Document
... Allelic associations reflect sharing of ancestral chromosomes, only alleles at loci tightly linked to the disease susceptibility locus will still be shared For a locus showing recombination fraction (θ) with the susceptibility locus, a proportion (θ ) of ancestral chromosome will lose the associatio ...
... Allelic associations reflect sharing of ancestral chromosomes, only alleles at loci tightly linked to the disease susceptibility locus will still be shared For a locus showing recombination fraction (θ) with the susceptibility locus, a proportion (θ ) of ancestral chromosome will lose the associatio ...
Genetics
... species makes a population better suited to adaptation to changes in the environment. ...
... species makes a population better suited to adaptation to changes in the environment. ...
RCN-2011-Desjardins-lightning
... Genus of fly parasitoid with diverse phenotypes N. vitripennis N. longicornis ...
... Genus of fly parasitoid with diverse phenotypes N. vitripennis N. longicornis ...
ARVC - GeneDx
... these devices have reduced patients’ comfort level with these devices. Therefore, we need to be absolutely certain that the device will benefit the patient before recommending this procedure. Family history: 40%-50% of ARVC/ARVD cases are known to have genetic or familial basis. ARVC/ARVD is usually ...
... these devices have reduced patients’ comfort level with these devices. Therefore, we need to be absolutely certain that the device will benefit the patient before recommending this procedure. Family history: 40%-50% of ARVC/ARVD cases are known to have genetic or familial basis. ARVC/ARVD is usually ...
Evolution Unit – PDQ`s 4-6 Evolution 4 – Measuring Evolution Due
... Apply the biological species definition, and identify circumstances where it is not applicable. Explain the circumstances that can lead to the production of a new species both allopatrically and sympatrically. Define all species barriers described in this presentation, and provide examples of these ...
... Apply the biological species definition, and identify circumstances where it is not applicable. Explain the circumstances that can lead to the production of a new species both allopatrically and sympatrically. Define all species barriers described in this presentation, and provide examples of these ...
Galter Health Sciences Library
... polymorphisms, when mapped to the genome, may serve as markers to identify and map other genes that do cause disease when mutated. If these non-disease-causing variations are found to be inherited with a particular trait, but do not cause the trait, they may provide evidence of where the trait's gen ...
... polymorphisms, when mapped to the genome, may serve as markers to identify and map other genes that do cause disease when mutated. If these non-disease-causing variations are found to be inherited with a particular trait, but do not cause the trait, they may provide evidence of where the trait's gen ...
Lecture 4 Linkage and Recombination
... • Because of this, he observed the following ratios in the offspring 1. Monohybrid cross (inheritance of a single trait) ...
... • Because of this, he observed the following ratios in the offspring 1. Monohybrid cross (inheritance of a single trait) ...
Learned traits - Warren County Schools
... • This can be homozygous recessive or dominant. • An organism with two different alleles is called heterozygous. ...
... • This can be homozygous recessive or dominant. • An organism with two different alleles is called heterozygous. ...
Insertional mutants: a foundation for assessing gene function
... RECOMBINATION has been the arrow that plant reverse genetics has lacked in the quiver. Recently, methodologies have advanced to alleviate this impediment. Currently, there are several large collections of insertion mutant lines available in Arabidopsis where the insertion sites have been sequenced [ ...
... RECOMBINATION has been the arrow that plant reverse genetics has lacked in the quiver. Recently, methodologies have advanced to alleviate this impediment. Currently, there are several large collections of insertion mutant lines available in Arabidopsis where the insertion sites have been sequenced [ ...
Assignment
... In the following assignment you will characterize a mutation that is associated with a deficiency in the human immune system’s response to bacterial infection. In this hypothetical situation, a patient has an unexplained immune deficiency that causes them to be susceptible to typhoid fever (Salmonel ...
... In the following assignment you will characterize a mutation that is associated with a deficiency in the human immune system’s response to bacterial infection. In this hypothetical situation, a patient has an unexplained immune deficiency that causes them to be susceptible to typhoid fever (Salmonel ...
Genetic Mutation Worksheet - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... “point mutations”, because a single base is changed, at one point in the gene. SOMETIMES, these base (A,T,C,G) substitutions lead to “Missense” or “Nonsense” mutations: ...
... “point mutations”, because a single base is changed, at one point in the gene. SOMETIMES, these base (A,T,C,G) substitutions lead to “Missense” or “Nonsense” mutations: ...
Genetics Minor - Montana State University
... who obtains enrollment in an upper division biology course without satisfying these requirements will be required to withdraw from the course. Specific courses may have additional prerequisites. ...
... who obtains enrollment in an upper division biology course without satisfying these requirements will be required to withdraw from the course. Specific courses may have additional prerequisites. ...
Father of Modern Genetics
... Genetics – the study of heredity Heredity – the passing of traits from one generation to the next Trait – a physical or physiological characteristic coded for by a gene Gene – a portion of a chromosome that codes for a particular protein Allele – a form of a gene ...
... Genetics – the study of heredity Heredity – the passing of traits from one generation to the next Trait – a physical or physiological characteristic coded for by a gene Gene – a portion of a chromosome that codes for a particular protein Allele – a form of a gene ...
Mosaic Analysis
... 2-D gel electrophoresis for separating proteins on the basis of charge and molecular weight Mass spectrometry for identifying proteins by measuring the mass-to-charge ratio of their ionized ...
... 2-D gel electrophoresis for separating proteins on the basis of charge and molecular weight Mass spectrometry for identifying proteins by measuring the mass-to-charge ratio of their ionized ...
Lect 4 JF 12
... • Because of this, he observed the following ratios in the offspring 1. Monohybrid cross (inheritance of a single trait) ...
... • Because of this, he observed the following ratios in the offspring 1. Monohybrid cross (inheritance of a single trait) ...
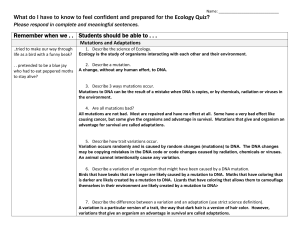
Remember when we . . Students should be able to
... Commensalism is a relationship where one animal benefits, but the other is not helped or harmed. A fern using a tree to anchor itself is an example of commensalism. Parasitism is a relationship where one animal benefits, but the other is harmed. A tick drawing blood from a cheetah benefits from the ...
... Commensalism is a relationship where one animal benefits, but the other is not helped or harmed. A fern using a tree to anchor itself is an example of commensalism. Parasitism is a relationship where one animal benefits, but the other is harmed. A tick drawing blood from a cheetah benefits from the ...
Mutations ATAR
... Mutations can vary from a small change in DNA or a gene or be a large change in chromosome structure or number ...
... Mutations can vary from a small change in DNA or a gene or be a large change in chromosome structure or number ...
Genetics Reference Sheet
... The Red and White alleles show incomplete dominance. The heterozygous combination expresses a “blending” of the two alleles producing a pink phenotype. ...
... The Red and White alleles show incomplete dominance. The heterozygous combination expresses a “blending” of the two alleles producing a pink phenotype. ...
Mutations
... Translocation • Involves two chromosomes that aren’t homologous • Part of one chromosome is transferred to another chromosomes ...
... Translocation • Involves two chromosomes that aren’t homologous • Part of one chromosome is transferred to another chromosomes ...
probability laws
... breeding pink flowering plants. • Codominance: both alleles equally expressed. Human blood type, cow coloring ...
... breeding pink flowering plants. • Codominance: both alleles equally expressed. Human blood type, cow coloring ...
Class Presentation Questions CH 11
... 1.__________-__________ __________________=Crosses that involve two traits, such as pod color and pod shape. 2._______________________________ states that during gamete formation, genes for different traits separate without influencing each other’s inheritance. This accounts for the many genetic var ...
... 1.__________-__________ __________________=Crosses that involve two traits, such as pod color and pod shape. 2._______________________________ states that during gamete formation, genes for different traits separate without influencing each other’s inheritance. This accounts for the many genetic var ...
Part 1 - Evolutionary Biology
... the differences described above? (A) The intermediate size pea plant seeds are aborted within the seedpod and thus will never develop. (B) The intermediate size pea plant seeds have deleterious alleles that prevent them from germinating. (C) These variations in humans are affected by lack of dominan ...
... the differences described above? (A) The intermediate size pea plant seeds are aborted within the seedpod and thus will never develop. (B) The intermediate size pea plant seeds have deleterious alleles that prevent them from germinating. (C) These variations in humans are affected by lack of dominan ...
The Theoretical Course Of Directional Selection.
... genes, all alike in effect, degree of dominance and gene frequency. ...
... genes, all alike in effect, degree of dominance and gene frequency. ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.