Characterization of ultrashort-period GaAsrAlAs superlattices by exciton photoluminescence V.G. Litovchenko
... non line and weak phonon-assisted sidebands at lower energy. Zero-phonon line originates from recombination of the excitons consisting of the X z electrons of AlAs and the G heavy holes of GaAs and will be discussed below. On the contrary, PL spectra of the 1r1, 2r2, 3r3 and 8r46 SLs are typical for ...
... non line and weak phonon-assisted sidebands at lower energy. Zero-phonon line originates from recombination of the excitons consisting of the X z electrons of AlAs and the G heavy holes of GaAs and will be discussed below. On the contrary, PL spectra of the 1r1, 2r2, 3r3 and 8r46 SLs are typical for ...
17588_lecture10-11_11795_laser-and-its-applications2
... At absolute zero all atoms will be in the ground state. There is such a lack of thermal motion among the electrons that there are no atoms in higher energy levels. As the temperature increases atoms change ...
... At absolute zero all atoms will be in the ground state. There is such a lack of thermal motion among the electrons that there are no atoms in higher energy levels. As the temperature increases atoms change ...
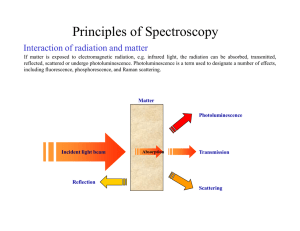
Principles of Spectroscopy
... • Not as widely used in analytical chemistry as non-resonance fluorescence – Hg analysis is one example Excitation Beam ...
... • Not as widely used in analytical chemistry as non-resonance fluorescence – Hg analysis is one example Excitation Beam ...
Chem 4631 - UNT Chemistry
... When radiation passes through a solid, liquid or gas, certain frequencies may be selectively removed. Absorption – process in which electromagnetic energy is transferred to the atoms, ion, or molecules of the sample. Absorption promotes these particles from ground state to one or more higher excited ...
... When radiation passes through a solid, liquid or gas, certain frequencies may be selectively removed. Absorption – process in which electromagnetic energy is transferred to the atoms, ion, or molecules of the sample. Absorption promotes these particles from ground state to one or more higher excited ...
Measuring the Hyperfine Splittings of Lowest Energy Atomic
... pump beam from the same laser. The pump beam saturated the absorption of the velocity equal zero atoms that the counter-propagating probe beam could have also interacted with due to no Doppler shift. At these frequencies the probe beam experienced less absorption that was measured by a photodiode. T ...
... pump beam from the same laser. The pump beam saturated the absorption of the velocity equal zero atoms that the counter-propagating probe beam could have also interacted with due to no Doppler shift. At these frequencies the probe beam experienced less absorption that was measured by a photodiode. T ...
Study of excited states of fluorinated copper phthalocyanine by inner
... the carbon and fluorine K-edge NEXAFS spectra on α, it is found that the average molecular tilt angle of FCuPc is 30◦ for the 50 Å-thick film on the MoS2 . This tilt angle of FCuPc is larger than that of the CuPc film on MoS2 (β = 10◦ ) [10]. A typical ion time-of-flight mass spectrum of FCuPc near ...
... the carbon and fluorine K-edge NEXAFS spectra on α, it is found that the average molecular tilt angle of FCuPc is 30◦ for the 50 Å-thick film on the MoS2 . This tilt angle of FCuPc is larger than that of the CuPc film on MoS2 (β = 10◦ ) [10]. A typical ion time-of-flight mass spectrum of FCuPc near ...
Introducing Photochemistry
... fluorescence, for detection of cracks in metal work, for tracing the course of river through caves, as microanalytical reagents and so on. Certain chemicals change their colour, that is, their absorption characteristics, when exposed to suitable radiation and reverse when the irradiation source is r ...
... fluorescence, for detection of cracks in metal work, for tracing the course of river through caves, as microanalytical reagents and so on. Certain chemicals change their colour, that is, their absorption characteristics, when exposed to suitable radiation and reverse when the irradiation source is r ...
Worksheet on Ionic and Atomic Size Trends
... 3. The size of atoms decreases from left to right across a period. 4. Na: 1s22s22p63s1 Cl: 1s22s22p63s23p5 Both of these electron configurations contain the same number of energy levels. The size of these atoms decreases because the number of protons increases from left to right, resulting in an inc ...
... 3. The size of atoms decreases from left to right across a period. 4. Na: 1s22s22p63s1 Cl: 1s22s22p63s23p5 Both of these electron configurations contain the same number of energy levels. The size of these atoms decreases because the number of protons increases from left to right, resulting in an inc ...
4.6 Quantized Radiation Field - Create and Use Your home
... And the total transition rate for an isotropic broadband source is: w k = ' ( w k ) k , j k,j ...
... And the total transition rate for an isotropic broadband source is: w k = ' ( w k ) k , j k,j ...
Quantum Mechanics
... 2.25 Calculate the minimum wavelength of the radiation emitted by an X-ray tube operated at 30 kV. [Adapted from the University of London, Royal Holloway 2005] 2.26 If the minimum wavelength from an 80 kV X-ray tube is 0.15 × 10−10 m, deduce a value for Planck’s constant. [Adapted from the Universit ...
... 2.25 Calculate the minimum wavelength of the radiation emitted by an X-ray tube operated at 30 kV. [Adapted from the University of London, Royal Holloway 2005] 2.26 If the minimum wavelength from an 80 kV X-ray tube is 0.15 × 10−10 m, deduce a value for Planck’s constant. [Adapted from the Universit ...
1000 Solved Problems in Modern Physics
... 2.25 Calculate the minimum wavelength of the radiation emitted by an X-ray tube operated at 30 kV. [Adapted from the University of London, Royal Holloway 2005] 2.26 If the minimum wavelength from an 80 kV X-ray tube is 0.15 × 10−10 m, deduce a value for Planck’s constant. [Adapted from the Universit ...
... 2.25 Calculate the minimum wavelength of the radiation emitted by an X-ray tube operated at 30 kV. [Adapted from the University of London, Royal Holloway 2005] 2.26 If the minimum wavelength from an 80 kV X-ray tube is 0.15 × 10−10 m, deduce a value for Planck’s constant. [Adapted from the Universit ...
Reflectivity measurements of a quantum well
... different optical materials. The most frequently used design is that of a quarter-wave mirror, where each optical layer thickness corresponding to one quarter of the wavelength for which the mirror is designed. The latter condition holds for normal incidence; if the mirror is designed for larger ang ...
... different optical materials. The most frequently used design is that of a quarter-wave mirror, where each optical layer thickness corresponding to one quarter of the wavelength for which the mirror is designed. The latter condition holds for normal incidence; if the mirror is designed for larger ang ...
9/6/12
... - Pure substances that are not elements are compounds. Compounds are composed of more than one kind of atom. o Example: carbon dioxide - There may be easier ways of preparing them, but compounds can be made from their elements. - Compounds can be broken down into their elements, often with difficult ...
... - Pure substances that are not elements are compounds. Compounds are composed of more than one kind of atom. o Example: carbon dioxide - There may be easier ways of preparing them, but compounds can be made from their elements. - Compounds can be broken down into their elements, often with difficult ...
Spin States in Graphene Quantum Dots
... The successive spin filling of orbital states is detected by measuring the difference between ground-state energies as a function of a magnetic field. For a magnetic field in-plane of the quantum dot the Zeeman splitting of spin states is measured. The results are compatible with a g factor of 2, an ...
... The successive spin filling of orbital states is detected by measuring the difference between ground-state energies as a function of a magnetic field. For a magnetic field in-plane of the quantum dot the Zeeman splitting of spin states is measured. The results are compatible with a g factor of 2, an ...
Mathcad - CO Rotational States.
... The absorption coefficient, γ(v), is a sum of the absorption coefficients, γJ(v), associated with the transition from each initial rotational energy level J to the final level J+1. Each γJ(v) can be written as a product of several factors that are defined below. C = all the constants that appear at ...
... The absorption coefficient, γ(v), is a sum of the absorption coefficients, γJ(v), associated with the transition from each initial rotational energy level J to the final level J+1. Each γJ(v) can be written as a product of several factors that are defined below. C = all the constants that appear at ...
Acrobat Distiller, Job 21
... As Slater pointed out, the molecular energy curve can be obtained from experiment (spectroscopy) or theory (ab initio quantum mechanics). The energy profile obtained is similar in both approaches. For example, Winn (19) offered the following analysis of the ab initio results of Kolos and Wolniewicz ...
... As Slater pointed out, the molecular energy curve can be obtained from experiment (spectroscopy) or theory (ab initio quantum mechanics). The energy profile obtained is similar in both approaches. For example, Winn (19) offered the following analysis of the ab initio results of Kolos and Wolniewicz ...
Properties of 6Li - NC State Physics
... the central-field approximation, takes only this fact into account, and computes the energy of the atom assuming that the valence electron is independent, and that the nucleus and closed electron shell produce a spherically-symmetric electric field. The resulting ground and excited states are schema ...
... the central-field approximation, takes only this fact into account, and computes the energy of the atom assuming that the valence electron is independent, and that the nucleus and closed electron shell produce a spherically-symmetric electric field. The resulting ground and excited states are schema ...
Optical Pumping of Natural Rubidium
... only important selection rules as other transitions are not possible). The light introduced will also be circularly polarized, which means that it will have a very particular angular momentum. It follows that for the atoms absorbing these photons, only transitions of ∆M=+1 are possible (however the ...
... only important selection rules as other transitions are not possible). The light introduced will also be circularly polarized, which means that it will have a very particular angular momentum. It follows that for the atoms absorbing these photons, only transitions of ∆M=+1 are possible (however the ...
Предположение о влиянии гравитации на скорость света
... and quasars with different red shift coefficients were visually located in the vicinity of one another. Considered also is the mechanism of change in the lapse of time in terms of different gravitational potentials. The computational experiment shows that supposedly the difference in lapse of time i ...
... and quasars with different red shift coefficients were visually located in the vicinity of one another. Considered also is the mechanism of change in the lapse of time in terms of different gravitational potentials. The computational experiment shows that supposedly the difference in lapse of time i ...
An Overview of Computational Chemistry
... •The BO approx. is usually very good, but breaks down when two (or more) electronic states are close in energy at particular nuclear geometries. •In such situations, a “ non-adiabatic” wave function - a product of nuclear and electronic wave functions - must be used. The electronic Hamiltonian becom ...
... •The BO approx. is usually very good, but breaks down when two (or more) electronic states are close in energy at particular nuclear geometries. •In such situations, a “ non-adiabatic” wave function - a product of nuclear and electronic wave functions - must be used. The electronic Hamiltonian becom ...
Lec5_Resonant_EM_interactions_atmospheres
... the energy to move water from the liquid phase to the gas phase but the extra energy to go from solid to liquid is only about another 10% and we are only trying to get a crude estimate. We convert J/kg to J/molecule using 0.018 kg/mole for water and 1 mole = 6x1023 molecules So the energy to free 1 ...
... the energy to move water from the liquid phase to the gas phase but the extra energy to go from solid to liquid is only about another 10% and we are only trying to get a crude estimate. We convert J/kg to J/molecule using 0.018 kg/mole for water and 1 mole = 6x1023 molecules So the energy to free 1 ...
Optical Pumping of Rubidium Vapor
... and D2 lines, respectively. In our experiment, the D2 line is removed from the light source by means of an narrow band filter—we are only concerned with exciting the transition between the 2 S1/2 state and the 2 P1/2 state. Both the difficulty and the great effectiveness of using radio waves in atom ...
... and D2 lines, respectively. In our experiment, the D2 line is removed from the light source by means of an narrow band filter—we are only concerned with exciting the transition between the 2 S1/2 state and the 2 P1/2 state. Both the difficulty and the great effectiveness of using radio waves in atom ...
the zeeman effect
... additional energy just as a bar magnet does and consequently the original energy level is shifted. The energy shift may be positive, zero, or even negative, depending on the angle between the electron magnetic dipole moment and the field. Due to Zeeman effect, some degenerate energy levels will spli ...
... additional energy just as a bar magnet does and consequently the original energy level is shifted. The energy shift may be positive, zero, or even negative, depending on the angle between the electron magnetic dipole moment and the field. Due to Zeeman effect, some degenerate energy levels will spli ...
Atomic Spectroscopy
... higher values of angular momentum (d, f ) are identical to the hydrogen energy spectrum. The spectrum of Na is shown in Fig. 2. One can immediately see that there are many more optical transitions because of the lifted degeneracy of energy states with different angular momenta. However, not all elec ...
... higher values of angular momentum (d, f ) are identical to the hydrogen energy spectrum. The spectrum of Na is shown in Fig. 2. One can immediately see that there are many more optical transitions because of the lifted degeneracy of energy states with different angular momenta. However, not all elec ...
Evidence for Two Different Solid Phases of Two-Dimensional Electrons in... * Z. H. Wang, Yong P. Chen, R. M. Lewis,
... energy dominates over their kinetic energy. In two dimensions, it is expected [2] that the formation of such a Wigner solid (WS) can be facilitated by a sufficiently strong perpendicular magnetic field (B). On the other hand, a two-dimensional electron system (2DES) with areal density n can condense ...
... energy dominates over their kinetic energy. In two dimensions, it is expected [2] that the formation of such a Wigner solid (WS) can be facilitated by a sufficiently strong perpendicular magnetic field (B). On the other hand, a two-dimensional electron system (2DES) with areal density n can condense ...
Mössbauer spectroscopy

Mössbauer spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique based on the Mössbauer effect. This effect, discovered by Rudolf Mössbauer in 1957, consists in the recoil-free, resonant absorption and emission of gamma rays in solids.Like NMR spectroscopy, Mössbauer spectroscopy probes tiny changes in the energy levels of an atomic nucleus in response to its environment. Typically, three types of nuclear interactions may be observed: an isomeric shift, also known as a chemical shift; quadrupole splitting; and magnetic or hyperfine splitting, also known as the Zeeman effect. Due to the high energy and extremely narrow line widths of gamma rays, Mössbauer spectroscopy is a very sensitive technique in terms of energy (and hence frequency) resolution, capable of detecting change in just a few parts per 1011.