Directional Positive Selection on an Allele of Arbitrary
... for smaller h. This effect on the genealogy is most notable in the value of up rather than uw and uH because this statistic is most sensitive to the height of the genealogy (Tajima 1989b). The second result stems from the difference in the shape of the trajectory. As shown in Figure 2a, when h is sm ...
... for smaller h. This effect on the genealogy is most notable in the value of up rather than uw and uH because this statistic is most sensitive to the height of the genealogy (Tajima 1989b). The second result stems from the difference in the shape of the trajectory. As shown in Figure 2a, when h is sm ...
PPT File
... Connected by Evolutionary History Unity of all organisms best explained by common ancestry. primitive “cells/organisms” provided raw material for diversity among currently living organisms. traits within populations became modified over time. ...
... Connected by Evolutionary History Unity of all organisms best explained by common ancestry. primitive “cells/organisms” provided raw material for diversity among currently living organisms. traits within populations became modified over time. ...
Human Pedigrees
... analysis for humans) • Genetic analysis of the biochemical process • Microscopic analysis of the chromosome structure • Direct analysis of the DNA Text ch. 1 p.11-12 ...
... analysis for humans) • Genetic analysis of the biochemical process • Microscopic analysis of the chromosome structure • Direct analysis of the DNA Text ch. 1 p.11-12 ...
LEB_5MP_Content1-2
... Discussion of why the species that students have identified have become extinct based on what they know about the species and what was discussed in the ...
... Discussion of why the species that students have identified have become extinct based on what they know about the species and what was discussed in the ...
ap evolution review - Blue Valley Schools
... drug resistance, name and represent the common modes of selection, and be able to deduce which is acting a particular example. 6. You be able to give examples of homologous and analogous structures and discuss how these idea support natural selection and speciation. 7. You should be able to explain ...
... drug resistance, name and represent the common modes of selection, and be able to deduce which is acting a particular example. 6. You be able to give examples of homologous and analogous structures and discuss how these idea support natural selection and speciation. 7. You should be able to explain ...
Genetics Supplement
... To answer this question your group will use model chromosomes to demonstrate meiosis and fertilization. The pair of homologous chromosomes for each parent will include one model chromosome with an A allele and another with an a allele. 4. One of you should be the mother and use your model chromosome ...
... To answer this question your group will use model chromosomes to demonstrate meiosis and fertilization. The pair of homologous chromosomes for each parent will include one model chromosome with an A allele and another with an a allele. 4. One of you should be the mother and use your model chromosome ...
PEDIGREE CHARTS - Rankin County School District
... Genes with three or more alleles are said to have multiple alleles. When traits are controlled by genes with multiple alleles, an individual can have only two of the possible alleles for that gene. Example: Blood types in humans ...
... Genes with three or more alleles are said to have multiple alleles. When traits are controlled by genes with multiple alleles, an individual can have only two of the possible alleles for that gene. Example: Blood types in humans ...
Probability section 4
... written across the top. All the possible alleles from the other parent are written down the left side. The combined alleles in the boxes of the Punnett square represent all the possible combinations in the offspring ...
... written across the top. All the possible alleles from the other parent are written down the left side. The combined alleles in the boxes of the Punnett square represent all the possible combinations in the offspring ...
Note 7.5 - Genetic Mutations
... Translocation – is the movement of entire genes or sequences of DNA from one chromosome to another. Large scale mutations may involve multiple nucleotide sequences, entire genes, or large regions of a chromosome. These mutations can an affect of the genome and the function of an organism. Gene dupli ...
... Translocation – is the movement of entire genes or sequences of DNA from one chromosome to another. Large scale mutations may involve multiple nucleotide sequences, entire genes, or large regions of a chromosome. These mutations can an affect of the genome and the function of an organism. Gene dupli ...
English 9 - Edmentum Support
... There is a steady rise in the population of bright-colored fish. Both populations thrive. Suppose that a short land barrier separates Lake A from another small lake with a population of only the normal dark-colored fish (Lake B). After torrential rains lasting for days, the lakes overflow and a few ...
... There is a steady rise in the population of bright-colored fish. Both populations thrive. Suppose that a short land barrier separates Lake A from another small lake with a population of only the normal dark-colored fish (Lake B). After torrential rains lasting for days, the lakes overflow and a few ...
Familial Segregation of Hemangiomas and
... This paper describes six rare families in which hemangiomas (common, benign vascular tumors of childhood— often known as “strawberry marks”) appear to be inherited from one generation to the next. This pattern of inheritance suggests the presence of a dominant gene mutation being passed from parents ...
... This paper describes six rare families in which hemangiomas (common, benign vascular tumors of childhood— often known as “strawberry marks”) appear to be inherited from one generation to the next. This pattern of inheritance suggests the presence of a dominant gene mutation being passed from parents ...
Alzheimer disease - GEC-KO
... • Late-onset familial AD (LOAD) has been associated with apolipoprotein E (APOE) • APOE is considered a risk modifier, especially APOE ...
... • Late-onset familial AD (LOAD) has been associated with apolipoprotein E (APOE) • APOE is considered a risk modifier, especially APOE ...
The Politics of Biology
... particular form of alcoholism (early-onset disorder in men, for example), just as often they reveal no pattern. This shouldn't be all that surprising, given the difficulty of defining alcoholism. Some researchers identify alcoholics by their drunk-driving record, while others focus on withdrawal sym ...
... particular form of alcoholism (early-onset disorder in men, for example), just as often they reveal no pattern. This shouldn't be all that surprising, given the difficulty of defining alcoholism. Some researchers identify alcoholics by their drunk-driving record, while others focus on withdrawal sym ...
Evolution Cont`d
... similarities species share from a common ancestor • Vestigial structures – are remnants of structures that may have had important functions in an ancestral species, but have no clear function in modern descendant. ...
... similarities species share from a common ancestor • Vestigial structures – are remnants of structures that may have had important functions in an ancestral species, but have no clear function in modern descendant. ...
Name Block ______ Unit 8 Evolution Biology 1 I. A Historic Voyage
... In this lab you will use fish crackers to help further your understanding of natural selection and the role of genetics and gene frequencies in evolution. Background: Facts about the 'Fish' 1. These little fish are the natural prey of the terrible fish-eating sharks - YOU! 2. Fish come with two phen ...
... In this lab you will use fish crackers to help further your understanding of natural selection and the role of genetics and gene frequencies in evolution. Background: Facts about the 'Fish' 1. These little fish are the natural prey of the terrible fish-eating sharks - YOU! 2. Fish come with two phen ...
Uses and abuses of genetic engineering
... in laboratory jargon) and overexpressing genes in particular lineages (“making transgenics”) has been with us for more than a decade. Today these earlier strategies are giving way to more sophisticated approaches, such as lineage-specific conditional knockouts in which a selected gene can be deleted ...
... in laboratory jargon) and overexpressing genes in particular lineages (“making transgenics”) has been with us for more than a decade. Today these earlier strategies are giving way to more sophisticated approaches, such as lineage-specific conditional knockouts in which a selected gene can be deleted ...
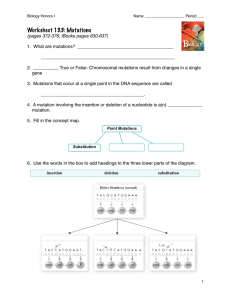
Worksheet 13.3
... 2. __________ True or False: Chromosomal mutations result from changes in a single gene 3. Mutations that occur at a single point in the DNA sequence are called ...
... 2. __________ True or False: Chromosomal mutations result from changes in a single gene 3. Mutations that occur at a single point in the DNA sequence are called ...
Homo Administrans
... been conspicuous by their absence. Dr Song has tried to fill this gap. His team have gathered and analysed DNA from 123 Singaporean couples to see if it can be matched with a host of work-related variables, starting with job satisfaction. In this case Dr Song first checked how prone each participant ...
... been conspicuous by their absence. Dr Song has tried to fill this gap. His team have gathered and analysed DNA from 123 Singaporean couples to see if it can be matched with a host of work-related variables, starting with job satisfaction. In this case Dr Song first checked how prone each participant ...
Species Concepts
... contain the best qualities of both parents 25-50% of plant species are polyploid Many are recent and/or important to humans: The grass Spartina angelica (2n = 122) evolved in the 1870s from S. maritima (2n = 60) and S. alternaflora (2n = 62) Bread wheat (Triticum aestivum) is a 42 chromosome hexaplo ...
... contain the best qualities of both parents 25-50% of plant species are polyploid Many are recent and/or important to humans: The grass Spartina angelica (2n = 122) evolved in the 1870s from S. maritima (2n = 60) and S. alternaflora (2n = 62) Bread wheat (Triticum aestivum) is a 42 chromosome hexaplo ...
BBHH BBHh
... 5. A shaded circle or square indicates a person has the trait 6. A circle or square NOT shaded represents an individual who does NOT have the trait 7. Partial shade indicates a carrier – someone who is heterozygous for the trait ...
... 5. A shaded circle or square indicates a person has the trait 6. A circle or square NOT shaded represents an individual who does NOT have the trait 7. Partial shade indicates a carrier – someone who is heterozygous for the trait ...
Evolutionary Algorithms
... The building block hypothesis suggests that improved solutions can be assembled from partial solutions which are aggregated in relatively small code blocks within the genome. Recombination allows merging favorable blocks and genetic repair of defective ...
... The building block hypothesis suggests that improved solutions can be assembled from partial solutions which are aggregated in relatively small code blocks within the genome. Recombination allows merging favorable blocks and genetic repair of defective ...
A new type of heredity described in Paramecia
... determined by the genome sequence but by small RNA sequences transmitted via the maternal cytoplasm, which specifically inactivate certain genes during development. A Paramecium can thus acquire a new mating type that will be inherited by its progeny without any genetic modification being involved. ...
... determined by the genome sequence but by small RNA sequences transmitted via the maternal cytoplasm, which specifically inactivate certain genes during development. A Paramecium can thus acquire a new mating type that will be inherited by its progeny without any genetic modification being involved. ...
Pedigree analysis
... certain substances, and even whether you have dry or sticky earwax! Other genes may actually cause disease. Sickle cell anemia, muscular dystrophy, cystic fibrosis are each caused by a specific allele of a human gene, and can therefore be inherited from one generation to the next. Inheritance of Alb ...
... certain substances, and even whether you have dry or sticky earwax! Other genes may actually cause disease. Sickle cell anemia, muscular dystrophy, cystic fibrosis are each caused by a specific allele of a human gene, and can therefore be inherited from one generation to the next. Inheritance of Alb ...
BIOL Unit 5
... • Genes are chemical factors that determine traits. • Alleles segregate from each other and each gamete carries a single copy of each gene. This is the law of segregation – the second law Mendel observed during his pea plant experiments. • TT is homozygous (“homo” = same; “zygous” = zygote) dominant ...
... • Genes are chemical factors that determine traits. • Alleles segregate from each other and each gamete carries a single copy of each gene. This is the law of segregation – the second law Mendel observed during his pea plant experiments. • TT is homozygous (“homo” = same; “zygous” = zygote) dominant ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.