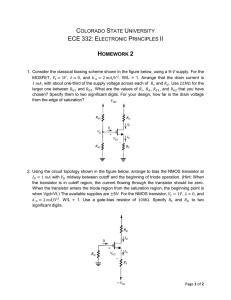
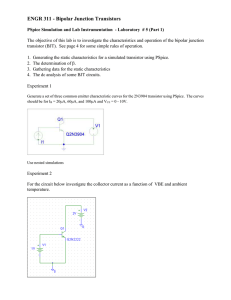
File
... Limited to materials where the resistance remains constant. Ohmic materials to which Ohm’s law applies. Ex: wires or lightbulb filaments. Nonohmic Ohm’s law does not apply. Ex: the internal workings of batteries and capacitors. Resistors circuit elements designed to create resistance to ...
... Limited to materials where the resistance remains constant. Ohmic materials to which Ohm’s law applies. Ex: wires or lightbulb filaments. Nonohmic Ohm’s law does not apply. Ex: the internal workings of batteries and capacitors. Resistors circuit elements designed to create resistance to ...
In-Plane Effective Thermal Conductivity of Plain
... Keywords: thermal conductivity, plain-weave, porosity, screen-laminates. ABSTRACT: A simple -to-fabricate woven mesh, consisting of bonded laminates of twodimensional plain-weave conductive screens is described. Geometric equations show that these porous matrices can be fabricated to have a wide ran ...
... Keywords: thermal conductivity, plain-weave, porosity, screen-laminates. ABSTRACT: A simple -to-fabricate woven mesh, consisting of bonded laminates of twodimensional plain-weave conductive screens is described. Geometric equations show that these porous matrices can be fabricated to have a wide ran ...
Application
... winding connected to an AC supply. The charge is kept in the crucible, which forms a single turn short circuited secondary circuit. The current in the charge is very high in the order of several thousand amperes. The charge is magnetically coupled to the primary ...
... winding connected to an AC supply. The charge is kept in the crucible, which forms a single turn short circuited secondary circuit. The current in the charge is very high in the order of several thousand amperes. The charge is magnetically coupled to the primary ...
Electric Current and Circuits
... • Assign variables to the current in each branch (I1, I2, I3…) and choose a direction for each. Draw the circuit with the current flow indicated by arrows. • Apply the Junction Rule • Apply the loop rule – If your loop goes against the current in a resistor, V is +. If your loop goes with the curren ...
... • Assign variables to the current in each branch (I1, I2, I3…) and choose a direction for each. Draw the circuit with the current flow indicated by arrows. • Apply the Junction Rule • Apply the loop rule – If your loop goes against the current in a resistor, V is +. If your loop goes with the curren ...
SMC490
... LEDs are sensitive to electrostatic discharge (ESD). Precautions against ESD must be taken when handling or operating these LEDs. Surge voltage or electrostatic discharge can result in complete failure of the device. ...
... LEDs are sensitive to electrostatic discharge (ESD). Precautions against ESD must be taken when handling or operating these LEDs. Surge voltage or electrostatic discharge can result in complete failure of the device. ...
Resistance and Resistivity
... Resistivity and Temperature Metals Resistivity increases with temperature is positive Semiconductors Resistivity decreases with temperature is negative ...
... Resistivity and Temperature Metals Resistivity increases with temperature is positive Semiconductors Resistivity decreases with temperature is negative ...
Principles of Computer Architecture Dr. Mike Frank
... • Sub-threshold power dissipation across “off” transistors is based on the leakage current density exp(−Vt / T) – Vt is the threshold voltage ...
... • Sub-threshold power dissipation across “off” transistors is based on the leakage current density exp(−Vt / T) – Vt is the threshold voltage ...
XP162A12A6PR-G - Torex Semiconductor
... 4. The products in this catalog are not developed, designed, or approved for use with such equipment whose failure of malfunction can be reasonably expected to directly endanger the life of, or cause significant injury to, the user. (e.g. Atomic energy; aerospace; transport; combustion and associate ...
... 4. The products in this catalog are not developed, designed, or approved for use with such equipment whose failure of malfunction can be reasonably expected to directly endanger the life of, or cause significant injury to, the user. (e.g. Atomic energy; aerospace; transport; combustion and associate ...
EEL 4915 Final Presentation
... fabrication are the gerber files Top layer did not allow for many layers – Size of board and amount of parts required two layers of signals due to lack of space Traces can run to other layers – Thermal relief pads ...
... fabrication are the gerber files Top layer did not allow for many layers – Size of board and amount of parts required two layers of signals due to lack of space Traces can run to other layers – Thermal relief pads ...
Chapter 17 Electric Current and Resistance
... Find the resistivity of platinum when the temperature is increased to 35ºC. ...
... Find the resistivity of platinum when the temperature is increased to 35ºC. ...
High Brightness LED Current Regulator A6260
... that the complete circuit, including LEDs, may remain connected to the power supply under all conditions. ...
... that the complete circuit, including LEDs, may remain connected to the power supply under all conditions. ...
AN 05-02_Capitalizing on the Advantages of the ISOPLUS Porducts
... materials and clamps can be used with the ISOPLUS packages. New high performance phase change materials often require much higher clamping forces to achieve the lowest possible thermal resistance. Kunze Folien offers a number of high force clamps for power packages. • The Power Clip KU4-498 is an ex ...
... materials and clamps can be used with the ISOPLUS packages. New high performance phase change materials often require much higher clamping forces to achieve the lowest possible thermal resistance. Kunze Folien offers a number of high force clamps for power packages. • The Power Clip KU4-498 is an ex ...
Temperature Measurement and Control
... • B, R, and S • Types B, R, and S thermocouples use platinum or a platinum–rhodium alloy for each conductor. These are among the most stable thermocouples, but have lower sensitivity, approximately 10 µV/°C, than other types. The high cost of these makes them unsuitable for general use. Generally, t ...
... • B, R, and S • Types B, R, and S thermocouples use platinum or a platinum–rhodium alloy for each conductor. These are among the most stable thermocouples, but have lower sensitivity, approximately 10 µV/°C, than other types. The high cost of these makes them unsuitable for general use. Generally, t ...
CBT - Coulomb Blockade Thermometer
... Thin insulating barrier between two electrodes QM: propability for electron to move to the other side Behaves like an ohmic resistor The junction has a capacitance ...
... Thin insulating barrier between two electrodes QM: propability for electron to move to the other side Behaves like an ohmic resistor The junction has a capacitance ...
Aalborg Universitet Simulations
... fulfilling the robustness and reliability requirements [1]. One of the critical robustness requirements for IGBT converters design is how to monitor power semiconductor’s junction temperature precisely and then control it at adequate level. This is because junction temperature is a key parameter for ...
... fulfilling the robustness and reliability requirements [1]. One of the critical robustness requirements for IGBT converters design is how to monitor power semiconductor’s junction temperature precisely and then control it at adequate level. This is because junction temperature is a key parameter for ...
Ohm`s Law Calculations
... For many devices, the resistance is constant regardless of the current. In this case, the potential difference is directly proportional to the current:V = I · R This is known as Ohm's law. Any device that follows Ohm's law is called an "ohmic" device; A device that does not obey Ohm's law is said to ...
... For many devices, the resistance is constant regardless of the current. In this case, the potential difference is directly proportional to the current:V = I · R This is known as Ohm's law. Any device that follows Ohm's law is called an "ohmic" device; A device that does not obey Ohm's law is said to ...
Thermal runaway

Thermal runaway refers to a situation where an increase in temperature changes the conditions in a way that causes a further increase in temperature, often leading to a destructive result. It is a kind of uncontrolled positive feedback.In other words, ""thermal runaway"" describes a process which is accelerated by increased temperature, in turn releasing energy that further increases temperature. In chemistry (and chemical engineering), this risk is associated with strongly exothermic reactions that are accelerated by temperature rise. In electrical engineering, thermal runaway is typically associated with increased current flow and power dissipation, although exothermic chemical reactions can be of concern here too. Thermal runaway can occur in civil engineering, notably when the heat released by large amounts of curing concrete is not controlled. In astrophysics, runaway nuclear fusion reactions in stars can lead to nova and several types of supernova explosions, and also occur as a less dramatic event in the normal evolution of solar mass stars, the ""helium flash"".There are also concerns regarding global warming that a global average increase of 3-4 degrees Celsius above the preindustrial baseline could lead to a further unchecked increase in surface temperatures. For example, releases of methane, a greenhouse gas more potent than CO2, from wetlands, melting permafrost and continental margin seabed clathrate deposits could be subject to positive feedback.