Document
... Frequencies of particular alleles may change by chance alone. important in small populations founder effect - few individuals found new population (small allelic pool) bottleneck effect - drastic reduction in population, and gene pool size ...
... Frequencies of particular alleles may change by chance alone. important in small populations founder effect - few individuals found new population (small allelic pool) bottleneck effect - drastic reduction in population, and gene pool size ...
ANTHR1 - Physical Anthropology
... Explain the statement: Evolution is a change in the relative frequencies of alleles in a population from one generation to the next. Be very precise in your explanation by giving an example. REMEMBER, this question is focusing on GENETICS. Explain how protein synthesis occurs. Be very complete in yo ...
... Explain the statement: Evolution is a change in the relative frequencies of alleles in a population from one generation to the next. Be very precise in your explanation by giving an example. REMEMBER, this question is focusing on GENETICS. Explain how protein synthesis occurs. Be very complete in yo ...
Name - Humble ISD
... Mass extinctions clear the way for _______________________ of other species. EX:____________________ B. Adaptive radiation-the process where a _______________species has evolved through _________________________ into diverse forms that live in ___________________________ways. EX: ____________ C.__ ...
... Mass extinctions clear the way for _______________________ of other species. EX:____________________ B. Adaptive radiation-the process where a _______________species has evolved through _________________________ into diverse forms that live in ___________________________ways. EX: ____________ C.__ ...
Dear-Family-Member-HBOC
... Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndrome. Among other topics, my genetics professional and I discussed the importance of this information for my biological relatives as you too may be at risk for Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndrome. The gene mutation identified in me was most likely i ...
... Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndrome. Among other topics, my genetics professional and I discussed the importance of this information for my biological relatives as you too may be at risk for Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndrome. The gene mutation identified in me was most likely i ...
GENETICS OF MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
... Coronary artery disease (CAD) remains the number one killer. Genetics account for over 50% of the risk for CAD. Coronary artery disease is a preventable disease. However, recognizing that about 50% of susceptibility to CAD is genetic, comprehensive prevention of CAD will require treating genetic and ...
... Coronary artery disease (CAD) remains the number one killer. Genetics account for over 50% of the risk for CAD. Coronary artery disease is a preventable disease. However, recognizing that about 50% of susceptibility to CAD is genetic, comprehensive prevention of CAD will require treating genetic and ...
Biology 101 Section 6
... Genes and Chromosomes Gene: a segment of DNA that codes fro a heritable trait - located at gene loci or loci - chromosomes are 1000's of genes Principle of Independent Assortment - Each trait's (gene's) alleles segregate, or split to opposite sides of the cell, independently from one another during ...
... Genes and Chromosomes Gene: a segment of DNA that codes fro a heritable trait - located at gene loci or loci - chromosomes are 1000's of genes Principle of Independent Assortment - Each trait's (gene's) alleles segregate, or split to opposite sides of the cell, independently from one another during ...
Populus Lab – Genetic Drift
... frequency within a population caused by random events. These changes can mean that a harmful allele may increase its frequency in a population or that rare advantageous alleles may be lost. One way that scientists have learned to study the effects of genetic drift is by focusing on neutral alleles. ...
... frequency within a population caused by random events. These changes can mean that a harmful allele may increase its frequency in a population or that rare advantageous alleles may be lost. One way that scientists have learned to study the effects of genetic drift is by focusing on neutral alleles. ...
hssv0402t_powerpres
... Evolution by Natural Selection • Natural selection is the process by which individuals that have favorable variations and are better adapted to their environment survive and reproduce more successfully than less well adapted individuals do. • Darwin proposed that over many generations, natural selec ...
... Evolution by Natural Selection • Natural selection is the process by which individuals that have favorable variations and are better adapted to their environment survive and reproduce more successfully than less well adapted individuals do. • Darwin proposed that over many generations, natural selec ...
Exam practice answers 8
... 2 (a) QqRr. (b) (i) Qr and qR. (ii) Qr, QR, qR and qr. (iii) Qr and qR. 3 (a) (i) meiosis = A (ii) mitosis = C (iii) fertilisation = B (b) Gametes are sex cells produced for sexual reproduction. During fertilisation, two gametes fuse and restore the diploid number of chromosomes (2n). 4 (a) When a s ...
... 2 (a) QqRr. (b) (i) Qr and qR. (ii) Qr, QR, qR and qr. (iii) Qr and qR. 3 (a) (i) meiosis = A (ii) mitosis = C (iii) fertilisation = B (b) Gametes are sex cells produced for sexual reproduction. During fertilisation, two gametes fuse and restore the diploid number of chromosomes (2n). 4 (a) When a s ...
outline
... Question 2. Are all organisms perfectly adapted to their environments? It is thought that many traits arise through the process of natural selection. If occasionally they arise by chance, then they are maintained by natural selection. Also, a given environment can change such that any given adaptat ...
... Question 2. Are all organisms perfectly adapted to their environments? It is thought that many traits arise through the process of natural selection. If occasionally they arise by chance, then they are maintained by natural selection. Also, a given environment can change such that any given adaptat ...
Genetics Vocabulary
... dominant allele is present A form of a gene that is expressed as the trait only when a dominant allele is not present An organism’s particular combination of paired alleles (genes) A gene composed of two different alleles (a dominant and a recessive allele) A gene composed of two identical alleles ( ...
... dominant allele is present A form of a gene that is expressed as the trait only when a dominant allele is not present An organism’s particular combination of paired alleles (genes) A gene composed of two different alleles (a dominant and a recessive allele) A gene composed of two identical alleles ( ...
Hardy-Weinberg problems 2015
... 10. In a large population of Biology instructors, 396 are red-sided individuals and 557 are tan-sided individuals. Assume that red is totally recessive. Calculate the following: A. The allele frequencies of each allele. B. The expected genotype frequencies. C. The number of heterozygous individuals ...
... 10. In a large population of Biology instructors, 396 are red-sided individuals and 557 are tan-sided individuals. Assume that red is totally recessive. Calculate the following: A. The allele frequencies of each allele. B. The expected genotype frequencies. C. The number of heterozygous individuals ...
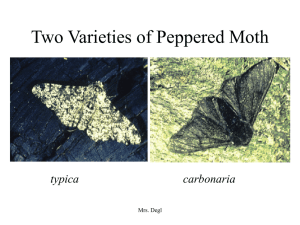
Peppered Moth
... of facts to support the theory of evolution by natural selection. One of his difficulties in demonstrating the theory, however, was the lack of an example of evolution over a short period of time, which could be observed as it was taking place in nature. Although Darwin was unaware of it, remarkable ...
... of facts to support the theory of evolution by natural selection. One of his difficulties in demonstrating the theory, however, was the lack of an example of evolution over a short period of time, which could be observed as it was taking place in nature. Although Darwin was unaware of it, remarkable ...
Evolving "elementary sight" strategies in predators via Genetic
... Witness the evolution of the predator "strategy". Imitate the evolution of the parts in the brain that handle the visual informal interpretation . Try to understand the development stages in the strategy. Try to analyze the usage of the photoreceptors as part of the brain function . Test if the deve ...
... Witness the evolution of the predator "strategy". Imitate the evolution of the parts in the brain that handle the visual informal interpretation . Try to understand the development stages in the strategy. Try to analyze the usage of the photoreceptors as part of the brain function . Test if the deve ...
4.4 Genetic engineering and biotechnology - McLain
... B. To determine the nucleotide sequence of all human chromosomes C. To determine how genes control biological processes D. To understand the evolution of species 12. Genetic modification involves the transfer of DNA from one species to another. Discuss the potential benefits and possible harmful eff ...
... B. To determine the nucleotide sequence of all human chromosomes C. To determine how genes control biological processes D. To understand the evolution of species 12. Genetic modification involves the transfer of DNA from one species to another. Discuss the potential benefits and possible harmful eff ...
biol2007 evolution of genetic diversity
... b) diversifying frequency-dependent selection - selection for rare forms when their frequencies are low: ...
... b) diversifying frequency-dependent selection - selection for rare forms when their frequencies are low: ...
Evolution - WordPress.com
... resistance and insecticide resistance. -Understanding relationships between organisms can help us make conclusions in medical research. It explains how HIV and influenza can change (mutate). ...
... resistance and insecticide resistance. -Understanding relationships between organisms can help us make conclusions in medical research. It explains how HIV and influenza can change (mutate). ...
Program of the SIMBAD seminar, second session
... Abstract : Evolutionary rescue occurs when a population genetically adapts to a new stressful environment that would otherwise cause its extinction. Forecasting the probability of persistence under stress, such as emergence of drug resistance or invasion of a new environment is a major concern in ec ...
... Abstract : Evolutionary rescue occurs when a population genetically adapts to a new stressful environment that would otherwise cause its extinction. Forecasting the probability of persistence under stress, such as emergence of drug resistance or invasion of a new environment is a major concern in ec ...
The neutral theory of molecular
... alleles (new sequence versions) per unit time The probability that a particular allele will become fixed in a population depends on its frequency, its fitness advantage or disadvantage, i.e. (Darwinian) selection increasing or decreasing its frequency, the effective population size Ne which affects ...
... alleles (new sequence versions) per unit time The probability that a particular allele will become fixed in a population depends on its frequency, its fitness advantage or disadvantage, i.e. (Darwinian) selection increasing or decreasing its frequency, the effective population size Ne which affects ...
Genome variation informatics: SNP discovery, demographic
... Redevelopment and expansion • Improve the detection of very rare alleles by taking into account recent results in Population Genetics (i.e. a priori, rare alleles are more frequent than common alleles) • Developing a rigorous statistical framework both for heterozygote polymorphisms and INDELs • Ca ...
... Redevelopment and expansion • Improve the detection of very rare alleles by taking into account recent results in Population Genetics (i.e. a priori, rare alleles are more frequent than common alleles) • Developing a rigorous statistical framework both for heterozygote polymorphisms and INDELs • Ca ...
Figures from Chapter 3
... • Genetic endowment • Common to the species • Governs maturation and aging ...
... • Genetic endowment • Common to the species • Governs maturation and aging ...
ws: Hardy Weinberg Practice Problems
... No one finds you and you start a new population totally isolated from the rest of the world. Two of your friends carry (i.e. are heterozygous for) the recessive cystic fibrosis allele (c). Assuming that the frequency of this allele does not change as the population grows, what will be the incidence ...
... No one finds you and you start a new population totally isolated from the rest of the world. Two of your friends carry (i.e. are heterozygous for) the recessive cystic fibrosis allele (c). Assuming that the frequency of this allele does not change as the population grows, what will be the incidence ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.