Exercises to Quantum Mechanics FYSN17
... We shall in this exercise study the effect of H Graphical depiction of the Morse potential with a harperturbation. monic potential for comparison, CC-BY-SA Mark Soˆ p in terms of a and a† of the harmonic moza (2006) a) Express H oscillator corresponding to V0 (x). ˆ p |ni between unperturbed harmoni ...
... We shall in this exercise study the effect of H Graphical depiction of the Morse potential with a harperturbation. monic potential for comparison, CC-BY-SA Mark Soˆ p in terms of a and a† of the harmonic moza (2006) a) Express H oscillator corresponding to V0 (x). ˆ p |ni between unperturbed harmoni ...
Symmetry breaking and the deconstruction of mass
... SU(3)-vector bosons, the gluons, the classical theory is invariant under scaling transformations. Namely, if Aμ represents the gluon fields, and Aμ is a classical solution to the equations of motion, then so is the scaled configuration: λA(λx), for any real parameter λ. Again, the quantum structure ...
... SU(3)-vector bosons, the gluons, the classical theory is invariant under scaling transformations. Namely, if Aμ represents the gluon fields, and Aμ is a classical solution to the equations of motion, then so is the scaled configuration: λA(λx), for any real parameter λ. Again, the quantum structure ...
Series 5 - Problems
... f) Find φ(x, t). Write your answer in terms of c1 (t) and c2 (t). What does this tell you (physically) about (x, t)? What does the relative contribution of each ”basis” state look like over time? Does φ(x, t) ever equal φ(x, 0) for t 6= 0? Compute |φ(t = 0)|2 then |φ(t)|2 . Take n1 = 1, n2 = 2 and ...
... f) Find φ(x, t). Write your answer in terms of c1 (t) and c2 (t). What does this tell you (physically) about (x, t)? What does the relative contribution of each ”basis” state look like over time? Does φ(x, t) ever equal φ(x, 0) for t 6= 0? Compute |φ(t = 0)|2 then |φ(t)|2 . Take n1 = 1, n2 = 2 and ...
PASCOS - CERN Indico
... using the scale invariance of the theory implies the vanishing of the imaginary parts in the forward kinematics when the operators are on shell. From unitarity one gets a chain of discontinuity equations . For example the six point amplitudes discontinuity requires the vanishing of the left diagram: ...
... using the scale invariance of the theory implies the vanishing of the imaginary parts in the forward kinematics when the operators are on shell. From unitarity one gets a chain of discontinuity equations . For example the six point amplitudes discontinuity requires the vanishing of the left diagram: ...
Higgs - Transcript - the Cassiopeia Project
... arises to describe something that can have a different value at every point in space… like the air temperature or like the wind velocity or like the strength and direction of some force such as the Earth’s magnetic field. There are only four forces that we know of, and they are all described by fiel ...
... arises to describe something that can have a different value at every point in space… like the air temperature or like the wind velocity or like the strength and direction of some force such as the Earth’s magnetic field. There are only four forces that we know of, and they are all described by fiel ...
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics AEP3610 Professor Scott
... energy is proportional to its frequency, and that light can only be emitted or absorbed in ‘packets’ (quanta) now called photons: E = hf • h is Planck’s constant: h = 6.626 x10–34 J∙s = 4.136 x10–15 eV∙s • incidentally, we often use ‘hbar’: ħ:=h/2 = 1.046 x10–34 J∙s • we assume that the energy to i ...
... energy is proportional to its frequency, and that light can only be emitted or absorbed in ‘packets’ (quanta) now called photons: E = hf • h is Planck’s constant: h = 6.626 x10–34 J∙s = 4.136 x10–15 eV∙s • incidentally, we often use ‘hbar’: ħ:=h/2 = 1.046 x10–34 J∙s • we assume that the energy to i ...
Quantum Potpourri
... and the Superposition Principle Electrons in atoms or molecules are characterized by their entire distributions, called wave functions or orbitals, rather than by instantaneous positions and velocities: an electron may be considered always to be, with appropriate probability, at all points of its di ...
... and the Superposition Principle Electrons in atoms or molecules are characterized by their entire distributions, called wave functions or orbitals, rather than by instantaneous positions and velocities: an electron may be considered always to be, with appropriate probability, at all points of its di ...
QFT II
... The Greens function (= correlation functions) in Euclidean coordinates G(xE1 , . . . , xE2 ) are called ’Schwinger functions’. In ’typical’ QFTs these can be analytically rotated back to Minkowski time. The Osterwald-Schrader theorem gives precise condition for when this is possible. Conclusion 2 wa ...
... The Greens function (= correlation functions) in Euclidean coordinates G(xE1 , . . . , xE2 ) are called ’Schwinger functions’. In ’typical’ QFTs these can be analytically rotated back to Minkowski time. The Osterwald-Schrader theorem gives precise condition for when this is possible. Conclusion 2 wa ...
PHYSICAL SCIENCES TIME: 3 HOURS MAXIMUM MARKS: 200
... This part shall contain 25 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) generally covering the topics given in the Part ‘A’ (CORE) of syllabus. Each question shall be of 3.5 Marks. The total marks allocated to this section shall be 70 out of 200.Candidates are required to answer any 20 questions. Part 'C' This ...
... This part shall contain 25 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) generally covering the topics given in the Part ‘A’ (CORE) of syllabus. Each question shall be of 3.5 Marks. The total marks allocated to this section shall be 70 out of 200.Candidates are required to answer any 20 questions. Part 'C' This ...
P410M: Relativistic Quantum Fields
... For example, the position-space wavefunction is hxjÃi = Ãx(x) and jhxjÃij2 = jÃx(x)j2 is the probability of finding the particle at position x. Sincejxi and jpi are not aligned bases, the state cannot be an eigenvector of position and momentum simultaneously. Also, since the measurements change the ...
... For example, the position-space wavefunction is hxjÃi = Ãx(x) and jhxjÃij2 = jÃx(x)j2 is the probability of finding the particle at position x. Sincejxi and jpi are not aligned bases, the state cannot be an eigenvector of position and momentum simultaneously. Also, since the measurements change the ...
The Higgs Boson and Fermion Masses
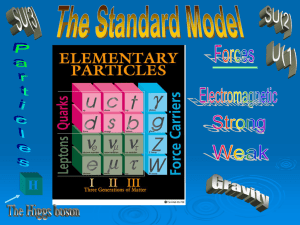
... three pairs of leptons. They are shown here with their year of discovery. ...
... three pairs of leptons. They are shown here with their year of discovery. ...
SU(3) Multiplets & Gauge Invariance
... L=[iħcgmm-mc2 -(qg m)Am and that Am Am + m defines its transformation under the same local gauge transformation ...
... L=[iħcgmm-mc2 -(qg m)Am and that Am Am + m defines its transformation under the same local gauge transformation ...