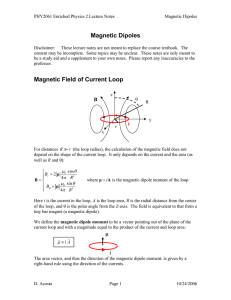
Magnetic Dipoles Magnetic Field of Current Loop i
... same curve in both directions. For example, when the external field returns to zero, the net magnetization may not be zero (and the sign will depend on whether you were raising or lowering the field). ...
... same curve in both directions. For example, when the external field returns to zero, the net magnetization may not be zero (and the sign will depend on whether you were raising or lowering the field). ...
Chapter 36 Summary – Magnetism
... can be produced by (batteries, motion of electric current). More specifically, voltage is induced in a loop of wire if there is a change in the (batteries, magnetic field in the loop). This phenomenon is called (electromagnetic waves, electromagnetic induction). When a magnet is plunged in and out o ...
... can be produced by (batteries, motion of electric current). More specifically, voltage is induced in a loop of wire if there is a change in the (batteries, magnetic field in the loop). This phenomenon is called (electromagnetic waves, electromagnetic induction). When a magnet is plunged in and out o ...
Magnetic-Instability-Induced Giant Magnetoelectric Coupling
... induced by hole/electron doping, temperature, magnetic field, pressure, and/or lattice strain. For the first time we here show that spin-state transitions can also be induced by an electric field in the case of magnetoelectric materials that display magnetic instabilities. Materials with pure ionic ...
... induced by hole/electron doping, temperature, magnetic field, pressure, and/or lattice strain. For the first time we here show that spin-state transitions can also be induced by an electric field in the case of magnetoelectric materials that display magnetic instabilities. Materials with pure ionic ...
ν =4/7 - Osaka University
... Summary of theoretical calculation Our treatment is simple and fundamental without any quasi-particle. We have found a unique electron-configuration with the minimum classical Coulomb energy. For this unique configuration there are many spin arrangements which are degenerate. ...
... Summary of theoretical calculation Our treatment is simple and fundamental without any quasi-particle. We have found a unique electron-configuration with the minimum classical Coulomb energy. For this unique configuration there are many spin arrangements which are degenerate. ...
Magnetism
... magnetize, but retain their magnetism domain alignment persists after an external field is removed the result is a permanent magnet ...
... magnetize, but retain their magnetism domain alignment persists after an external field is removed the result is a permanent magnet ...
Chapter 7 Handout 1 Atomic Orbitals Quantum Numbers: Principal
... a. Electrons fill up orbitals of lowest energy first b. Orbitals in the same sublevel are equal in energy c. Sometimes energy levels overlap 2. Pauli Exculsion Principle a. There is a max of 2 electrons in any one orbital b. These 2 electrons must have opposite spins ...
... a. Electrons fill up orbitals of lowest energy first b. Orbitals in the same sublevel are equal in energy c. Sometimes energy levels overlap 2. Pauli Exculsion Principle a. There is a max of 2 electrons in any one orbital b. These 2 electrons must have opposite spins ...
Atoms, electrons, nuclei J.J. Thomson discovered the electron (1897
... beam of Hydrogen atoms used in the experiment was split into two parts, proving the quantized nature of magnetic momentum, but based on the azimuthal and magnetic quantum numbers Hydrogen atom should have zero angular momentum in the ground state (we expect that the magnetic momentum will also be ze ...
... beam of Hydrogen atoms used in the experiment was split into two parts, proving the quantized nature of magnetic momentum, but based on the azimuthal and magnetic quantum numbers Hydrogen atom should have zero angular momentum in the ground state (we expect that the magnetic momentum will also be ze ...
ppt
... for use in turbosuperchargers and aircraft turbine engines that required high performance at elevated temperatures. The range of applications for which superalloys are used has expanded to many other areas and now includes aircraft and land-based gas turbines, rocket engines, chemical, and petroleum ...
... for use in turbosuperchargers and aircraft turbine engines that required high performance at elevated temperatures. The range of applications for which superalloys are used has expanded to many other areas and now includes aircraft and land-based gas turbines, rocket engines, chemical, and petroleum ...
Facilitator`s Guide to Magnetism Planetary Magnetic Fields
... Facilitator’s Guide to Magnetism Magnetism, along with gravity and electricity, is a universal force of nature. This force is prevalent in our everyday lives: Magnetism is a property of certain metals and is also generated by electric currents inside circuits and, on a much larger scale, within plan ...
... Facilitator’s Guide to Magnetism Magnetism, along with gravity and electricity, is a universal force of nature. This force is prevalent in our everyday lives: Magnetism is a property of certain metals and is also generated by electric currents inside circuits and, on a much larger scale, within plan ...
For a long straight wire B = ( ìo I )/ ( 2 ð r) ìo = 4 ð x 10-7
... characteristics: a) the magnetic field is either zero or has a constant value on segments of the path b) the magnetic field is either parallel or perpendicular to the path. 2. Determine the net current that penetrates the area bounded by the closed path. 3. Multiply B by the length of each segment o ...
... characteristics: a) the magnetic field is either zero or has a constant value on segments of the path b) the magnetic field is either parallel or perpendicular to the path. 2. Determine the net current that penetrates the area bounded by the closed path. 3. Multiply B by the length of each segment o ...
Measuring Metal Magnetism - Name
... which directly measure the number of magnetic flux quanta being produced by a sample as it moved through a set of detection coils. SQUID magnetometers typically operate at temperatures of 2-400K, and can give accurate magnetic data on samples with masses as small as 1 mg. However, the excellent sens ...
... which directly measure the number of magnetic flux quanta being produced by a sample as it moved through a set of detection coils. SQUID magnetometers typically operate at temperatures of 2-400K, and can give accurate magnetic data on samples with masses as small as 1 mg. However, the excellent sens ...
Physics 100 Name: Electricity Notes, Part IV: Odds, Ends, and Lenz
... the current is going into the paper or out of the paper. 5. Show the directions of the magnetic field created by the solenoids on the right. ...
... the current is going into the paper or out of the paper. 5. Show the directions of the magnetic field created by the solenoids on the right. ...
Draw it Out! Draw the Earth show: its magnetic field. Label the
... Using different colored pencils show the various paths that the electrical current can take. ...
... Using different colored pencils show the various paths that the electrical current can take. ...
Magnetic Fields and Forces
... 7. Force between two wires carrying current: There are many examples of a wire carrying current in the neighborhood of other current carrying wires and interacting through the mechanism of magnetic fields. The simplest example is two long straight wires separated by a distance. In this example we ar ...
... 7. Force between two wires carrying current: There are many examples of a wire carrying current in the neighborhood of other current carrying wires and interacting through the mechanism of magnetic fields. The simplest example is two long straight wires separated by a distance. In this example we ar ...
Chapter 2 Learning Objectives
... 1. Understand how electromagnetic radiation is characterized by its wavelength, frequency and energy and be able to convert between them. 2. Be able to explain the data observed in the photoelectric effect, including: a. The threshold frequency b. The correlation between radiant intensity and the nu ...
... 1. Understand how electromagnetic radiation is characterized by its wavelength, frequency and energy and be able to convert between them. 2. Be able to explain the data observed in the photoelectric effect, including: a. The threshold frequency b. The correlation between radiant intensity and the nu ...
PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS Tejada et al. Reply: Our suggestion
... ferritin particles. Besides that uncertainty, the dependence of the energy barrier on the magnetic field should be more complicated than for a ferromagnetic particle due to the fact that the noncompensated moment of a ferritin particle arises from the contribution of two sublattices. For the very sa ...
... ferritin particles. Besides that uncertainty, the dependence of the energy barrier on the magnetic field should be more complicated than for a ferromagnetic particle due to the fact that the noncompensated moment of a ferritin particle arises from the contribution of two sublattices. For the very sa ...
I. Characteristics of Magnets - Otterville R
... D. Magnetic Domain Magnetic Domain groups of atoms with aligned magnetic poles domain ...
... D. Magnetic Domain Magnetic Domain groups of atoms with aligned magnetic poles domain ...
Ferromagnetism

Not to be confused with Ferrimagnetism; for an overview see Magnetism.Ferromagnetism is the basic mechanism by which certain materials (such as iron) form permanent magnets, or are attracted to magnets. In physics, several different types of magnetism are distinguished. Ferromagnetism (including ferrimagnetism) is the strongest type: it is the only one that typically creates forces strong enough to be felt, and is responsible for the common phenomena of magnetism in magnets encountered in everyday life. Substances respond weakly to magnetic fields with three other types of magnetism, paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, but the forces are usually so weak that they can only be detected by sensitive instruments in a laboratory. An everyday example of ferromagnetism is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. The attraction between a magnet and ferromagnetic material is ""the quality of magnetism first apparent to the ancient world, and to us today"".Permanent magnets (materials that can be magnetized by an external magnetic field and remain magnetized after the external field is removed) are either ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic, as are other materials that are noticeably attracted to them. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic. The common ones are iron, nickel, cobalt and most of their alloys, some compounds of rare earth metals, and a few naturally-occurring minerals such as lodestone.Ferromagnetism is very important in industry and modern technology, and is the basis for many electrical and electromechanical devices such as electromagnets, electric motors, generators, transformers, and magnetic storage such as tape recorders, and hard disks.