Electromagnetic Induction
... Field goes from south to North inside a magnet • Field goes away from North and towards south, outside magnet • Magnets always have two poles ...
... Field goes from south to North inside a magnet • Field goes away from North and towards south, outside magnet • Magnets always have two poles ...
Lesson Sheet
... Many of the greatest scientific discoveries have been lucky accidents. Electromagnetism was one of those. During a lecture in the year 1819, Hans Oersted had a compass sitting next to a wire. When Oersted completed the circuit by connecting the wire to a battery, the direction that the needle was po ...
... Many of the greatest scientific discoveries have been lucky accidents. Electromagnetism was one of those. During a lecture in the year 1819, Hans Oersted had a compass sitting next to a wire. When Oersted completed the circuit by connecting the wire to a battery, the direction that the needle was po ...
Magnetism - WordPress.com
... The space around a magnet where the magnet can attract or repel magnetic materials is called Magnetic field. The Magnetic field lines: - show the direction of the magnetic force at each point. - never cross each other. - are more near the poles of the magnet. (So that the poles have more magnetic st ...
... The space around a magnet where the magnet can attract or repel magnetic materials is called Magnetic field. The Magnetic field lines: - show the direction of the magnetic force at each point. - never cross each other. - are more near the poles of the magnet. (So that the poles have more magnetic st ...
Electromagnetism - Lecture 10 Magnetic Materials
... Introduction to Magnetic Materials There are three main types of magnetic materials with different magnetic susceptibilities, χM : • Diamagnetic - magnetization is opposite to external B χM is small and negative. • Paramagnetic - magnetization is parallel to external B χM is small and positive. • F ...
... Introduction to Magnetic Materials There are three main types of magnetic materials with different magnetic susceptibilities, χM : • Diamagnetic - magnetization is opposite to external B χM is small and negative. • Paramagnetic - magnetization is parallel to external B χM is small and positive. • F ...
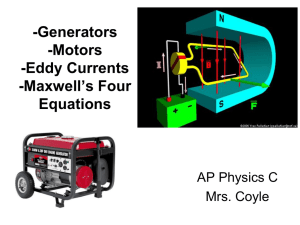
3 Generators, Motors, Eddy Currents, Maxwell`s Four Equations
... – This induced emf always acts to reduce the current in the coil and is called back emf – The back emf increases in magnitude as the rotational speed of the coil increases ...
... – This induced emf always acts to reduce the current in the coil and is called back emf – The back emf increases in magnitude as the rotational speed of the coil increases ...
VOICE OVER FOR TLM for Project 5 - Class CBSE
... Now, consider that the charged particle is projected at an angle, theta, to the uniform magnetic field, which is anything other than 90 degrees. It can be shown that the charged particle has a velocity in the direction of the magnetic field and also in a circular path, whose plane is perpendicular ...
... Now, consider that the charged particle is projected at an angle, theta, to the uniform magnetic field, which is anything other than 90 degrees. It can be shown that the charged particle has a velocity in the direction of the magnetic field and also in a circular path, whose plane is perpendicular ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... Magnetic field is present only when current is flowing in the wire coil Increase strength of the magnetic field by adding coils to the wire or increasing the current flowing through the wire Magnetic properties of electromagnets can be controlled by changing the electric current flowing through the ...
... Magnetic field is present only when current is flowing in the wire coil Increase strength of the magnetic field by adding coils to the wire or increasing the current flowing through the wire Magnetic properties of electromagnets can be controlled by changing the electric current flowing through the ...
Even if the forces acting on a body are balanced in
... The direction of the force is reversed if either the direction of the current or the direction of the magnetic field is reversed – so you must switch the battery connections round or turn the magnet round A coil of wire current carrying wire placed between the poles of a fixed magnet rotates because ...
... The direction of the force is reversed if either the direction of the current or the direction of the magnetic field is reversed – so you must switch the battery connections round or turn the magnet round A coil of wire current carrying wire placed between the poles of a fixed magnet rotates because ...
PHYS632_C12_32_Maxwe..
... Iron, cobalt, nickel, and rare earth alloys exhibit ferromagnetism. The so called exchange coupling causes electron magnetic moments of one atom to align with electrons of other atoms. This alignment produces magnetism. Whole groups of atoms align and form domains. (See Figure 32-12 on page 756) A m ...
... Iron, cobalt, nickel, and rare earth alloys exhibit ferromagnetism. The so called exchange coupling causes electron magnetic moments of one atom to align with electrons of other atoms. This alignment produces magnetism. Whole groups of atoms align and form domains. (See Figure 32-12 on page 756) A m ...
Problems for week 10
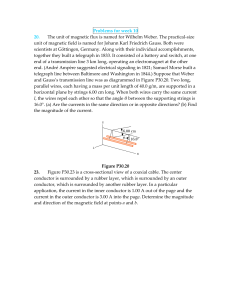
... end of a transmission line 3 km long, operating an electromagnet at the other end. (André Ampère suggested electrical signaling in 1821; Samuel Morse built a telegraph line between Baltimore and Washington in 1844.) Suppose that Weber and Gauss’s transmission line was as diagrammed in Figure P30.20. ...
... end of a transmission line 3 km long, operating an electromagnet at the other end. (André Ampère suggested electrical signaling in 1821; Samuel Morse built a telegraph line between Baltimore and Washington in 1844.) Suppose that Weber and Gauss’s transmission line was as diagrammed in Figure P30.20. ...
Q.5. What is a magnetic field?
... Q.2. What happens when compass needle is brought near a bar magnet? Q.3. A compass needle is bar magnet. Explain. Q.4. Why do iron filings arrange themselves in a pattern when brought near a magnet? Q.5. What is a magnetic field? Q.6. How can we observe relative strength of the magnetic field? Q.7. ...
... Q.2. What happens when compass needle is brought near a bar magnet? Q.3. A compass needle is bar magnet. Explain. Q.4. Why do iron filings arrange themselves in a pattern when brought near a magnet? Q.5. What is a magnetic field? Q.6. How can we observe relative strength of the magnetic field? Q.7. ...