Lecture 5 Motion of a charged particle in a magnetic field
... qi ≡ xi = (x1 , x2 , x3 ) and q̇i ≡ vi = (ẋ1 , ẋ2 , ẋ3 ) N.B. form of Lagrangian more natural in relativistic formulation: −qv µ Aµ = −qϕ + qv · A where v µ = (c, v) and Aµ = (ϕ/c, A) Canonical momentum: pi = ∂ẋi L = mvi + qAi no longer given by mass × velocity – there is an extra term! ...
... qi ≡ xi = (x1 , x2 , x3 ) and q̇i ≡ vi = (ẋ1 , ẋ2 , ẋ3 ) N.B. form of Lagrangian more natural in relativistic formulation: −qv µ Aµ = −qϕ + qv · A where v µ = (c, v) and Aµ = (ϕ/c, A) Canonical momentum: pi = ∂ẋi L = mvi + qAi no longer given by mass × velocity – there is an extra term! ...
Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur
... Instructor : Prof . D. Chowdhury. ...
... Instructor : Prof . D. Chowdhury. ...
UVM Physics MS: Comprehensive Exam Date: Saturday January 11, 2013 Time:
... (a) Find the electrostatic field everywhere in space. (b) The shell is now rotating around its axis (ẑ-axis) with the frequency ω0 = const. The rotating insulator produces a surface current density. Find the magnetic field generated everywhere in space. (c) After a while the cylinder starts to slow ...
... (a) Find the electrostatic field everywhere in space. (b) The shell is now rotating around its axis (ẑ-axis) with the frequency ω0 = const. The rotating insulator produces a surface current density. Find the magnetic field generated everywhere in space. (c) After a while the cylinder starts to slow ...
wu.pdf
... systematic and powerful tool to study the low energy or large distance behavior of a many-body system, in particular the critical behavior near a second order (or continuous) phase transition point. A prototype of such phase transition occurs in the Landau-Ginzburg model, namely a real φ4 theory wit ...
... systematic and powerful tool to study the low energy or large distance behavior of a many-body system, in particular the critical behavior near a second order (or continuous) phase transition point. A prototype of such phase transition occurs in the Landau-Ginzburg model, namely a real φ4 theory wit ...
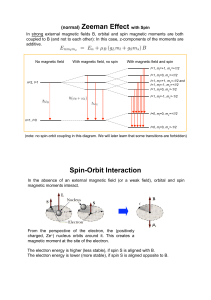
(normal) Zeeman Effect with Spin Spin
... magnetic moment at the site of the electron. The electron energy is higher (less stable), if spin S is aligned with B. The electron energy is lower (more stable), if spin S is aligned opposite to B. ...
... magnetic moment at the site of the electron. The electron energy is higher (less stable), if spin S is aligned with B. The electron energy is lower (more stable), if spin S is aligned opposite to B. ...
An Introduction to the Standard Model of Particle Physics
... 12.6 Mass terms in : an attempted generalisation Experimental tests of the Weinberg–Salam theory 13.1 The search for the gauge bosons 13.2 The W± bosons 13.3 The Z boson 13.4 The number of lepton families 13.5 The measurement of partial widths 13.6 Left–right production cross-section asymmetry and l ...
... 12.6 Mass terms in : an attempted generalisation Experimental tests of the Weinberg–Salam theory 13.1 The search for the gauge bosons 13.2 The W± bosons 13.3 The Z boson 13.4 The number of lepton families 13.5 The measurement of partial widths 13.6 Left–right production cross-section asymmetry and l ...
P10_Ferreira
... Coupling to fermions MODEL I: Only Φ2 couples to fermions. MODEL II: Φ2 couples to up-quarks, Φ1 to down quarks and leptons. ...
... Coupling to fermions MODEL I: Only Φ2 couples to fermions. MODEL II: Φ2 couples to up-quarks, Φ1 to down quarks and leptons. ...
String Theory
... Later experiments in the 1970s revealed that many of the theory's predictions were noticeable only with experimental data. Point-particle theory succeeded and string theory was left behind The reason for this was that String vibrations produce observable properties that we see in fundamental particl ...
... Later experiments in the 1970s revealed that many of the theory's predictions were noticeable only with experimental data. Point-particle theory succeeded and string theory was left behind The reason for this was that String vibrations produce observable properties that we see in fundamental particl ...
Quantum physics I
... •Each photon should have a definite value at all angles, whether measured or not; since QT doesn’t account for this attribute, it’s incomplete ...
... •Each photon should have a definite value at all angles, whether measured or not; since QT doesn’t account for this attribute, it’s incomplete ...
B.3 Time dependent quantum mechanics
... to be compared with eq. 2. Such pairs of coupled differential equations for two functions, one having a (-) sign, the other a (+) sign, are called symplectic, or ‘area preserving.’ Classically this means an area xp is mapped into an equal area in phase space at a later time. Quantum mechanically i ...
... to be compared with eq. 2. Such pairs of coupled differential equations for two functions, one having a (-) sign, the other a (+) sign, are called symplectic, or ‘area preserving.’ Classically this means an area xp is mapped into an equal area in phase space at a later time. Quantum mechanically i ...