Evolution: Natural Selection & Adaptation
... ind. vary within pops. some variation is inherited and affects survival more offspring are produced than env. can support offspring with most adaptive traits will survive and produce more of their own offspring ...
... ind. vary within pops. some variation is inherited and affects survival more offspring are produced than env. can support offspring with most adaptive traits will survive and produce more of their own offspring ...
Ch. 15.2 Evidence ofEvolution
... Insecticide resistance • Spray the field, but… – insecticide didn’t kill all individuals • variation ...
... Insecticide resistance • Spray the field, but… – insecticide didn’t kill all individuals • variation ...
File - Ms. Leigh`s Science Resource
... Evolution by Random Processes • Mutation- occur randomly and can add to the genetic variation of a population. • Genetic drift- change in the genetic composition of a population over time as a result of random mating. • Bottleneck effect- a reduction in the genetic diversity of a population caused ...
... Evolution by Random Processes • Mutation- occur randomly and can add to the genetic variation of a population. • Genetic drift- change in the genetic composition of a population over time as a result of random mating. • Bottleneck effect- a reduction in the genetic diversity of a population caused ...
8th International Rosaceae Genomics Conference
... range of topics including cross-disciplinary research on flower initiation, plant development, fruit quality, and abiotic and biotic stresses alongside descriptions of domestication, evolutionary genetics and marker development in Rosaceous plants. As a molecular breeder, I found four of the present ...
... range of topics including cross-disciplinary research on flower initiation, plant development, fruit quality, and abiotic and biotic stresses alongside descriptions of domestication, evolutionary genetics and marker development in Rosaceous plants. As a molecular breeder, I found four of the present ...
Laws of Adaptation
... natural selection. Maximization of mean fitness when constant selection acts on many variants (alleles) of a single gene. "Lotka-Volterra" equations of population dynamics under competition for limited resources. A biological model for the competition parameters. Short term evolution driven by densi ...
... natural selection. Maximization of mean fitness when constant selection acts on many variants (alleles) of a single gene. "Lotka-Volterra" equations of population dynamics under competition for limited resources. A biological model for the competition parameters. Short term evolution driven by densi ...
Allelic Association
... •We should concern ourselves with the apparent effect size at the marker, which results from 1) difference in frequency of marker and trait alleles 2) LD between the marker and trait loci 3) effect size of trait allele ...
... •We should concern ourselves with the apparent effect size at the marker, which results from 1) difference in frequency of marker and trait alleles 2) LD between the marker and trait loci 3) effect size of trait allele ...
Unit 4 review questions
... 5. Define complete dominance, incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, pleiotropy, epistasis, and polygenic inheritance. 6. Explain how one allele can be dominant over another at the molecular level. 7. How is a pedigree used in genetics? 8. Distinguish between recessively and dominantly ...
... 5. Define complete dominance, incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, pleiotropy, epistasis, and polygenic inheritance. 6. Explain how one allele can be dominant over another at the molecular level. 7. How is a pedigree used in genetics? 8. Distinguish between recessively and dominantly ...
Genetic Diseases: Cystic Fibrosis
... genes. All of the information from the organism’s genes determines the traits of the organism. Some of the genes carry information that determines common traits such as eye color and height. Some genes carry traits that can e traits can cause problems for people. These include genetic diseases. used ...
... genes. All of the information from the organism’s genes determines the traits of the organism. Some of the genes carry information that determines common traits such as eye color and height. Some genes carry traits that can e traits can cause problems for people. These include genetic diseases. used ...
Genetics - Our Lady Of The Wayside School
... Every organism has 2 forms of the gene for each trait True breeding: TT (tall plant) or tt (small plant) ...
... Every organism has 2 forms of the gene for each trait True breeding: TT (tall plant) or tt (small plant) ...
Evolution and Natural Selection
... that enhanced the organisms chances of survival. • He began to form a theory that as organisms gradually accumulated new adaptations, they would form a new species. o One of the best examples of this theory is the different species of finches on the islands. o The birds were all very similar except ...
... that enhanced the organisms chances of survival. • He began to form a theory that as organisms gradually accumulated new adaptations, they would form a new species. o One of the best examples of this theory is the different species of finches on the islands. o The birds were all very similar except ...
One more funny wrinkle. . . Another example
... feeding, and setters which tend to stay in one place as they feed • This is governed by one gene with two alleles: forR and fors • Work by Sokolowski et al. (1997) suggests that density-dependent selection maintains these two alleles in the population—when one is most common, the other has the s ...
... feeding, and setters which tend to stay in one place as they feed • This is governed by one gene with two alleles: forR and fors • Work by Sokolowski et al. (1997) suggests that density-dependent selection maintains these two alleles in the population—when one is most common, the other has the s ...
The Genetic Counseling Outcome Scale
... Gene analysis tells us there are a large number of different forms - ?100 -200 ...
... Gene analysis tells us there are a large number of different forms - ?100 -200 ...
Natural selection
... explain what causes natural selection to occur. 1) All living things have variety within species. 2) Traits are inherited from parents to offspring. 3) Species compete with one another for limited resources (food, shelter, water, nutrients etc.). 4) Those individuals that inherit an advantageous tra ...
... explain what causes natural selection to occur. 1) All living things have variety within species. 2) Traits are inherited from parents to offspring. 3) Species compete with one another for limited resources (food, shelter, water, nutrients etc.). 4) Those individuals that inherit an advantageous tra ...
Natural Selection
... favorable traits are more likely to survive and reproduce than those with unfavorable traits. • The genotypes associated with the favored traits will increase in frequency in the next generation. Given enough time, this passive process results in adaptations and speciation ...
... favorable traits are more likely to survive and reproduce than those with unfavorable traits. • The genotypes associated with the favored traits will increase in frequency in the next generation. Given enough time, this passive process results in adaptations and speciation ...
Natural selection of spermatozoids
... the evaluation of the genotype is about one generation late. Natural selection at the spermatozoon stage is the cause of the phenomena that the genotype formation takes place after selection. It means that probability of the egg fertilization with already selected spermatozoon increased. In animals ...
... the evaluation of the genotype is about one generation late. Natural selection at the spermatozoon stage is the cause of the phenomena that the genotype formation takes place after selection. It means that probability of the egg fertilization with already selected spermatozoon increased. In animals ...
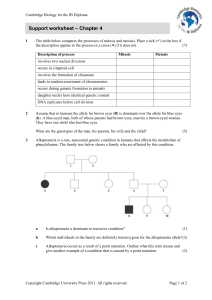
Support worksheet – Chapter 4 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... Assume that in humans the allele for brown eyes (B) is dominant over the allele for blue eyes (b). A blue-eyed man, both of whose parents had brown eyes, marries a brown-eyed woman. They have one child who has blue eyes. What are the genotypes of the man, his parents, his wife and the child? ...
... Assume that in humans the allele for brown eyes (B) is dominant over the allele for blue eyes (b). A blue-eyed man, both of whose parents had brown eyes, marries a brown-eyed woman. They have one child who has blue eyes. What are the genotypes of the man, his parents, his wife and the child? ...
Final Exam Spring 2016 Thursday June 2, Verified plagiarism on
... a. How do cell structures/organelles work together to accomplish the task of protein production? Include in your answer the role of the ribosomes, nucleus, DNA, and RNA. b. Protein production is essential to life. State and briefly discuss 2 functions of proteins. ...
... a. How do cell structures/organelles work together to accomplish the task of protein production? Include in your answer the role of the ribosomes, nucleus, DNA, and RNA. b. Protein production is essential to life. State and briefly discuss 2 functions of proteins. ...
Darwin and Evolution
... Hardy-Weinberg Principle • Genetic Equilibrium – situation in which allele frequencies in the gene pool of a population remain constant • The concept that the shuffling of genes that occurs during sexual reproduction, by itself, cannot change the overall genetic makeup of a population. • Shows math ...
... Hardy-Weinberg Principle • Genetic Equilibrium – situation in which allele frequencies in the gene pool of a population remain constant • The concept that the shuffling of genes that occurs during sexual reproduction, by itself, cannot change the overall genetic makeup of a population. • Shows math ...
Letter Microbial Variome Database: Point
... 2008). The gene pool of a species is represented by the combination of all genes and their variants that occur in individuals belonging to the given species. The pool is continuously enriched by mutation, sifting and shifting of representative genes, either by random genetic drift or by various sele ...
... 2008). The gene pool of a species is represented by the combination of all genes and their variants that occur in individuals belonging to the given species. The pool is continuously enriched by mutation, sifting and shifting of representative genes, either by random genetic drift or by various sele ...
ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS
... Modern genetics, the science that helps us to understand how and why we get traits from our parents, was not born until the nineteenth century. The father of modern genetics was Gregor Mendel, an Austrian scientist. Through eight years of experiments on pea plants, Mendel proved that characteristics ...
... Modern genetics, the science that helps us to understand how and why we get traits from our parents, was not born until the nineteenth century. The father of modern genetics was Gregor Mendel, an Austrian scientist. Through eight years of experiments on pea plants, Mendel proved that characteristics ...
AA - Bryn Mawr School Faculty Web Pages
... No migration: There is no movement of individuals into or out of the population (no gene flow). ...
... No migration: There is no movement of individuals into or out of the population (no gene flow). ...
Honors Biology - WordPress.com
... 3. In sexual reproduction, each parent contributes only one allele to the offspring. 4. This is why meiosis takes diploid cells and makes them haploid. The process of meiosis separates the homologous pairs, separating the alleles from each other. Each gamete (sperm and egg) when fused will result wi ...
... 3. In sexual reproduction, each parent contributes only one allele to the offspring. 4. This is why meiosis takes diploid cells and makes them haploid. The process of meiosis separates the homologous pairs, separating the alleles from each other. Each gamete (sperm and egg) when fused will result wi ...
Know More About Genetic Disease
... demonstrate clustering within families. In other words, these diseases often affect more than one members within a family. Genetic diseases by nature are often familial, due to sharing of common genetic material among family members. However, familial clustering does not necessarily indicate that th ...
... demonstrate clustering within families. In other words, these diseases often affect more than one members within a family. Genetic diseases by nature are often familial, due to sharing of common genetic material among family members. However, familial clustering does not necessarily indicate that th ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.