Introduction to Angelfish Genetics
... that have been submitted for the photo contests over the years or have been otherwise donated for use by TAS members. We expect to add this variety to the phenotype library and the to the genetics ...
... that have been submitted for the photo contests over the years or have been otherwise donated for use by TAS members. We expect to add this variety to the phenotype library and the to the genetics ...
Intro to Genetics
... Law of Independent Assortment • Each pair of alleles assorts independently of other pairs of alleles during gamete formation • The inheritance of one character has no effect on the inheritance of another • For example– Pea plant with genotype AaBb – A and a will separate from one another and B and ...
... Law of Independent Assortment • Each pair of alleles assorts independently of other pairs of alleles during gamete formation • The inheritance of one character has no effect on the inheritance of another • For example– Pea plant with genotype AaBb – A and a will separate from one another and B and ...
public exam_basic genetics_R1
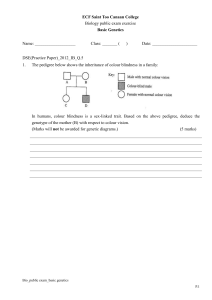
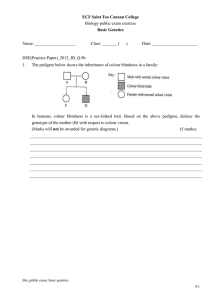
... (c) Students 19 and 20 are twin brothers. Are they identical or non-identical twins? Give a reason for your answer. ...
... (c) Students 19 and 20 are twin brothers. Are they identical or non-identical twins? Give a reason for your answer. ...
Human Genetics - Grant County Schools
... • Human blood is separated into different classifications because of the varying proteins on the surface of blood cells. • These proteins are there to identify whether or not the blood in the individual's body is it's own and not something the immunity system should destroy. ...
... • Human blood is separated into different classifications because of the varying proteins on the surface of blood cells. • These proteins are there to identify whether or not the blood in the individual's body is it's own and not something the immunity system should destroy. ...
The art and genetics of color in plants and animals
... • Treatment of each mutant strain with gibberellic acid restores normal height suggesting that they have the same primary defect • You cross dwarf strain 1 X dwarf strain 3 and the untreated F1 are dwarf • But when you cross dwarf strain 1 X dwarf strain 2 the untreated F1 are wild-type in height (n ...
... • Treatment of each mutant strain with gibberellic acid restores normal height suggesting that they have the same primary defect • You cross dwarf strain 1 X dwarf strain 3 and the untreated F1 are dwarf • But when you cross dwarf strain 1 X dwarf strain 2 the untreated F1 are wild-type in height (n ...
Chapter 6: Cancer - Mendelian and Quantitative Genetics
... genes with multiple alleles produces a large number of phenotypes. Environment can also have big effects. For quantitative traits, it is difficult to predict the phenotype of children from the phenotypes of the parents Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... genes with multiple alleles produces a large number of phenotypes. Environment can also have big effects. For quantitative traits, it is difficult to predict the phenotype of children from the phenotypes of the parents Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
The Genetics of Parkinson A version for the interested lay
... PARK 2 is autosomal recessive. If both genes are affected, the individual will develop the disease at a young age, usually before age 40. If only one gene is affected, there is the possibility – still unclear – that there is a PREDISPOSITION to develop the disease. ...
... PARK 2 is autosomal recessive. If both genes are affected, the individual will develop the disease at a young age, usually before age 40. If only one gene is affected, there is the possibility – still unclear – that there is a PREDISPOSITION to develop the disease. ...
Student Exploration: Hardy
... 7. Test: Click Begin, Breed, and Hatch. What are the resulting genotype percentages? Actual percentages: ...
... 7. Test: Click Begin, Breed, and Hatch. What are the resulting genotype percentages? Actual percentages: ...
public exam_basic genetics_R1
... (c) Students 19 and 20 are twin brothers. Are they identical or non-identical twins? Give a reason for your answer. ...
... (c) Students 19 and 20 are twin brothers. Are they identical or non-identical twins? Give a reason for your answer. ...
Smooth Response Surface - University of British Columbia
... In this study, each gene is represented by a node in a graphical model, which is denoted by Gi , where i = 1, 2, …, N. The edge Si , j represents the gene-gene interaction between Gi and G j , where the enhancer gene Gi plays a key role in activating or repressing the target gene G j . ...
... In this study, each gene is represented by a node in a graphical model, which is denoted by Gi , where i = 1, 2, …, N. The edge Si , j represents the gene-gene interaction between Gi and G j , where the enhancer gene Gi plays a key role in activating or repressing the target gene G j . ...
Biology - Bonnabel Home Page
... He wanted to know if the 2 dominant alleles would stay together or if they would “segregate independently” F2 plants produced 556 peas 315 round, yellow 32 wrinkled, green 209 had a combination of the phenotypes The results were close to a 9:3:3:1 ratio The Principle of Independent Assortment states ...
... He wanted to know if the 2 dominant alleles would stay together or if they would “segregate independently” F2 plants produced 556 peas 315 round, yellow 32 wrinkled, green 209 had a combination of the phenotypes The results were close to a 9:3:3:1 ratio The Principle of Independent Assortment states ...
Introduction to Genetics Genetics and Probability Punnet Square
... F1 Cross • Because the allele for tallness (T) is dominant over the allele for shortness (t), 3/4 of the F2 plants should be tall. • The ratio of tall plants (TT or Tt) to short (tt) plants is 3:1. • The predicted ratio showed up in Mendel’s experiments indicating that segregation did occur. The Nor ...
... F1 Cross • Because the allele for tallness (T) is dominant over the allele for shortness (t), 3/4 of the F2 plants should be tall. • The ratio of tall plants (TT or Tt) to short (tt) plants is 3:1. • The predicted ratio showed up in Mendel’s experiments indicating that segregation did occur. The Nor ...
Chapter 5 - Online Open Genetics
... OB alleles produce non-orange (often black) fur. Note however, that because of X-chromosome inactivation the result is mosaicism in expression. In OO / OB female heterozygotes patches of black and orange are seen, which produces the tortoise shell pattern (Figure 5-16 on page 46 A,B). This is a rare ...
... OB alleles produce non-orange (often black) fur. Note however, that because of X-chromosome inactivation the result is mosaicism in expression. In OO / OB female heterozygotes patches of black and orange are seen, which produces the tortoise shell pattern (Figure 5-16 on page 46 A,B). This is a rare ...
Fundamentals of Genetics Power Point
... How do you plan to develop the skills to become a life long learner? ...
... How do you plan to develop the skills to become a life long learner? ...
Alleles - lynchscience
... 1. Alternative versions of genes (alleles) cause variation in inherited traits. 2. Offspring inherit one copy (one allele) of a gene from each parent. 3. An allele is dominant if, when paired with a different allele, it has exclusive control over an individual’s phenotype. 4. The two copies (alleles ...
... 1. Alternative versions of genes (alleles) cause variation in inherited traits. 2. Offspring inherit one copy (one allele) of a gene from each parent. 3. An allele is dominant if, when paired with a different allele, it has exclusive control over an individual’s phenotype. 4. The two copies (alleles ...
Basic Principles of Heredity
... • Caused by a rare autosomal dominant allele that affects the nervous system ▫ Gene found at one end of chromosome #4 ...
... • Caused by a rare autosomal dominant allele that affects the nervous system ▫ Gene found at one end of chromosome #4 ...
1.Mendelian Patterns of Inheritance
... • In children with CF, the mucus in the bronchial tubes and pancreatic ducts is particularly thick and viscous, interfering with the function of the lungs and pancreas. • CF is caused by a defective chloride ion channel that is encoded by the CFTR allele on chromosome 7. • It is hoped that other nov ...
... • In children with CF, the mucus in the bronchial tubes and pancreatic ducts is particularly thick and viscous, interfering with the function of the lungs and pancreas. • CF is caused by a defective chloride ion channel that is encoded by the CFTR allele on chromosome 7. • It is hoped that other nov ...
C9 Lesson 2 Review and Reinforce
... 3. Punnett Square A shows a cross between two black guinea pigs. What is the probability that an offspring will be black? ________White? ________ 4. What color are the parents shown in Punnett Square B? ______________________ 5. Which guinea pig parent(s) in Punnett Square B is homozygous? _________ ...
... 3. Punnett Square A shows a cross between two black guinea pigs. What is the probability that an offspring will be black? ________White? ________ 4. What color are the parents shown in Punnett Square B? ______________________ 5. Which guinea pig parent(s) in Punnett Square B is homozygous? _________ ...
Punnett Squares Online
... 11. Human blood type is determined by co-dominant alleles. There are three different alleles, known as IA, IB, and i. The IA and IB alleles are co-dominant, and the i allele is recessive. The possible human phenotypes for blood group are type A, type B, type AB, and type O. Type A and B individuals ...
... 11. Human blood type is determined by co-dominant alleles. There are three different alleles, known as IA, IB, and i. The IA and IB alleles are co-dominant, and the i allele is recessive. The possible human phenotypes for blood group are type A, type B, type AB, and type O. Type A and B individuals ...
chapter 9 test bank
... 23) Which of the following statements best explains why dominant alleles that cause lethal disorders are less common than recessive alleles that cause lethal disorders? A) Lethal disorders caused by dominant alleles are usually more severe than lethal disorders caused by recessive alleles. B) Unlik ...
... 23) Which of the following statements best explains why dominant alleles that cause lethal disorders are less common than recessive alleles that cause lethal disorders? A) Lethal disorders caused by dominant alleles are usually more severe than lethal disorders caused by recessive alleles. B) Unlik ...
Quantitative developmental genetic analysis reveals that the
... test. Table 1 indicates the significance of P-values associated with the genotype by line interaction term in the ANOVA for each mutation tested against up to six different wild-type lines. Since six different traits (two warps for each of three intervein regions) were measured for each mutation, a ...
... test. Table 1 indicates the significance of P-values associated with the genotype by line interaction term in the ANOVA for each mutation tested against up to six different wild-type lines. Since six different traits (two warps for each of three intervein regions) were measured for each mutation, a ...
415 - MITF gene locus is associated with coat color variation of
... 0.82; G = 0.18) and plain coat color (A = 0.53; G = 0.47) phenotypes. The average homozygous genotype (AA) frequency was higher in Begait, and Fogera (0.65), whereas it was only 0.23 in solid or unspotted populations. These results revealed that the A allele was favored over the G allele in spotted ...
... 0.82; G = 0.18) and plain coat color (A = 0.53; G = 0.47) phenotypes. The average homozygous genotype (AA) frequency was higher in Begait, and Fogera (0.65), whereas it was only 0.23 in solid or unspotted populations. These results revealed that the A allele was favored over the G allele in spotted ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.