Human Biology
... - The DNA contains instructions on how the cell should work - Genes control the development of characteristics (“it’s in the genes”) by issuing instructions to the cell to produce certain proteins - These proteins are either structural (used for cell growth and repair) or enzymes (used for speeding ...
... - The DNA contains instructions on how the cell should work - Genes control the development of characteristics (“it’s in the genes”) by issuing instructions to the cell to produce certain proteins - These proteins are either structural (used for cell growth and repair) or enzymes (used for speeding ...
Evolutionary Learning
... Evolution – An inevitable Process Just a few examples may include: Domestic Animals Breeding ...
... Evolution – An inevitable Process Just a few examples may include: Domestic Animals Breeding ...
DNA replication - Understanding Evolution
... Students will understand that 1) molecular mechanisms that preserve the fidelity of the genetic sequence have been favored by natural selection, 2) some entities, such as HIV, lack some of these mechanisms and so have a higher rate of mutation and evolution, and 3) many challenges posed to medical s ...
... Students will understand that 1) molecular mechanisms that preserve the fidelity of the genetic sequence have been favored by natural selection, 2) some entities, such as HIV, lack some of these mechanisms and so have a higher rate of mutation and evolution, and 3) many challenges posed to medical s ...
Chapter 10
... Mendel’s law of dominance When an organism has two different alleles for a given trait, the allele that is expressed, overshadowing the expression of the other allele, is said to be dominant. The gene whose expression is overshadowed is said to be recessive. Mendel’s law of segregation When gametes ...
... Mendel’s law of dominance When an organism has two different alleles for a given trait, the allele that is expressed, overshadowing the expression of the other allele, is said to be dominant. The gene whose expression is overshadowed is said to be recessive. Mendel’s law of segregation When gametes ...
answers to worksheet
... 4) What fraction of the children will be AA? BB? AB or BA? How many of the 1000 children do you expect to be AA? BB? AB or BA? Answer: Expected Fraction AA=0.09, Fraction BB=0.49, and Fraction AB or BA=0.42 Expected number AA=90, number BB=490, number AB or BA=420 5) How do the results compare to th ...
... 4) What fraction of the children will be AA? BB? AB or BA? How many of the 1000 children do you expect to be AA? BB? AB or BA? Answer: Expected Fraction AA=0.09, Fraction BB=0.49, and Fraction AB or BA=0.42 Expected number AA=90, number BB=490, number AB or BA=420 5) How do the results compare to th ...
Glossary and abbreviations
... Construct = a synthetic DNA sequence introduced using recombinant molecular DNA techniques into the chromosomes of an organism. Once a genetic construct has been inserted into an individuals or stock it is considered transgeneic. Dominant = A genetic term used to identify traits which are apparent i ...
... Construct = a synthetic DNA sequence introduced using recombinant molecular DNA techniques into the chromosomes of an organism. Once a genetic construct has been inserted into an individuals or stock it is considered transgeneic. Dominant = A genetic term used to identify traits which are apparent i ...
selection - Center of Statistical Genetics
... A case that illustrates a more complex relation of fitness to environment is sickle-cell anemia. An allelic substitution at the structural-gene locus for the β chain of hemoglobin results in substitution of valine for the normal glutamic acid at chain position 6. The abnormal hemoglobin crystallizes ...
... A case that illustrates a more complex relation of fitness to environment is sickle-cell anemia. An allelic substitution at the structural-gene locus for the β chain of hemoglobin results in substitution of valine for the normal glutamic acid at chain position 6. The abnormal hemoglobin crystallizes ...
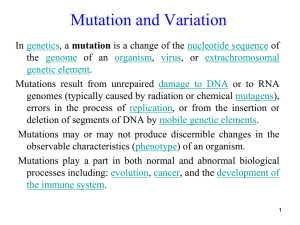
Mutation
... Mutations do not occur randomly throughout the genome. Some regions are hotspots of mutation. One such hotspot is the dinucleotide 5'CG3' (CpG), in which the cytosine is frequently methylated in many animal genomes, and may mutate to 5'TG3'. ...
... Mutations do not occur randomly throughout the genome. Some regions are hotspots of mutation. One such hotspot is the dinucleotide 5'CG3' (CpG), in which the cytosine is frequently methylated in many animal genomes, and may mutate to 5'TG3'. ...
Mendelian Genetics
... A. These disorders tend to be very harmful to the organism. B. They ONLY occur in the HOMOZYGOUS RECESSIVE state. 1. There is nothing to be dominated by, so the disorder is present. C. Carriers – These are organisms that are heterozygous in genotype. (They are 50/50 in terms of passing on the trait. ...
... A. These disorders tend to be very harmful to the organism. B. They ONLY occur in the HOMOZYGOUS RECESSIVE state. 1. There is nothing to be dominated by, so the disorder is present. C. Carriers – These are organisms that are heterozygous in genotype. (They are 50/50 in terms of passing on the trait. ...
Lecture#10 - Classification of mutations and gene function Readings
... - form the tissues of the organism and not used in reproduction - not passed on to the next generation Germline cells - form the germ cells used in reproduction - are passed on to the next generation Particularly important in animals less so in plants where somatic cells become germ tissue. The chan ...
... - form the tissues of the organism and not used in reproduction - not passed on to the next generation Germline cells - form the germ cells used in reproduction - are passed on to the next generation Particularly important in animals less so in plants where somatic cells become germ tissue. The chan ...
Molecular Genetics And Otolaryngology
... recombinant DNA, vectors, probes, polymerase chain reaction, DNA sequence analysis and protein analysis. Molecular cloning requires the use of restriction endonucleases to cleave a DNA strand at a specific site. For example, EcoRI cleaves DNA at a palindromic site on each DNA strand. There are hundr ...
... recombinant DNA, vectors, probes, polymerase chain reaction, DNA sequence analysis and protein analysis. Molecular cloning requires the use of restriction endonucleases to cleave a DNA strand at a specific site. For example, EcoRI cleaves DNA at a palindromic site on each DNA strand. There are hundr ...
Pregnancy: Expecting a Child with OI
... Sometimes, women who do not have osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) become concerned about it during pregnancy. Two situations typically give rise to this concern. 1. The woman’s partner has OI. 2. Prenatal testing suggests the presence of OI symptoms in the fetus. In both situations, the woman and her pa ...
... Sometimes, women who do not have osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) become concerned about it during pregnancy. Two situations typically give rise to this concern. 1. The woman’s partner has OI. 2. Prenatal testing suggests the presence of OI symptoms in the fetus. In both situations, the woman and her pa ...
Answers PDP Chapter 11.2
... ratio of phenotypes was observed in Mendel’s pea plants, therefore showing that segregation of alleles did occur. ...
... ratio of phenotypes was observed in Mendel’s pea plants, therefore showing that segregation of alleles did occur. ...
SELECTION * * I - Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology
... We will consider a panmictic population, of infinite size, with non-overlapping generations, and which is not affected by any factors for evolutionary change other than selection. It is assumed that the effect of the selective factors remains constant over time (constant selective values model), and ...
... We will consider a panmictic population, of infinite size, with non-overlapping generations, and which is not affected by any factors for evolutionary change other than selection. It is assumed that the effect of the selective factors remains constant over time (constant selective values model), and ...
mutations
... undergo a further mutation which restores the UUA codon (a true back mutation) The effect of a mutation can also be negated by a second, unrelated mutation; this effect is known as suppression. There are two types of suppression that are of more general importance. 1. The first occurs with framesh ...
... undergo a further mutation which restores the UUA codon (a true back mutation) The effect of a mutation can also be negated by a second, unrelated mutation; this effect is known as suppression. There are two types of suppression that are of more general importance. 1. The first occurs with framesh ...
Population genetics and the modern synthesis of evolutionary theory
... − but sometimes have traits that are not intermediate between their parents − This is an important way in which “new” variants are produced for natural selection to act on − they are not new alleles, but rather new combinations of alleles − they may not even really be new combinations, just combinat ...
... − but sometimes have traits that are not intermediate between their parents − This is an important way in which “new” variants are produced for natural selection to act on − they are not new alleles, but rather new combinations of alleles − they may not even really be new combinations, just combinat ...
LAMARCKIAN EVOLUTION
... Lamarck’s theory required adaptation to create new variations This was followed by the inheritance of these characteristics Darwin’s theory requires random hereditary variation first, followed by selection of the variations The argument was over when Mendel’s laws of genetics were rediscovered at th ...
... Lamarck’s theory required adaptation to create new variations This was followed by the inheritance of these characteristics Darwin’s theory requires random hereditary variation first, followed by selection of the variations The argument was over when Mendel’s laws of genetics were rediscovered at th ...
Lecture 31: Genetic Heterogeneity and Complex Traits
... scores from different families might obscure rather than clarify the situation. However, this trap can be avoided if one can identify a family with sufficient numbers of affected individuals (and informative meioses) to provide, by itself, a LOD score of 3. Approach 2: Direct search for mutations in ...
... scores from different families might obscure rather than clarify the situation. However, this trap can be avoided if one can identify a family with sufficient numbers of affected individuals (and informative meioses) to provide, by itself, a LOD score of 3. Approach 2: Direct search for mutations in ...
Disproportionate Roles for the X Chromosome and
... By this metric, cis-regulatory mutations are disproportionately responsible for adaptation. However, the relative significance of mutation classes in adaptive change depends on both the number of substitutions and their effects on fitness. Measuring fitness properties is more difficult than estimating s ...
... By this metric, cis-regulatory mutations are disproportionately responsible for adaptation. However, the relative significance of mutation classes in adaptive change depends on both the number of substitutions and their effects on fitness. Measuring fitness properties is more difficult than estimating s ...
Quantitative-Genetic Models and Changing Environments
... Charlesworth 1998; Chapter 9). Since many mutations affect several traits and the developmental pathways are complex, their fitness effects may also depend on the genetic background in which they occur, and on the kind of selective pressure to which the population is exposed. For instance, if for a g ...
... Charlesworth 1998; Chapter 9). Since many mutations affect several traits and the developmental pathways are complex, their fitness effects may also depend on the genetic background in which they occur, and on the kind of selective pressure to which the population is exposed. For instance, if for a g ...
Lecture 31: Genetic Heterogeneity and Complex Traits
... scores from different families might obscure rather than clarify the situation. However, this trap can be avoided if one can identify a family with sufficient numbers of affected individuals (and informative meioses) to provide, by itself, a LOD score of 3. ...
... scores from different families might obscure rather than clarify the situation. However, this trap can be avoided if one can identify a family with sufficient numbers of affected individuals (and informative meioses) to provide, by itself, a LOD score of 3. ...
Stabilizing, directional, and diversifying selection either
... furtive copulations with the females in an alpha male's territory. In this case, both the alpha males and the "sneaking" males will be selected for, but mediumsized males, which cannot overtake the alpha males and are too big to sneak copulations, are selected against. ...
... furtive copulations with the females in an alpha male's territory. In this case, both the alpha males and the "sneaking" males will be selected for, but mediumsized males, which cannot overtake the alpha males and are too big to sneak copulations, are selected against. ...
Ertertewt ertwetr - Campbell County Schools
... Finches with large beaks did travel back and forth between islands, but females would only mate with other finches with large beaks. This is behavioral reproductive isolation – they can mate, but they don’t. The gene pools of each population remained isolated – even though they were living together. ...
... Finches with large beaks did travel back and forth between islands, but females would only mate with other finches with large beaks. This is behavioral reproductive isolation – they can mate, but they don’t. The gene pools of each population remained isolated – even though they were living together. ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.