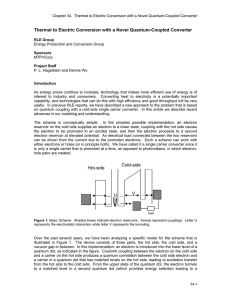
Thermal to Electric Conversion with a Novel Quantum-Coupled Converter
... of the image charge would constitute a surface current, and associated resistive loss as well. Such power dissipation, which could be estimated classically, would provide the rate at which power is dissipated in the hot side by the return current of the cold side converter. If one could develop an a ...
... of the image charge would constitute a surface current, and associated resistive loss as well. Such power dissipation, which could be estimated classically, would provide the rate at which power is dissipated in the hot side by the return current of the cold side converter. If one could develop an a ...
ir = -r
... Power, potential and Emf When a emf device does work to establish a current i in the circuit, the device transfers its chemical energy to the charge carrier. It loses power in its internal resistance r. Energy transfer rate P from emf to charge carrier ...
... Power, potential and Emf When a emf device does work to establish a current i in the circuit, the device transfers its chemical energy to the charge carrier. It loses power in its internal resistance r. Energy transfer rate P from emf to charge carrier ...
MAX8510/MAX8511/MAX8512 Ultra-Low-Noise, High PSRR, Low-Dropout, 120mA Linear Regulators General Description
... The MAX8510/MAX8511/MAX8512 are ultra-low-noise, low-dropout, low-quiescent current linear regulators designed for space-restricted applications. The parts are available with preset output voltages ranging from 1.5V to 4.5V in 100mV increments. These devices can supply loads up to 120mA. As shown in ...
... The MAX8510/MAX8511/MAX8512 are ultra-low-noise, low-dropout, low-quiescent current linear regulators designed for space-restricted applications. The parts are available with preset output voltages ranging from 1.5V to 4.5V in 100mV increments. These devices can supply loads up to 120mA. As shown in ...
reading
... IPTAT2 = aT2, derive the conditions so that both first order and second order partial derivative of Vref with respect to T are canceled at a given temperature T0. 2. Suggest a circuit schematic that can be used to generated IPTAT2 current. You can use some of the circuit elements that we talked abou ...
... IPTAT2 = aT2, derive the conditions so that both first order and second order partial derivative of Vref with respect to T are canceled at a given temperature T0. 2. Suggest a circuit schematic that can be used to generated IPTAT2 current. You can use some of the circuit elements that we talked abou ...
ZXCL SERIES Micropower SC70-5 & SOT23-5 low dropout regulators
... Note2:Output voltage will start to rise when VIN exceeds a value or approximately 1.3V. For normal operation, VIN(min) > VOUT(nom) + 0.5V. Note3:Dropout voltage is defined as the difference between VIN and VO, when VO has dropped 100mV below its nominal value. Nominal value of VO is defined at VIN=V ...
... Note2:Output voltage will start to rise when VIN exceeds a value or approximately 1.3V. For normal operation, VIN(min) > VOUT(nom) + 0.5V. Note3:Dropout voltage is defined as the difference between VIN and VO, when VO has dropped 100mV below its nominal value. Nominal value of VO is defined at VIN=V ...
TGA8399B-SCC 数据资料DataSheet下载
... dB. The device features high gain of 26 dB across the band, while providing a nominal output power at P1dB gain compression of 11dBm. Typical input and output return loss is 18 dB. Ground is provided to the circuitry through vias to the backside metallization. The TGA8399B-SCC low noise amplifier is ...
... dB. The device features high gain of 26 dB across the band, while providing a nominal output power at P1dB gain compression of 11dBm. Typical input and output return loss is 18 dB. Ground is provided to the circuitry through vias to the backside metallization. The TGA8399B-SCC low noise amplifier is ...
5 Dynamic Characteristics I
... 5.1 Switching Times In practice, changes in the state of conduction of the transistor take time to occur. These cause delays in the response of the output to changes at the input. Consider the circuit in Fig. 5.1. ...
... 5.1 Switching Times In practice, changes in the state of conduction of the transistor take time to occur. These cause delays in the response of the output to changes at the input. Consider the circuit in Fig. 5.1. ...
Surge Current Protection Using Super Conductors Report New
... SCFCL can be tailored by varying the electric field induced along tube’s circumference during the fault. The decisive parameters for this SCFCL design are the number of primary turns and the height, diameter and wall thickness of the superconducting tube. The cross section of the iron core is design ...
... SCFCL can be tailored by varying the electric field induced along tube’s circumference during the fault. The decisive parameters for this SCFCL design are the number of primary turns and the height, diameter and wall thickness of the superconducting tube. The cross section of the iron core is design ...
Document
... two back-to-back P-N junctions. However, it cannot be made with two independent back-to-back diodes and is not symmetric. BJTs can be made either as PNP or as NPN. They have three regions and three terminals, emitter, base, and collector represented by E, B, and C respectively. The arrow indicates t ...
... two back-to-back P-N junctions. However, it cannot be made with two independent back-to-back diodes and is not symmetric. BJTs can be made either as PNP or as NPN. They have three regions and three terminals, emitter, base, and collector represented by E, B, and C respectively. The arrow indicates t ...
AD8560 16 V Rail-to-Rail Buffer Amplifier Data
... As with any semiconductor device, whenever the input exceeds either supply voltage, attention needs to be paid to the input overvoltage characteristics. As an overvoltage occurs, the amplifier could be damaged depending on the voltage level and the magnitude of the fault current. When the input volt ...
... As with any semiconductor device, whenever the input exceeds either supply voltage, attention needs to be paid to the input overvoltage characteristics. As an overvoltage occurs, the amplifier could be damaged depending on the voltage level and the magnitude of the fault current. When the input volt ...
TPS2043, TPS2053
... power-switch rise times and fall times to minimize current surges during switching. The charge pump, requiring no external components, allows operation from supplies as low as 2.7 V. ...
... power-switch rise times and fall times to minimize current surges during switching. The charge pump, requiring no external components, allows operation from supplies as low as 2.7 V. ...
Lecture 17: BJT Biasing. Current Mirror.
... In this current mirror, Q1 is called a diode-connected BJT because the collector and base terminals are connected together. For proper operation of this circuit, it is very important that the BJTs be “matched,” meaning they having the same , characteristic curves, etc. Usually this means that the B ...
... In this current mirror, Q1 is called a diode-connected BJT because the collector and base terminals are connected together. For proper operation of this circuit, it is very important that the BJTs be “matched,” meaning they having the same , characteristic curves, etc. Usually this means that the B ...
Thermal runaway

Thermal runaway refers to a situation where an increase in temperature changes the conditions in a way that causes a further increase in temperature, often leading to a destructive result. It is a kind of uncontrolled positive feedback.In other words, ""thermal runaway"" describes a process which is accelerated by increased temperature, in turn releasing energy that further increases temperature. In chemistry (and chemical engineering), this risk is associated with strongly exothermic reactions that are accelerated by temperature rise. In electrical engineering, thermal runaway is typically associated with increased current flow and power dissipation, although exothermic chemical reactions can be of concern here too. Thermal runaway can occur in civil engineering, notably when the heat released by large amounts of curing concrete is not controlled. In astrophysics, runaway nuclear fusion reactions in stars can lead to nova and several types of supernova explosions, and also occur as a less dramatic event in the normal evolution of solar mass stars, the ""helium flash"".There are also concerns regarding global warming that a global average increase of 3-4 degrees Celsius above the preindustrial baseline could lead to a further unchecked increase in surface temperatures. For example, releases of methane, a greenhouse gas more potent than CO2, from wetlands, melting permafrost and continental margin seabed clathrate deposits could be subject to positive feedback.