Magnetic field
... The strength of the magnetic field is proportional to the current in the wire. If you double the current, the magnetic force is doubled. Since Voltage = Current x Resistance (V = I*R), you can double the current in a wire by doubling the voltage of the source of electricity. Turns of coil If you wra ...
... The strength of the magnetic field is proportional to the current in the wire. If you double the current, the magnetic force is doubled. Since Voltage = Current x Resistance (V = I*R), you can double the current in a wire by doubling the voltage of the source of electricity. Turns of coil If you wra ...
Michael Faraday (1791-1867) The laws of electricity and magnetism
... Induced currents (c) • If an AC (time varying) current is used in the primary circuit, a current is induced in the secondary windings. • If the current in the primary windings were DC, there would be NO induced current in the secondary circuit. ...
... Induced currents (c) • If an AC (time varying) current is used in the primary circuit, a current is induced in the secondary windings. • If the current in the primary windings were DC, there would be NO induced current in the secondary circuit. ...
APPLICATION OF THE ABOVE TO RADIOGRAPHY
... using X-rays or Ultrasound. Very strong magnetic fields are produced using electromagnets in which the current-carrying coils are cooled low enough to become superconductors. The patient is put into a combination of a strong uniform magnetic field, and a non-uniform magnetic field which increases in ...
... using X-rays or Ultrasound. Very strong magnetic fields are produced using electromagnets in which the current-carrying coils are cooled low enough to become superconductors. The patient is put into a combination of a strong uniform magnetic field, and a non-uniform magnetic field which increases in ...
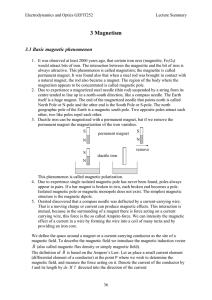
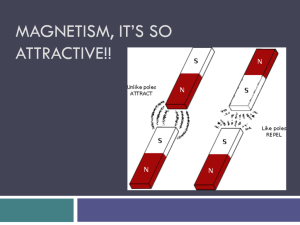
3 Magnetism
... appear in pairs. If a bar magnet is broken in two, each broken end becomes a pole. Isolated magnetic pole or magnetic monopole does not exist. The simplest magnetic structure is the magnetic dipole. 5. Oersted discovered that a compass needle was deflected by a current-carrying wire. That is a movin ...
... appear in pairs. If a bar magnet is broken in two, each broken end becomes a pole. Isolated magnetic pole or magnetic monopole does not exist. The simplest magnetic structure is the magnetic dipole. 5. Oersted discovered that a compass needle was deflected by a current-carrying wire. That is a movin ...
Magnetic.. - PhysicsEducation.net
... 1. Using the Magnaprobe or the smallest compasses, make a map of the magnetic field in the neighborhood around the bar magnet. First, place the bar magnet on a piece of notebook paper, trace its outline, and label north and south poles. Then, keeping the magnet in place, place the Magnaprobe at many ...
... 1. Using the Magnaprobe or the smallest compasses, make a map of the magnetic field in the neighborhood around the bar magnet. First, place the bar magnet on a piece of notebook paper, trace its outline, and label north and south poles. Then, keeping the magnet in place, place the Magnaprobe at many ...
1 Early observations of and knowledge on air electricity and
... the magnetic needle came back to its former position.” Remarks in Ephemerides 1783 Duke de la Cepede is cited, who established as a result of relevant experiments, “that the many deviations of the magnetic needle originate from electrical matter in the air. If so, the magnetic needle must show many ...
... the magnetic needle came back to its former position.” Remarks in Ephemerides 1783 Duke de la Cepede is cited, who established as a result of relevant experiments, “that the many deviations of the magnetic needle originate from electrical matter in the air. If so, the magnetic needle must show many ...
Outline_CH16_Klein
... 1) Nuclear Spin and Magnetic Resonant Frequency A) Spin Angular Momentum and Magnetic Moments o Spin quantum number I = ½ nuclei o Odd atomic number or odd mass number I≠0 o Spin ½ nuclei have 2 spin degenerate spin states and o When nucleus is not in the presence of an external magnetic field, ...
... 1) Nuclear Spin and Magnetic Resonant Frequency A) Spin Angular Momentum and Magnetic Moments o Spin quantum number I = ½ nuclei o Odd atomic number or odd mass number I≠0 o Spin ½ nuclei have 2 spin degenerate spin states and o When nucleus is not in the presence of an external magnetic field, ...












![L 29 Electricity and Magnetism [6] Laws of Magnetism The electric](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001482032_1-b69d1eb7a0f8c001e0e2a09bf26d62d2-300x300.png)