An Introduction to the Seafloor and Plate Tectonics
... 1) Investigate the components of the lithosphere and lithospheric plates. 2) Identify the associations among various seafloor features, continental features, and plate boundaries. 3) Compare the different types of lithosphere (oceanic & continental). 4) Compare and contrast the differences among the ...
... 1) Investigate the components of the lithosphere and lithospheric plates. 2) Identify the associations among various seafloor features, continental features, and plate boundaries. 3) Compare the different types of lithosphere (oceanic & continental). 4) Compare and contrast the differences among the ...
Science A-43
... oceans, where new sea floor is created, Generally higher than the average depth of the sea floor Typically result in normal fault Can also occur in continental rock (East African Rift) ex. Mid-Atlantic ridge, Nazca Plate/Pacific Plate o Convergent Boundary – Plate boundaries where two plates ...
... oceans, where new sea floor is created, Generally higher than the average depth of the sea floor Typically result in normal fault Can also occur in continental rock (East African Rift) ex. Mid-Atlantic ridge, Nazca Plate/Pacific Plate o Convergent Boundary – Plate boundaries where two plates ...
Section 11-3
... and upper mantle are broken into sections called plates, that slowly move around on the mantle. • The lithosphere is the rigid, outermost layer of Earth composed of the crust and upper mantle. It is about 100 kilometers thick. • The asthenosphere is the plastic-like layer below the lithosphere in Ea ...
... and upper mantle are broken into sections called plates, that slowly move around on the mantle. • The lithosphere is the rigid, outermost layer of Earth composed of the crust and upper mantle. It is about 100 kilometers thick. • The asthenosphere is the plastic-like layer below the lithosphere in Ea ...
Read Intro. to Lab #1 - Oregon State University
... Image courtesy of Dan Fornari, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution ...
... Image courtesy of Dan Fornari, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution ...
Key concepts
... -know the difference between oceanic crust & continental crust -know how pressure and temperature change as you move through the layers of the earth and their effects on the behavior of rocks -know the internal source of heat inside the earth and how heat moves by conduction or convection -know how ...
... -know the difference between oceanic crust & continental crust -know how pressure and temperature change as you move through the layers of the earth and their effects on the behavior of rocks -know the internal source of heat inside the earth and how heat moves by conduction or convection -know how ...
Features of Caucasian Segment of the Alpine
... 4. Late Cenozoic volcanism of the Caucasus An important feature of the area of syntaxis is a large belt of Late Cenozoic (up to practically present‐day) volcanism, which extends in submeridional (Transcaucasian) direction from the eastern Anatolia via the Lesser to the Greater Caucasus, w ...
... 4. Late Cenozoic volcanism of the Caucasus An important feature of the area of syntaxis is a large belt of Late Cenozoic (up to practically present‐day) volcanism, which extends in submeridional (Transcaucasian) direction from the eastern Anatolia via the Lesser to the Greater Caucasus, w ...
Plate Tectonics II - Clark Science Center
... According to this model, subducted slabs of oceanic lithosphere sink through the 660-km boundary between the asthenosphere and lower mantle, all the way down to the core-mantle boundary, where they melt. ...
... According to this model, subducted slabs of oceanic lithosphere sink through the 660-km boundary between the asthenosphere and lower mantle, all the way down to the core-mantle boundary, where they melt. ...
Divergent Boundaries
... Divergent boundaries occur along spreading centers where plates are moving apart and new crust is created by magma pushing up from the mantle. Picture two giant conveyor belts, facing each other but slowly moving in opposite directions as they transport newly formed oceanic crust away from the ridge ...
... Divergent boundaries occur along spreading centers where plates are moving apart and new crust is created by magma pushing up from the mantle. Picture two giant conveyor belts, facing each other but slowly moving in opposite directions as they transport newly formed oceanic crust away from the ridge ...
The Ocean Floor Bethany Ostlund 4th Grade The Ocean Floor
... underlying oceanic plate creates a trench where it drags the edge of the continental crust down as it descends underneath. ...
... underlying oceanic plate creates a trench where it drags the edge of the continental crust down as it descends underneath. ...
key - Scioly.org
... fatse: There exists exposed land (NoT undenarater) on Earth that is more than 100 mBters-below sea level. ...
... fatse: There exists exposed land (NoT undenarater) on Earth that is more than 100 mBters-below sea level. ...
Understanding Plate Motions - My Science Class / FrontPage
... Aleutian Islands have formed and why they experience numerous strong earthquakes. Magmas that form island arcs are produced by the partial melting of the descending plate and/or the overlying oceanic lithosphere. The descending plate also provides a source of stress as the two plates interact, leadi ...
... Aleutian Islands have formed and why they experience numerous strong earthquakes. Magmas that form island arcs are produced by the partial melting of the descending plate and/or the overlying oceanic lithosphere. The descending plate also provides a source of stress as the two plates interact, leadi ...
Geological maps
... • Mid-ocean ridge = the high range of mountains that runs under the oceans and is the site of “spreading” • Seamount chain = line of undersea peaks that extends from a “hot spot” in the mantle (only one end of the chain can be volcanically active and there is no associated “trench”) ...
... • Mid-ocean ridge = the high range of mountains that runs under the oceans and is the site of “spreading” • Seamount chain = line of undersea peaks that extends from a “hot spot” in the mantle (only one end of the chain can be volcanically active and there is no associated “trench”) ...
theory of plate tectonics
... a. thin outer shell of earth b. less dense than material below which causes movement of plates = broken into sections 1) have identified 30 so far 2) interact together to create major surface features a) move toward each other and collide b) moving apart c) slide past one another c. composed of gran ...
... a. thin outer shell of earth b. less dense than material below which causes movement of plates = broken into sections 1) have identified 30 so far 2) interact together to create major surface features a) move toward each other and collide b) moving apart c) slide past one another c. composed of gran ...
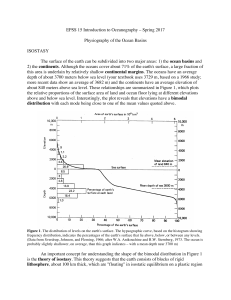
EPSS 15 Introduction to Oceanography – Spring 2017 Physiography
... floor. Sediments deposited by turbidity currents are often triggered by earthquakes. A classic example of this kind of activity was provided during the Grand Banks Earthquake off Newfoundland on November 19, 1929 (Figures 5 and 6). Slumping and turbidity currents triggered by the earthquake resulted ...
... floor. Sediments deposited by turbidity currents are often triggered by earthquakes. A classic example of this kind of activity was provided during the Grand Banks Earthquake off Newfoundland on November 19, 1929 (Figures 5 and 6). Slumping and turbidity currents triggered by the earthquake resulted ...
Outer Core - Wikispaces
... Divergent oceanic plate boundary Undersea mountain ranges Rift Valley – where volcanism occurs and new crust is created ...
... Divergent oceanic plate boundary Undersea mountain ranges Rift Valley – where volcanism occurs and new crust is created ...
Name - Schoolwires.net
... North American Plate-The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Greenland, Cuba, Bahamas, and parts of Siberia, Iceland and the Azores. Marianas Trench -the deepest part of the world's oceans. It is located in the western Pacific Ocean, to the east of the Mariana Is ...
... North American Plate-The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Greenland, Cuba, Bahamas, and parts of Siberia, Iceland and the Azores. Marianas Trench -the deepest part of the world's oceans. It is located in the western Pacific Ocean, to the east of the Mariana Is ...
Tectonic activity in the Caribbean Abstract The main tectonic
... destructive plate boundary along the Pacific Coast. Earthquakes are very common here and there are many active volcanoes. Zone 5: There are more fold mountains along the southern edge of the Caribbean, in Northern Venezuela and Trinidad. Earthquakes occur at all margins but most volcanic activity oc ...
... destructive plate boundary along the Pacific Coast. Earthquakes are very common here and there are many active volcanoes. Zone 5: There are more fold mountains along the southern edge of the Caribbean, in Northern Venezuela and Trinidad. Earthquakes occur at all margins but most volcanic activity oc ...
Tectonic activity in the Caribbean
... destructive plate boundary along the Pacific Coast. Earthquakes are very common here and there are many active volcanoes. Zone 5: There are more fold mountains along the southern edge of the Caribbean, in Northern Venezuela and Trinidad. Earthquakes occur at all margins but most volcanic activity oc ...
... destructive plate boundary along the Pacific Coast. Earthquakes are very common here and there are many active volcanoes. Zone 5: There are more fold mountains along the southern edge of the Caribbean, in Northern Venezuela and Trinidad. Earthquakes occur at all margins but most volcanic activity oc ...
4.2 The Theory of Plate Tectonics
... Tectonics: The study of the formation of features in the earth’s crust Open textbook to p. 72 ...
... Tectonics: The study of the formation of features in the earth’s crust Open textbook to p. 72 ...
Origin of magma (pg.270-273)
... Magma forms when SOLID rock and minerals, located in the asthenosphere and upper mantle, melt Factors that form magma: • Heat • Pressure • Volatiles (refers to the volatile or reactive components of magma [mostly water vapor and carbon dioxide]) ...
... Magma forms when SOLID rock and minerals, located in the asthenosphere and upper mantle, melt Factors that form magma: • Heat • Pressure • Volatiles (refers to the volatile or reactive components of magma [mostly water vapor and carbon dioxide]) ...
Chapter 3: Plate Tectonics
... supercontinent called Pangaea. • He thought the continents seemed to fit together as a puzzle. ...
... supercontinent called Pangaea. • He thought the continents seemed to fit together as a puzzle. ...
UCLA, ESS
... submerged volcanic mountains and associated central "rift valleys" where basaltic magmas rise to the surface and are extruded as lavas onto the ocean floor. This example represents an advanced stage of rifting and is characterized ...
... submerged volcanic mountains and associated central "rift valleys" where basaltic magmas rise to the surface and are extruded as lavas onto the ocean floor. This example represents an advanced stage of rifting and is characterized ...
Ocean Basin Physiography
... floor. Sediments deposited by turbidity currents are often triggered by earthquakes. A classic example of this kind of activity was provided during the Grand Banks Earthquake off Newfoundland on November 19, 1929 (Figures 5 and 6). Slumping and turbidity currents triggered by the earthquake resulte ...
... floor. Sediments deposited by turbidity currents are often triggered by earthquakes. A classic example of this kind of activity was provided during the Grand Banks Earthquake off Newfoundland on November 19, 1929 (Figures 5 and 6). Slumping and turbidity currents triggered by the earthquake resulte ...
Plate Tectonics - Down To Earth Science
... evidence. The oldest part of the sea floor is only 160 to 180 million years old, while the continental crust is much older (up to 4 billion years old). This confirmed that the ocean floor is constantly forming and moving away from the mid-ocean ridges like a conveyor belt. ...
... evidence. The oldest part of the sea floor is only 160 to 180 million years old, while the continental crust is much older (up to 4 billion years old). This confirmed that the ocean floor is constantly forming and moving away from the mid-ocean ridges like a conveyor belt. ...