Δk/k
... of the energy levels of a coupled quantum mechanical system: When there is state mixing, the levels repel each other. ...
... of the energy levels of a coupled quantum mechanical system: When there is state mixing, the levels repel each other. ...
DOC - Uni Basel Research Database
... model peptides. The modular assembly of peptides is ideally suited to study the correlation between their molecular mass and number of fluorous chains required. The features introduced by the tag can also be combined for example with a porphyrin tag exposing long perfluorinated alkyl chain. Of parti ...
... model peptides. The modular assembly of peptides is ideally suited to study the correlation between their molecular mass and number of fluorous chains required. The features introduced by the tag can also be combined for example with a porphyrin tag exposing long perfluorinated alkyl chain. Of parti ...
Special Rotational Dynamics Outline
... Torques Due to Wrapped Strings: Frequently, the AP exam includes problems in which a string is wrapped around an object (kind of like a yo-yo) and then is pulled. If the string does not slip, the torque is the tension at that point times the radius of the object. ...
... Torques Due to Wrapped Strings: Frequently, the AP exam includes problems in which a string is wrapped around an object (kind of like a yo-yo) and then is pulled. If the string does not slip, the torque is the tension at that point times the radius of the object. ...
lecture1
... Double bond stretching region (λ = 5.4 – 6.4 µm). This include C = C, C = O, C = N with C = O at 5.9 µm. Acids (-C=O-OH) and esters (-C=O-OR) absorb at lower wavelength while amides (-C=O-NH2) absorb at longer wavelength with two peaks, hence discrimination is possible. These three regions are the “ ...
... Double bond stretching region (λ = 5.4 – 6.4 µm). This include C = C, C = O, C = N with C = O at 5.9 µm. Acids (-C=O-OH) and esters (-C=O-OR) absorb at lower wavelength while amides (-C=O-NH2) absorb at longer wavelength with two peaks, hence discrimination is possible. These three regions are the “ ...
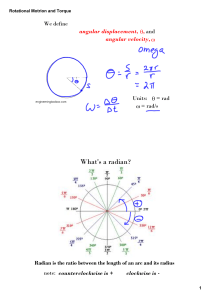
What is angular velocity? Angular speed
... xf = x0 + vt + ½ at2 If you take the top two equations, solve them for t, and set them equal to each other, you get ωf2 = ω02 + 2α α (θ θ - θ0). One morr comparison – this is the ...
... xf = x0 + vt + ½ at2 If you take the top two equations, solve them for t, and set them equal to each other, you get ωf2 = ω02 + 2α α (θ θ - θ0). One morr comparison – this is the ...
Rotational spectroscopy

Rotational spectroscopy is concerned with the measurement of the energies of transitions between quantized rotational states of molecules in the gas phase. The spectra of polar molecules can be measured in absorption or emission by microwave spectroscopy or by far infrared spectroscopy. The rotational spectra of non-polar molecules cannot be observed by those methods, but can be observed and measured by Raman spectroscopy. Rotational spectroscopy is sometimes referred to as pure rotational spectroscopy to distinguish it from rotational-vibrational spectroscopy where changes in rotational energy occur together with changes in vibrational energy, and also from ro-vibronic spectroscopy (or just vibronic spectroscopy) where rotational, vibrational and electronic energy changes occur simultaneously.For rotational spectroscopy, molecules are classified according to symmetry into spherical top, linear and symmetric top; analytical expressions can be derived for the rotational energy terms of these molecules. Analytical expressions can be derived for the fourth category, asymmetric top, for rotational levels up to J=3, but higher energy levels need to be determined using numerical methods. The rotational energies are derived theoretically by considering the molecules to be rigid rotors and then applying extra terms to account for centrifugal distortion, fine structure, hyperfine structure and Coriolis coupling. Fitting the spectra to the theoretical expressions gives numerical values of the angular moments of inertia from which very precise values of molecular bond lengths and angles can be derived in favorable cases. In the presence of an electrostatic field there is Stark splitting which allows molecular electric dipole moments to be determined.An important application of rotational spectroscopy is in exploration of the chemical composition of the interstellar medium using radio telescopes.