Chapter 5.3 – Human Genetics (Part I)
... 3. Show the results of a cross between an individual that is homozygous for A type blood and an individual that is heterozygous for B type blood. List the probably genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the offspring. AA x BO = AB, AO 4. Show the results of a cross between two individuals that have type ...
... 3. Show the results of a cross between an individual that is homozygous for A type blood and an individual that is heterozygous for B type blood. List the probably genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the offspring. AA x BO = AB, AO 4. Show the results of a cross between two individuals that have type ...
Slide 1
... Charles Darwin Scientist during the 1800’s that traveled around the world making observations of nature. Darwin discovered from his travels that organisms have structural characteristics that enable them to live in their environment – Adaptations! ...
... Charles Darwin Scientist during the 1800’s that traveled around the world making observations of nature. Darwin discovered from his travels that organisms have structural characteristics that enable them to live in their environment – Adaptations! ...
Cook, Robert. 1937. A chronology of genetics. Yearbook of
... breeding plants from very early times. The records left by the Babylonians and Egyptians leave no doubt that at least 5,000 years ago distinct breeds of domesticated animals were recognized. Certain of the types depicted on those ancient monuments bear a remarkable resemblance to modern breeds. Exce ...
... breeding plants from very early times. The records left by the Babylonians and Egyptians leave no doubt that at least 5,000 years ago distinct breeds of domesticated animals were recognized. Certain of the types depicted on those ancient monuments bear a remarkable resemblance to modern breeds. Exce ...
A newly discovered founder population: the
... the list of private mutations and aiming to understand their molecular epidemiology, has revealed a peculiar combination of genetic homogeneity and mutation sharing by affected subjects across Europe(10 –12) and, at the same time, an internal mosaic of striking differences in the prevalence of genet ...
... the list of private mutations and aiming to understand their molecular epidemiology, has revealed a peculiar combination of genetic homogeneity and mutation sharing by affected subjects across Europe(10 –12) and, at the same time, an internal mosaic of striking differences in the prevalence of genet ...
A View of Life
... Genetic Mutations – Once alleles have mutated, certain combinations of alleles might be more adaptive than others in a particular environment. Gene Flow – Movement of alleles between populations by migration of breeding individuals. Continual gene flow reduces variability between populations. Made ...
... Genetic Mutations – Once alleles have mutated, certain combinations of alleles might be more adaptive than others in a particular environment. Gene Flow – Movement of alleles between populations by migration of breeding individuals. Continual gene flow reduces variability between populations. Made ...
emergence and maintenance of sex among diploid organisms aided
... experimenter, was phenotipically expressed if present in the diploid genome. For example, in experiments assessing the relative evolutionary between diploid hermaphrodites and diploid monosexuals (Fig 1) when the allele for hermaphroditism was programmed as dominant, then, if the corresponding allel ...
... experimenter, was phenotipically expressed if present in the diploid genome. For example, in experiments assessing the relative evolutionary between diploid hermaphrodites and diploid monosexuals (Fig 1) when the allele for hermaphroditism was programmed as dominant, then, if the corresponding allel ...
GENETIC ALGORITHMS IN FATIGUE CRACK DETECTION Marek
... The genetic algorithm is a search technique based on ideas from the science of genetics and the process of natural selection. A simple genetic algorithm consists of three basic operations: reproduction, crossover and mutation. The algorithm starts with a randomly generated initial population. Member ...
... The genetic algorithm is a search technique based on ideas from the science of genetics and the process of natural selection. A simple genetic algorithm consists of three basic operations: reproduction, crossover and mutation. The algorithm starts with a randomly generated initial population. Member ...
Unit Test: Genetics The diagram shows a plant cell. The part of the
... A. offspring identical to one another but different from the parent B. offspring that are identical to each other and the parent C. three diverse offspring D. offspring that will not able to reproduce ...
... A. offspring identical to one another but different from the parent B. offspring that are identical to each other and the parent C. three diverse offspring D. offspring that will not able to reproduce ...
Bikini Bottom Genetics
... recessive individual to determine the dominate individual’s genotype. Mendel also studied ______________ _____________, crosses of individual’s with 2 differing characters. His results led him to develop the principle of _______________ ______________, which states that the alleles for different gen ...
... recessive individual to determine the dominate individual’s genotype. Mendel also studied ______________ _____________, crosses of individual’s with 2 differing characters. His results led him to develop the principle of _______________ ______________, which states that the alleles for different gen ...
Biological Approach
... their DNA in a region on chromosome 7. Participants with both maladies were most likely to have the genetic similarity. Within that region of the chromosome, researchers isolated the CHRM2 gene, which is involved in attention, learning, memory and cognition. Goate's team found the gene was strongly ...
... their DNA in a region on chromosome 7. Participants with both maladies were most likely to have the genetic similarity. Within that region of the chromosome, researchers isolated the CHRM2 gene, which is involved in attention, learning, memory and cognition. Goate's team found the gene was strongly ...
Complex Traits
... autosomal or sex-linked, dominant or recessive. These patterns are fairly easy to see when pedigrees are examined. However, there are also a large number of traits that don’t easily fit the Mendelian patterns. We can call them “multifactorial”. ...
... autosomal or sex-linked, dominant or recessive. These patterns are fairly easy to see when pedigrees are examined. However, there are also a large number of traits that don’t easily fit the Mendelian patterns. We can call them “multifactorial”. ...
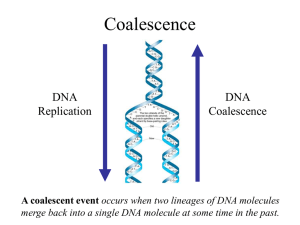
t - nslc.wustl.edu
... Gene trees are genealogies of genes. They describe how different copies at a homologous gene locus are “related” by ordering coalescent events. The only branches in the gene tree that we can observe from sequence data are those marked by a mutation. All branches in the gene tree that are caused by D ...
... Gene trees are genealogies of genes. They describe how different copies at a homologous gene locus are “related” by ordering coalescent events. The only branches in the gene tree that we can observe from sequence data are those marked by a mutation. All branches in the gene tree that are caused by D ...
Practice Questions, Lectures 6-13 (259 KB pdf file)
... Most genetic variation for many human loci lies within local populations rather than between populations or races. What does this observation tell you about human genetic evolution? Question 20 Most genetic variation for many human loci lies within local populations rather than between populations o ...
... Most genetic variation for many human loci lies within local populations rather than between populations or races. What does this observation tell you about human genetic evolution? Question 20 Most genetic variation for many human loci lies within local populations rather than between populations o ...
bYTEBoss Doc
... • Display of the chromosomes of a cell. • Usually displayed as an arrangement of chromosome pairs in descending order of size. • Homologous chromosomes are matched up. • Identifies and evaluates the size, shape, and number of chromosomes in a sample of body ...
... • Display of the chromosomes of a cell. • Usually displayed as an arrangement of chromosome pairs in descending order of size. • Homologous chromosomes are matched up. • Identifies and evaluates the size, shape, and number of chromosomes in a sample of body ...
Identical vs. Fraternal Twins
... Parents of multiples are often asked, “are your twins identical or fraternal?” The terms identical and fraternal are common words that refer to zygosity -- the characteristics of the cell union that happened at conception. Identical (monozygotic) twins form when a single fertilized egg splits into t ...
... Parents of multiples are often asked, “are your twins identical or fraternal?” The terms identical and fraternal are common words that refer to zygosity -- the characteristics of the cell union that happened at conception. Identical (monozygotic) twins form when a single fertilized egg splits into t ...
Multiplex STR Analysis by Capillary Electrophoresis
... in length, with allele sizes between 100bp and 300bp. Table 1 lists some of the commonly used STRs. The relatively small size of STR alleles reduces the effects of preferential amplification. Thus, more highly degraded samples can be analyzed than with LTRs. STRs tend to be less discriminating than ...
... in length, with allele sizes between 100bp and 300bp. Table 1 lists some of the commonly used STRs. The relatively small size of STR alleles reduces the effects of preferential amplification. Thus, more highly degraded samples can be analyzed than with LTRs. STRs tend to be less discriminating than ...
4) Genetics evaluation
... schizophrenia if our biological (real) rather than adopted parents have the disorder • BUT – not 100% concordance rates and not all children with schizophrenia in the family develop the disorder so must be other factors involved ...
... schizophrenia if our biological (real) rather than adopted parents have the disorder • BUT – not 100% concordance rates and not all children with schizophrenia in the family develop the disorder so must be other factors involved ...
Relevance Feedback
... • The best few of these solutions is chosen and replicated, while the poor ones eliminated • Replicated solutions creates a breeding population, from which new solutions arise • The breeding is accomplished by by an exchange of some of the characteristics of the chosen solutions in a crossover opera ...
... • The best few of these solutions is chosen and replicated, while the poor ones eliminated • Replicated solutions creates a breeding population, from which new solutions arise • The breeding is accomplished by by an exchange of some of the characteristics of the chosen solutions in a crossover opera ...
Transposable elements: Barbara McClintock and early experiments
... However, Ac mapped to various positions in different crosses. McClintock proposed that both Ac and Ds were mobile genetic elements and Ac was required for the activity of Ds. Ds can move into a gene, generating an unstable allele Some of the most interesting observations were those involving unstabl ...
... However, Ac mapped to various positions in different crosses. McClintock proposed that both Ac and Ds were mobile genetic elements and Ac was required for the activity of Ds. Ds can move into a gene, generating an unstable allele Some of the most interesting observations were those involving unstabl ...
generic algorithms: evolution ,encoding and their applications
... Perhaps it isn't obvious why such an algorithm should lead to accurate solutions for optimization problems. Crossover is a crucial aspect of any genetic algorithm, but it may seem that it will dramatically change parents with a high fitness function so that they will no longer be fit. However, this ...
... Perhaps it isn't obvious why such an algorithm should lead to accurate solutions for optimization problems. Crossover is a crucial aspect of any genetic algorithm, but it may seem that it will dramatically change parents with a high fitness function so that they will no longer be fit. However, this ...
Ch 4 Extensions of Mendelian Genetics
... Trait appears in more males than females. Mutation and trait never pass from father to son. Affected male does pass X-linked mutation to all daughters, who are heterozygous carriers. Trait often skips a generation. Trait only appears in successive generations if sister of an affected male is a carri ...
... Trait appears in more males than females. Mutation and trait never pass from father to son. Affected male does pass X-linked mutation to all daughters, who are heterozygous carriers. Trait often skips a generation. Trait only appears in successive generations if sister of an affected male is a carri ...
II. Types of Mutations
... C. Insertions and deletions of larger DNA fragments 1. Gain or loss of 100-1000’s (or more) of bases 2. Results in complete loss of gene function 3. Some deletions might wipe out entire gene cluster 4. Translocation: ...
... C. Insertions and deletions of larger DNA fragments 1. Gain or loss of 100-1000’s (or more) of bases 2. Results in complete loss of gene function 3. Some deletions might wipe out entire gene cluster 4. Translocation: ...
Genetic Variation
... Genetic variation. It is this variation that is the essence of evolution. Without genetic differences among individuals, "survival of the fittest" would not be likely. Either all survive, or all perish. Genetic Variation ...
... Genetic variation. It is this variation that is the essence of evolution. Without genetic differences among individuals, "survival of the fittest" would not be likely. Either all survive, or all perish. Genetic Variation ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.