Genetics Review
... Peter J. Russell, iGenetics: Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings. ...
... Peter J. Russell, iGenetics: Copyright © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings. ...
Genetic Linkage Mapping of Zebrafish Genes and
... individuals produced by heat shock treatment of haploid embryos at the one-cell stage (HS diploids). This “doubled haploid” strategy combines the advantages of mapping in haploid and standard diploid systems, because heat shock diploid individuals have only one allele at each locus and can survive t ...
... individuals produced by heat shock treatment of haploid embryos at the one-cell stage (HS diploids). This “doubled haploid” strategy combines the advantages of mapping in haploid and standard diploid systems, because heat shock diploid individuals have only one allele at each locus and can survive t ...
Evolutionary consequences of polyploidy in prokaryotes and the
... transforms a polyploid cell into a functionally monoploid one with multiple unique, highly redundant chromosomes. Specialization of chromosomes makes the previously evolved modes of promiscuous chromosome shuffling deleterious. This can result in selective pressure to develop accurate mechanisms of ...
... transforms a polyploid cell into a functionally monoploid one with multiple unique, highly redundant chromosomes. Specialization of chromosomes makes the previously evolved modes of promiscuous chromosome shuffling deleterious. This can result in selective pressure to develop accurate mechanisms of ...
Gregor Mendel
... In all of Mendel’s crosses, only one form of the trait appeared in the F1 generation. However, in the F2 generation, the “lost” form of the trait always reappeared in about one fourth of the plants. P1 F1 ...
... In all of Mendel’s crosses, only one form of the trait appeared in the F1 generation. However, in the F2 generation, the “lost” form of the trait always reappeared in about one fourth of the plants. P1 F1 ...
TheraGuide 5-FU Slide Set
... – Three common variations account for the majority of known 5-FU toxicity to date • IVS14+1 G>A, D949V, and I560S ...
... – Three common variations account for the majority of known 5-FU toxicity to date • IVS14+1 G>A, D949V, and I560S ...
Genetic Testing for Colorectal Cancer Susceptibility GENE.00028
... Individual has a personal history of colorectal or endometrial cancer and tumor shows high Micro-satellite Instability (MSI) Other (please describe): Page 1 of 3 ...
... Individual has a personal history of colorectal or endometrial cancer and tumor shows high Micro-satellite Instability (MSI) Other (please describe): Page 1 of 3 ...
genetics-lo-powerpoint
... • Use a model to illustrate the role of cellular division (mitosis) and differentiation in producing and maintaining complex organisms. HS-LS3-1. • Ask questions to clarify relationships about the role of DNA and chromosomes in coding the instructions for characteristic traits passed from parents to ...
... • Use a model to illustrate the role of cellular division (mitosis) and differentiation in producing and maintaining complex organisms. HS-LS3-1. • Ask questions to clarify relationships about the role of DNA and chromosomes in coding the instructions for characteristic traits passed from parents to ...
Punctuated equilibrium theory represents shifting balance theory (of
... Though we cheerfully admit our prejudices, we find it hard to view Kellogg's pattern as anything but a series of three plateaux, periods of stasis interrupted by very rapid rates of change, all admittedly in the same direction [15]. Therefore, the punctuated equilibrium theory advocated long period ...
... Though we cheerfully admit our prejudices, we find it hard to view Kellogg's pattern as anything but a series of three plateaux, periods of stasis interrupted by very rapid rates of change, all admittedly in the same direction [15]. Therefore, the punctuated equilibrium theory advocated long period ...
Geographical variation in postzygotic isolation and its genetic basis
... responsible for effecting this isolation differ among the populations tested. Hence, we conclude that they evolve and spread only at the local scale. Keywords: speciation; reproductive isolation; hybrid sterility; hybrid inviability; asymmetric isolation; Bateson – Dobzhansky – Muller incompatibilit ...
... responsible for effecting this isolation differ among the populations tested. Hence, we conclude that they evolve and spread only at the local scale. Keywords: speciation; reproductive isolation; hybrid sterility; hybrid inviability; asymmetric isolation; Bateson – Dobzhansky – Muller incompatibilit ...
Patterns of Inheritance in Maize written by JD Hendrix
... Contemporary understanding: A segment on a DNA molecule, usually at a specific location (locus) on a chromosome, characterized by its nucleotide sequence. Genes play three notable roles: to encode the amino acid sequences of proteins, to encode the nucleotide sequences of tRNA or rRNA, and to regula ...
... Contemporary understanding: A segment on a DNA molecule, usually at a specific location (locus) on a chromosome, characterized by its nucleotide sequence. Genes play three notable roles: to encode the amino acid sequences of proteins, to encode the nucleotide sequences of tRNA or rRNA, and to regula ...
A Genome Scan for Eye Color in 502 Twin Families: Most Variation
... twins are expected to share two alleles IBS with a variance of zero (since they will share two alleles across all loci), and so can be quite easily distinguished from full siblings who are roughly expected to share one allele IBS with variance one half, and from parents who are expected to share one ...
... twins are expected to share two alleles IBS with a variance of zero (since they will share two alleles across all loci), and so can be quite easily distinguished from full siblings who are roughly expected to share one allele IBS with variance one half, and from parents who are expected to share one ...
Emerging model systems in evo-devo: cavefish and microevolution
... Microevolution is defined as evolutionary changes of relatively small scale that operate within a single species (Dobzhansky 1951). In recent years, evolutionary developmental biologists have made considerable progress in understanding the molecular basis of developmental changes during evolution. In ...
... Microevolution is defined as evolutionary changes of relatively small scale that operate within a single species (Dobzhansky 1951). In recent years, evolutionary developmental biologists have made considerable progress in understanding the molecular basis of developmental changes during evolution. In ...
Publication Appendices
... Evolution can be described as a change in the frequency of alleles (version of the gene) in the gene pool of a population. The frequency of alleles in a population would remain the same as long as the following conditions are met: No natural selection occurs No mutations occur No genetic drift ...
... Evolution can be described as a change in the frequency of alleles (version of the gene) in the gene pool of a population. The frequency of alleles in a population would remain the same as long as the following conditions are met: No natural selection occurs No mutations occur No genetic drift ...
Tutorial Slides
... denominator is zero. • < - will return a value of 1 if its first argument is less than or equal to its second and -1 otherwise. ...
... denominator is zero. • < - will return a value of 1 if its first argument is less than or equal to its second and -1 otherwise. ...
Making Babies
... 6. What are gametes? ____________________________________________ 7. How many copies of each gene do gametes have? _________ 8. Look at the gametes you made. Are they exactly the same? _________ Explain why or why not. ...
... 6. What are gametes? ____________________________________________ 7. How many copies of each gene do gametes have? _________ 8. Look at the gametes you made. Are they exactly the same? _________ Explain why or why not. ...
Gene interactions
... Lethal alleles are gene mutations that result in a gene product which is not only non-functional, but affects organism survival. Some lethal alleles are fully dominant and are therefore lethal in the heterozygote. Dominant lethal alleles are usually eliminated rapidly, because their expression is fa ...
... Lethal alleles are gene mutations that result in a gene product which is not only non-functional, but affects organism survival. Some lethal alleles are fully dominant and are therefore lethal in the heterozygote. Dominant lethal alleles are usually eliminated rapidly, because their expression is fa ...
ch 9 notes
... alleles; a genotype is the listing of alleles an individual carries for a specific gene 2. For each characteristic, an organism inherits two alleles, one from each parent; the alleles can be the same or different – A homozygous genotype has identical alleles – A heterozygous genotype has two differe ...
... alleles; a genotype is the listing of alleles an individual carries for a specific gene 2. For each characteristic, an organism inherits two alleles, one from each parent; the alleles can be the same or different – A homozygous genotype has identical alleles – A heterozygous genotype has two differe ...
Analysis of mutant strains
... will be looking for correct usage in your reports! Pay close attention to italics and capital letters. Gene names are placed in italics, while proteins and phenotypes are referred to with normal font. Gene names that begin with capital letters refer to dominant alleles, while gene names beginning wi ...
... will be looking for correct usage in your reports! Pay close attention to italics and capital letters. Gene names are placed in italics, while proteins and phenotypes are referred to with normal font. Gene names that begin with capital letters refer to dominant alleles, while gene names beginning wi ...
Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance
... alleles; a genotype is the listing of alleles an individual carries for a specific gene 2. For each characteristic, an organism inherits two alleles, one from each parent; the alleles can be the same or different – A homozygous genotype has identical alleles – A heterozygous genotype has two differe ...
... alleles; a genotype is the listing of alleles an individual carries for a specific gene 2. For each characteristic, an organism inherits two alleles, one from each parent; the alleles can be the same or different – A homozygous genotype has identical alleles – A heterozygous genotype has two differe ...
Chapter 9
... alleles; a genotype is the listing of alleles an individual carries for a specific gene 2. For each characteristic, an organism inherits two alleles, one from each parent; the alleles can be the same or different – A homozygous genotype has identical alleles – A heterozygous genotype has two differe ...
... alleles; a genotype is the listing of alleles an individual carries for a specific gene 2. For each characteristic, an organism inherits two alleles, one from each parent; the alleles can be the same or different – A homozygous genotype has identical alleles – A heterozygous genotype has two differe ...
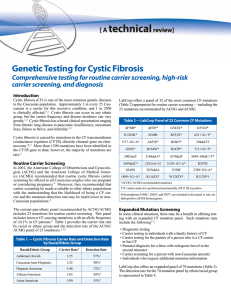
Genetic Testing for Cystic Fibrosis
... same chromosome as the R117H mutation (in cis).1-2 In addition, when IVS8-5T is found on the chromosome opposite another CF mutation (in trans), or when a person inherits two copies of the 5T allele, the phenotype is highly variable.1 Clinical symptoms range from having no symptoms to male patients ...
... same chromosome as the R117H mutation (in cis).1-2 In addition, when IVS8-5T is found on the chromosome opposite another CF mutation (in trans), or when a person inherits two copies of the 5T allele, the phenotype is highly variable.1 Clinical symptoms range from having no symptoms to male patients ...
Genetics Understanding Inheritance What controls traits?
... Mendel studied traits influenced by only one gene with two alleles. We know now that not all traits are inherited this way. Some traits have more complex inheritance patterns. ...
... Mendel studied traits influenced by only one gene with two alleles. We know now that not all traits are inherited this way. Some traits have more complex inheritance patterns. ...
ARTICLE A wide variety of mutations in the parkin gene are
... Taken together, our three families with previously reported exon deletions (18) and the nine families with mutations detected in the present study demonstrate that mutations in the parkin gene are the cause of the disease in ∼30% of the families with autosomal recessive parkinsonism analysed (12/38) ...
... Taken together, our three families with previously reported exon deletions (18) and the nine families with mutations detected in the present study demonstrate that mutations in the parkin gene are the cause of the disease in ∼30% of the families with autosomal recessive parkinsonism analysed (12/38) ...
Genetic predisposition to sarcoidosis: another brick in the wall EDITORIAL
... During the past few years, GWASs have revolutionised human genetics and led to the identification of thousands of loci that affect susceptibility to complex diseases [7, 8]. In just 5 years, the GWAS methodology has moved from extraordinary to commonplace. This hypothesis-free and unbiased approach ...
... During the past few years, GWASs have revolutionised human genetics and led to the identification of thousands of loci that affect susceptibility to complex diseases [7, 8]. In just 5 years, the GWAS methodology has moved from extraordinary to commonplace. This hypothesis-free and unbiased approach ...
A combinational theory for maintenance of sex
... Polyploidy and hybridity alter genotype and phenotype in many different ways, which violates the basic assumptions of current hypotheses that lower genotypic variation or higher mutational load of asexual lineages would be disadvantageous, ‘all else being equal’. Polyploidy can mask effects of delet ...
... Polyploidy and hybridity alter genotype and phenotype in many different ways, which violates the basic assumptions of current hypotheses that lower genotypic variation or higher mutational load of asexual lineages would be disadvantageous, ‘all else being equal’. Polyploidy can mask effects of delet ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.