler than supernovae, galaxies or AGN Fewer projection effects with X-ray selection X-rays are more peaked than galaxy distribution Fewer foreground/background objects Confining hot gas requires a real object of high mass Close relation of X-ray observable to cluster mass X-ray bright so seen to ...
... Simpler than supernovae, galaxies or AGN Fewer projection effects with X-ray selection X-rays are more peaked than galaxy distribution Fewer foreground/background objects Confining hot gas requires a real object of high mass Close relation of X-ray observable to cluster mass X-ray bright so seen to ...
Cartwheel Galaxy - Chandra X
... 9. Why might there not be new star formation in the elliptical galaxy on the left? 10. A study of ULXs has determined that very few X-ray sources with luminosity greater than 1040 erg s−1 remain after ~15 Myr and few remain after ~30 Myr. 11. In the Cartwheel galaxy, it appears that a shock wave is ...
... 9. Why might there not be new star formation in the elliptical galaxy on the left? 10. A study of ULXs has determined that very few X-ray sources with luminosity greater than 1040 erg s−1 remain after ~15 Myr and few remain after ~30 Myr. 11. In the Cartwheel galaxy, it appears that a shock wave is ...
Document
... Blazars are powerful gamma-ray sources. The most powerful of them have equivalent isotropic luminosity 1049 erg/s. Collimation θ2/2 ~ 10-2 – 10-3. θ – jet opening angle. EGRET detected 66 (+27) sources of this type. New breakthrough is expected after the launch of GLAST. Several sources have been de ...
... Blazars are powerful gamma-ray sources. The most powerful of them have equivalent isotropic luminosity 1049 erg/s. Collimation θ2/2 ~ 10-2 – 10-3. θ – jet opening angle. EGRET detected 66 (+27) sources of this type. New breakthrough is expected after the launch of GLAST. Several sources have been de ...
AGN jets
... Blazars are powerful gamma-ray sources. The most powerful of them have equivalent isotropic luminosity 1049 erg/s. Collimation θ2/2 ~ 10-2 – 10-3. θ – jet opening angle. EGRET detected 66 (+27) sources of this type. New breakthrough is expected after the launch of GLAST. Several sources have been de ...
... Blazars are powerful gamma-ray sources. The most powerful of them have equivalent isotropic luminosity 1049 erg/s. Collimation θ2/2 ~ 10-2 – 10-3. θ – jet opening angle. EGRET detected 66 (+27) sources of this type. New breakthrough is expected after the launch of GLAST. Several sources have been de ...
University of Groningen Colliding winds in Wolf-Rayet
... are yet to be determined. When unexpectedly-bright radio emission was observed from a few Wolf-Rayet stars in the 70-80s, the exciting interpretation was that a compact, unseen companion was the origin, accreting matter from the WR star; that neutron stars or even black holes had been detected! Twen ...
... are yet to be determined. When unexpectedly-bright radio emission was observed from a few Wolf-Rayet stars in the 70-80s, the exciting interpretation was that a compact, unseen companion was the origin, accreting matter from the WR star; that neutron stars or even black holes had been detected! Twen ...
the xmm-newton wide-field survey in the cosmos field
... sources with greater than 100 net counts in the 0.3Y10 keV energy band and optical spectroscopic identification. We further remove one source that has been identified as a star (Trump et al. 2007). The final sample comprises 135 objects. We show the distribution of their net counts in the 0.3Y10 keV ...
... sources with greater than 100 net counts in the 0.3Y10 keV energy band and optical spectroscopic identification. We further remove one source that has been identified as a star (Trump et al. 2007). The final sample comprises 135 objects. We show the distribution of their net counts in the 0.3Y10 keV ...
Reconnaissance of the TRAPPIST-1 exoplanet system in the Lyman
... 5. Hydrogen exospheres around TRAPPIST-1b/c Using the out-of-transit Ly-α line as a reference, we identified marginal flux decreases (Fig. 3) during the transit of TRAPPIST-1b (40±21% in [-95 ; -55] km s−1 ) and after the transit of TRAPPIST-1c (41±18% in [-135 ; -40] km s−1 ). Since the star has a ...
... 5. Hydrogen exospheres around TRAPPIST-1b/c Using the out-of-transit Ly-α line as a reference, we identified marginal flux decreases (Fig. 3) during the transit of TRAPPIST-1b (40±21% in [-95 ; -55] km s−1 ) and after the transit of TRAPPIST-1c (41±18% in [-135 ; -40] km s−1 ). Since the star has a ...
L171 COULD BLACK HOLE X-RAY BINARIES BE DETECTED IN
... duration of the mass transfer is then set by the RGB lifetime tRGB of the stellar companion to the BH. For a 0.8 M, star, we have tRGB ⱗ 10 9 yr. This is still shorter than the interaction timescale tex ⯝ 3 # 10 9 yr estimated for a cluster like NGC 6397. Therefore, for all clusters where exchanges ...
... duration of the mass transfer is then set by the RGB lifetime tRGB of the stellar companion to the BH. For a 0.8 M, star, we have tRGB ⱗ 10 9 yr. This is still shorter than the interaction timescale tex ⯝ 3 # 10 9 yr estimated for a cluster like NGC 6397. Therefore, for all clusters where exchanges ...
Today in Astronomy 102: black hole observations, v.2
... neighborhood of Sgr A*’s black hole to provide a quasarlike luminosity. This would also explain the lack of jets. It’s also not quite massive enough for quasar-size luminosity, as we shall see. 30 October 2001 ...
... neighborhood of Sgr A*’s black hole to provide a quasarlike luminosity. This would also explain the lack of jets. It’s also not quite massive enough for quasar-size luminosity, as we shall see. 30 October 2001 ...
DAVID A. RIETHMILLER - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Ph.D. Thesis Topic – Ohio University (current): My current research explores the hydrodynamic history of elliptical galaxies, simulating various prescriptions for interstellar gas cooling and AGN energy feedback against real X-ray observations of ellipticals. The goal is to isolate those prescriptio ...
... Ph.D. Thesis Topic – Ohio University (current): My current research explores the hydrodynamic history of elliptical galaxies, simulating various prescriptions for interstellar gas cooling and AGN energy feedback against real X-ray observations of ellipticals. The goal is to isolate those prescriptio ...
PDF
... aperture, which would account for the instrumental and cosmic X-ray backgrounds. However, the blank-sky background would not include contributions from the diffuse Galactic plane emission, and most importantly, would not include the scattered flux from GX 13+1. Hence, we relied upon a relatively con ...
... aperture, which would account for the instrumental and cosmic X-ray backgrounds. However, the blank-sky background would not include contributions from the diffuse Galactic plane emission, and most importantly, would not include the scattered flux from GX 13+1. Hence, we relied upon a relatively con ...
Giant “Pulsar” Studies with the Compact Array Abstract
... that these transients are periodic, or stellar pulsars. Isolated radio flares of few-minute durations, nonthermal brightness temperatures and almost total circular polarisation have been observed from stars of almost all types with spectral classes F or cooler. Non-thermal radio emission from stars ...
... that these transients are periodic, or stellar pulsars. Isolated radio flares of few-minute durations, nonthermal brightness temperatures and almost total circular polarisation have been observed from stars of almost all types with spectral classes F or cooler. Non-thermal radio emission from stars ...
Astronomy
... Astronomy Unit 1 Early Astronomy Notes 1. Early astronomers identified celestial objects with _________ and ___________. 2. List five phenomena that early astronomers linked to celestial changes. ...
... Astronomy Unit 1 Early Astronomy Notes 1. Early astronomers identified celestial objects with _________ and ___________. 2. List five phenomena that early astronomers linked to celestial changes. ...
1410.PDF
... *Radii of all targets was about 3 mm, yielding an area of about 0.283 cm2. The volume of each target was 0.029 cm3 except for sample 8 which was 0.038 cm ...
... *Radii of all targets was about 3 mm, yielding an area of about 0.283 cm2. The volume of each target was 0.029 cm3 except for sample 8 which was 0.038 cm ...
Diffuse TeV Emission from the Galactic Center
... The two-temperature plasma component does a decent job of modeling the 1-10 keV spectrum, but cannot account for the emission flux > 20 keV ...
... The two-temperature plasma component does a decent job of modeling the 1-10 keV spectrum, but cannot account for the emission flux > 20 keV ...
Carolina Kehrig
... (Crowther & Hadfield 2006), ≥ 100 WRs is required to explain the Q(HeII)obs , but such very large WR population is not compatible with: (> 8 times) Total stellar mass of the NW cluster WR/O stars ratio at the metallicity of IZw18 (e.g. Maeder & Meynet 2012) Stellar evolutionary models for single mas ...
... (Crowther & Hadfield 2006), ≥ 100 WRs is required to explain the Q(HeII)obs , but such very large WR population is not compatible with: (> 8 times) Total stellar mass of the NW cluster WR/O stars ratio at the metallicity of IZw18 (e.g. Maeder & Meynet 2012) Stellar evolutionary models for single mas ...
X-ray activity cycle on the active ultra
... gratings. These two reflection-grating spectrometers (RGS) provide high spectral resolution (E/ΔE ≈ 200–800) in the energy range 0.35–2.5 keV. Useful data were obtained from the EPIC and the RGS detectors (see Table 1 for a detailed account). AB Dor A, which is a very bright target with many emissio ...
... gratings. These two reflection-grating spectrometers (RGS) provide high spectral resolution (E/ΔE ≈ 200–800) in the energy range 0.35–2.5 keV. Useful data were obtained from the EPIC and the RGS detectors (see Table 1 for a detailed account). AB Dor A, which is a very bright target with many emissio ...
Altair -- the ``hottest`` magnetically active star in X-rays
... Rotational modulation can be studied with our X-ray data that covers in total three to four stellar rotations. However, the uncertainties in the relevant stellar parameters (V sin i, i, R) allow a range of rotation periods with values around 9.5 ± 1 h. Further, our data is not continuous, and especi ...
... Rotational modulation can be studied with our X-ray data that covers in total three to four stellar rotations. However, the uncertainties in the relevant stellar parameters (V sin i, i, R) allow a range of rotation periods with values around 9.5 ± 1 h. Further, our data is not continuous, and especi ...
white dwarf
... – irradiation of the stream and secondary by X-ray flux – more astrophysics in the post-shock flow models (such as the separation of electron and ion fluids) • Combinations of high quality data (e.g. eclipse mapping of spectra) and new astrophysical fluid computations will transform the field and al ...
... – irradiation of the stream and secondary by X-ray flux – more astrophysics in the post-shock flow models (such as the separation of electron and ion fluids) • Combinations of high quality data (e.g. eclipse mapping of spectra) and new astrophysical fluid computations will transform the field and al ...
Observing Nebulosities: The Cygnus Superbubble Chris
... Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Wisconsin Oshkosh Oshkosh, WI 54901 Abstract The Galactic star-forming complexes are best delineated by the distribution of the ionized interstellar matter which is always associated with active star-formation. Observations of these regions at specif ...
... Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Wisconsin Oshkosh Oshkosh, WI 54901 Abstract The Galactic star-forming complexes are best delineated by the distribution of the ionized interstellar matter which is always associated with active star-formation. Observations of these regions at specif ...
X-ray astronomy

X-ray astronomy is an observational branch of astronomy which deals with the study of X-ray observation and detection from astronomical objects. X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to high altitude by balloons, sounding rockets, and satellites. X-ray astronomy is the space science related to a type of space telescope that can see farther than standard light-absorption telescopes, such as the Mauna Kea Observatories, via x-ray radiation.X-ray emission is expected from astronomical objects that contain extremely hot gasses at temperatures from about a million kelvin (K) to hundreds of millions of kelvin (MK). Although X-rays have been observed emanating from the Sun since the 1940s, the discovery in 1962 of the first cosmic X-ray source was a surprise. This source is called Scorpius X-1 (Sco X-1), the first X-ray source found in the constellation Scorpius. The X-ray emission of Scorpius X-1 is 10,000 times greater than its visual emission, whereas that of the Sun is about a million times less. In addition, the energy output in X-rays is 100,000 times greater than the total emission of the Sun in all wavelengths. Based on discoveries in this new field of X-ray astronomy, starting with Scorpius X-1, Riccardo Giacconi received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2002. It is now known that such X-ray sources as Sco X-1 are compact stars, such as neutron stars or black holes. Material falling into a black hole may emit X-rays, but the black hole itself does not. The energy source for the X-ray emission is gravity. Infalling gas and dust is heated by the strong gravitational fields of these and other celestial objects.Many thousands of X-ray sources are known. In addition, the space between galaxies in galaxy clusters is filled with a very hot, but very dilute gas at a temperature between 10 and 100 megakelvins (MK). The total amount of hot gas is five to ten times the total mass in the visible galaxies.