Genetics Lesson 5 ALL vocabulary
... 6. dominant allele- will always show its effect even when only one dominate allele is present in an organisms genotype. 7. genotype- the actual genes (alleles) the organism has. 8. heterozygous- when the two alleles for a trait are different (one dominant and one recessive) 9. homozygous- when ...
... 6. dominant allele- will always show its effect even when only one dominate allele is present in an organisms genotype. 7. genotype- the actual genes (alleles) the organism has. 8. heterozygous- when the two alleles for a trait are different (one dominant and one recessive) 9. homozygous- when ...
evolution - Richard Dawkins Foundation
... the chromosomes) which an organism carries inside. Phenotype: The outward, physical expression of those genes. Mutation: A permanent change in the DNA of an organism. If it is passed on to the organism’s offspring, it may be harmful, harmless, or helpful for the offspring. ...
... the chromosomes) which an organism carries inside. Phenotype: The outward, physical expression of those genes. Mutation: A permanent change in the DNA of an organism. If it is passed on to the organism’s offspring, it may be harmful, harmless, or helpful for the offspring. ...
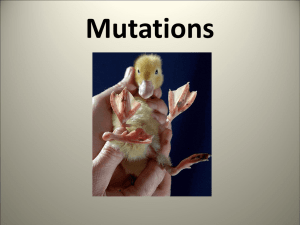
Mutations
... egg. If fertilized this mistake would be passed on to the child. Example: Sickle cell anemia ...
... egg. If fertilized this mistake would be passed on to the child. Example: Sickle cell anemia ...
Evolution - Georgia Standards
... In 1859 Darwin published his views in 'On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection', sparking a major controversy between theologians and scientists. Even scientists argued with each other over how the traits Darwin thought were subject to natural selection could be inherited. Ironically, ...
... In 1859 Darwin published his views in 'On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection', sparking a major controversy between theologians and scientists. Even scientists argued with each other over how the traits Darwin thought were subject to natural selection could be inherited. Ironically, ...
Chapter 10: Natural Selection
... Variations in traits are variations in phenotypes Traits are controlled by genes Inheritable variation comes from differences in genes (genetic diversity) Differences in genes come from mutations and gene shuffling ...
... Variations in traits are variations in phenotypes Traits are controlled by genes Inheritable variation comes from differences in genes (genetic diversity) Differences in genes come from mutations and gene shuffling ...
The Evolution of Altruistic Behavior
... slowness of any evolution based on group selection compared to the simultaneous trends that can occur by selection of the classical kind, based on individual advantage, this explanation must be treated with reserve so long as it remains unsupported by mathematical models. Fisher in the second editio ...
... slowness of any evolution based on group selection compared to the simultaneous trends that can occur by selection of the classical kind, based on individual advantage, this explanation must be treated with reserve so long as it remains unsupported by mathematical models. Fisher in the second editio ...
Exam 5 Review - Iowa State University
... 14. Which of the following might be occurring if a population is not in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? A) natural selection B) random matng C) no migration D) no gene flow 15. If the allele frequencies in a population are A: 0.6 and a: 0.4. what is the frequency of the Aa genotype if the population is ...
... 14. Which of the following might be occurring if a population is not in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? A) natural selection B) random matng C) no migration D) no gene flow 15. If the allele frequencies in a population are A: 0.6 and a: 0.4. what is the frequency of the Aa genotype if the population is ...
Population Genetics
... ¾ What is the probability that the d allele will become fixed in the population? ¾ If fixation occurs, how long will it take? ¾ How will the growth of the population, from generation to generation, affect the answers to parts a and b? ...
... ¾ What is the probability that the d allele will become fixed in the population? ¾ If fixation occurs, how long will it take? ¾ How will the growth of the population, from generation to generation, affect the answers to parts a and b? ...
Basic Principles of Genetics: Printable Crossword Puzzle
... 5. Mendel's principle of genetic inheritance stating that different pairs of genes are passed to offspring independently so that new combinations of genes, present in neither parent, are possible. 9. An alternate form of the same gene. 11. The genetic makeup of an individual for a trait or for all o ...
... 5. Mendel's principle of genetic inheritance stating that different pairs of genes are passed to offspring independently so that new combinations of genes, present in neither parent, are possible. 9. An alternate form of the same gene. 11. The genetic makeup of an individual for a trait or for all o ...
Paternal Age Risks
... syndrome, and osteogenesis imperfecta (“brittle bone” disease). Because there is such a variety of dominant genetic disorders that may be related to advanced paternal age, there is no single test available for prenatal diagnosis. An ultrasound can be performed to evaluate fetal growth and developmen ...
... syndrome, and osteogenesis imperfecta (“brittle bone” disease). Because there is such a variety of dominant genetic disorders that may be related to advanced paternal age, there is no single test available for prenatal diagnosis. An ultrasound can be performed to evaluate fetal growth and developmen ...
LE - 7 - Genetic Engineering
... • Take selected object you want modified, open pores of the cell membrane, and insert gene into cell. • By various methods (like particle guns) selected genes will combine with the natural DNA, therefore altering the original sequence. This phase of genetic engineering varies depending on the organi ...
... • Take selected object you want modified, open pores of the cell membrane, and insert gene into cell. • By various methods (like particle guns) selected genes will combine with the natural DNA, therefore altering the original sequence. This phase of genetic engineering varies depending on the organi ...
Mechanisms for Evolution
... adaptation is an physical structure, physiological process or behavioral trait of an organism that has evolved over a period of time by the process of natural selection. Adaptations increase the reproductive success of the organism. ...
... adaptation is an physical structure, physiological process or behavioral trait of an organism that has evolved over a period of time by the process of natural selection. Adaptations increase the reproductive success of the organism. ...
Honors Evolution Power Point 201
... • Natural selection acts on individuals-their char. Affect their chances of survival and reproduction. • Evolution is only apparent when a population is tracked over time ...
... • Natural selection acts on individuals-their char. Affect their chances of survival and reproduction. • Evolution is only apparent when a population is tracked over time ...
Introduction
... researched. This new field is called Conservation genetics. The main goal of conservation genetics is to develop effective management strategies for the conservation of endangered species. One of the most important strategies is maintaining genetic diversity within the captive tiger population. The ...
... researched. This new field is called Conservation genetics. The main goal of conservation genetics is to develop effective management strategies for the conservation of endangered species. One of the most important strategies is maintaining genetic diversity within the captive tiger population. The ...
Homework - District 273 Technology Services
... • Moth color appeared to change as surface of environment changed • They both existed, just relative numbers were changed with majority matching environment ...
... • Moth color appeared to change as surface of environment changed • They both existed, just relative numbers were changed with majority matching environment ...
Lecture PPT - Carol Eunmi LEE
... Random Mating: Mixes up combination of alleles at a given locus (increases genotypic variation) This shuffling of alleles is thought to have many advantages, as a major engine of generating genotypic variation ...
... Random Mating: Mixes up combination of alleles at a given locus (increases genotypic variation) This shuffling of alleles is thought to have many advantages, as a major engine of generating genotypic variation ...
Sex - Carol Lee Lab
... • The non-random association of alleles at two or more loci, not necessarily on the same chromosome. • The occurrence of some combinations of alleles or genetic markers in a population more often or less often than would be expected from a random formation of haplotypes from alleles based on the ...
... • The non-random association of alleles at two or more loci, not necessarily on the same chromosome. • The occurrence of some combinations of alleles or genetic markers in a population more often or less often than would be expected from a random formation of haplotypes from alleles based on the ...
AP Biology Study Guide
... 8. Describe two examples of natural selection known to occur in nature. Note three key points about how natural selection works. 9. Explain how fossils form, noting examples of each process. 10. Explain how the fossil record provides some of the strongest evidence of evolution. 11. Explain how bioge ...
... 8. Describe two examples of natural selection known to occur in nature. Note three key points about how natural selection works. 9. Explain how fossils form, noting examples of each process. 10. Explain how the fossil record provides some of the strongest evidence of evolution. 11. Explain how bioge ...
before
... Individuals Do Not Evolve • Individuals vary, but populations evolve • Natural selection pressures make an individual more or less likely to survive and reproduce • But, it is the cumulative effects of selection on the genetic makeup of the whole population that results in changes to the species Th ...
... Individuals Do Not Evolve • Individuals vary, but populations evolve • Natural selection pressures make an individual more or less likely to survive and reproduce • But, it is the cumulative effects of selection on the genetic makeup of the whole population that results in changes to the species Th ...
Various forms of the same gene are called
... An organism that has two copies of the same allele for a gene is ___________________ or also known as _______________________ . An organism that has two different alleles for the same gene is _____________________. A cross between two true-breeding parents following the inheritance of only one genet ...
... An organism that has two copies of the same allele for a gene is ___________________ or also known as _______________________ . An organism that has two different alleles for the same gene is _____________________. A cross between two true-breeding parents following the inheritance of only one genet ...
Who Is My Mommy?
... GPS for our study of Genetics • S7L3 Students will recognize how biological traits are passed on to successive generations. • S7L3a Students will explain the role of genes and chromosomes in the process of inheriting a specific trait. • S7L3c Students will recognize that selective breeding can produ ...
... GPS for our study of Genetics • S7L3 Students will recognize how biological traits are passed on to successive generations. • S7L3a Students will explain the role of genes and chromosomes in the process of inheriting a specific trait. • S7L3c Students will recognize that selective breeding can produ ...
Lecture PPT - Carol Lee Lab
... a given locus (increases genotypic variation) This shuffling of alleles is thought to have many advantages, as a major engine of generating genotypic variation ...
... a given locus (increases genotypic variation) This shuffling of alleles is thought to have many advantages, as a major engine of generating genotypic variation ...
Genes - Revision World
... 2) Population numbers in a species stay constant over time 3) Each species displays a wide variation in features 4) Some of these variations are passed on to offspring ...
... 2) Population numbers in a species stay constant over time 3) Each species displays a wide variation in features 4) Some of these variations are passed on to offspring ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.