Electromagnetic Radiation
... have 3 and 2 unpaired electrons in their electron diagrams respectively, what can be going on in the video? •Ground state diagrams do work very well for the Transition metals but not many others because of bonding, which forms pairs of electrons. (molecular orbitals vs. atomic orbitals).Eg. water, n ...
... have 3 and 2 unpaired electrons in their electron diagrams respectively, what can be going on in the video? •Ground state diagrams do work very well for the Transition metals but not many others because of bonding, which forms pairs of electrons. (molecular orbitals vs. atomic orbitals).Eg. water, n ...
Chapter 5 PPT/Notes B
... • Ground-state configuration would be an atom at its lowest energy level. • We use 3 rules to write configurations… • The Aufbau principle says electrons fill the lowest energy levels first. • Hund’s rule says to place one electron in each orbital before placing the 2nd one of opposite spin. • The P ...
... • Ground-state configuration would be an atom at its lowest energy level. • We use 3 rules to write configurations… • The Aufbau principle says electrons fill the lowest energy levels first. • Hund’s rule says to place one electron in each orbital before placing the 2nd one of opposite spin. • The P ...
Chapter 5 Worksheet 1
... 1. State Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle as it pertains to atomic theory. It is impossible to determine the exact location and momentum of a moving object at the same time. 2. Why does the observation of a very small object such as an electron cause the electron to have its motion changed? The po ...
... 1. State Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle as it pertains to atomic theory. It is impossible to determine the exact location and momentum of a moving object at the same time. 2. Why does the observation of a very small object such as an electron cause the electron to have its motion changed? The po ...
S. Mayboroda:
... The property of the localization of the eigenfunctions in rough domains or rough materials permeates acoustics, quantum physics, elasticity, to name just a few. Localization on fractal domains was used for noise abatement walls which up to date hold world efficiency record. Anderson localization of ...
... The property of the localization of the eigenfunctions in rough domains or rough materials permeates acoustics, quantum physics, elasticity, to name just a few. Localization on fractal domains was used for noise abatement walls which up to date hold world efficiency record. Anderson localization of ...
Summary/Abstract:
... Positron emission tomography (PET) is a readily used diagnostic tool in neurology, cardiology and oncology. PET’s major strength is the ability to visualize and quantify metabolic processes. The challenge to developing PET technology for imaging small laboratory animals with anatomical parody with h ...
... Positron emission tomography (PET) is a readily used diagnostic tool in neurology, cardiology and oncology. PET’s major strength is the ability to visualize and quantify metabolic processes. The challenge to developing PET technology for imaging small laboratory animals with anatomical parody with h ...
Part II - TTU Physics
... This electric field is related to the potential difference across the ends of the conductor: V = E ℓ =B ℓ v. This potential difference is maintained between the ends of the conductor as long as it continues to move through the uniform magnetic field. If the direction of the motion is reversed, the ...
... This electric field is related to the potential difference across the ends of the conductor: V = E ℓ =B ℓ v. This potential difference is maintained between the ends of the conductor as long as it continues to move through the uniform magnetic field. If the direction of the motion is reversed, the ...
Electric charge - Willmar Public Schools
... electric charge that regularly reverses its direction. Resistance is opposition to the flow of electric charges in an electric current as it travels through matter. The SI unit for resistance is the ohm. Resistance occurs because moving electrons in current bump into atoms of matter. Resistance redu ...
... electric charge that regularly reverses its direction. Resistance is opposition to the flow of electric charges in an electric current as it travels through matter. The SI unit for resistance is the ohm. Resistance occurs because moving electrons in current bump into atoms of matter. Resistance redu ...
Lecture 19: The Solar Magnetic Field
... up, just like a tether ball. And just like a tether ball, the Sun’s magnetic field bounces back! ...
... up, just like a tether ball. And just like a tether ball, the Sun’s magnetic field bounces back! ...
The Quantum Spin Hall Effect
... • Graphene – spin-orbit coupling only about 10-3meV. Not realizable in experiments. (Kane and Mele, 2005, Yao et al, 2006, MacDonald group 2006) • Quantum spin Hall with Landau levels – spin-orbit coupling in GaAs too small. (Bernevig and Zhang, PRL, 2006) • QSH ...
... • Graphene – spin-orbit coupling only about 10-3meV. Not realizable in experiments. (Kane and Mele, 2005, Yao et al, 2006, MacDonald group 2006) • Quantum spin Hall with Landau levels – spin-orbit coupling in GaAs too small. (Bernevig and Zhang, PRL, 2006) • QSH ...
Lecture 8a - Magnetism
... 27-3 Force on an Electric Current in a Magnetic Field; Definition of B Example 27-2: Measuring a magnetic field. A rectangular loop of wire hangs vertically as shown. A magnetic field B is directed horizontally, perpendicular to the wire, and points out of the page at all points. The magnetic field ...
... 27-3 Force on an Electric Current in a Magnetic Field; Definition of B Example 27-2: Measuring a magnetic field. A rectangular loop of wire hangs vertically as shown. A magnetic field B is directed horizontally, perpendicular to the wire, and points out of the page at all points. The magnetic field ...
Electric Current and Magnetism - Mr-Durands
... • One end of the electromagnet is a north pole and the other end is a south pole. • If placed in a magnetic field, an electromagnet will align itself along the magnetic field lines, just as a compass needle will. • An electromagnet also will attract magnetic materials and be attracted or repelled by ...
... • One end of the electromagnet is a north pole and the other end is a south pole. • If placed in a magnetic field, an electromagnet will align itself along the magnetic field lines, just as a compass needle will. • An electromagnet also will attract magnetic materials and be attracted or repelled by ...
Unit 2: Atoms and their Electrons
... larger than sodium because not only does the number of protons increase but so do the number of shielding electrons as well as the number of layers of shielding electrons, increasing the distance the outer valence electrons are from the nucleus thereby making the atom larger than sodium. In this lis ...
... larger than sodium because not only does the number of protons increase but so do the number of shielding electrons as well as the number of layers of shielding electrons, increasing the distance the outer valence electrons are from the nucleus thereby making the atom larger than sodium. In this lis ...
File
... According to the quantum theory of an atom, in an orbital a. an electron's position cannot be known precisely. b. an electron has no energy. c. electrons cannot be found. d. electrons travel around the nucleus on paths of specific radii. ...
... According to the quantum theory of an atom, in an orbital a. an electron's position cannot be known precisely. b. an electron has no energy. c. electrons cannot be found. d. electrons travel around the nucleus on paths of specific radii. ...
The Magnetic Field
... • When the ignition switch is turned on (when the key is turned to start the car), the small electric current forces the starter solenoid to close a pair of heavy contacts, thus relaying the large electric current to the starter motor. • If a starter solenoid receives insufficient power from the bat ...
... • When the ignition switch is turned on (when the key is turned to start the car), the small electric current forces the starter solenoid to close a pair of heavy contacts, thus relaying the large electric current to the starter motor. • If a starter solenoid receives insufficient power from the bat ...
Particle motion (powerpoint)
... For 10 keV and B = 5T. The Larmor radius of the Deuterium ions is around 4 mm for the electrons around 0.07 mm Note that the alpha particles have an energy of 3.5 MeV and consequently a Larmor radius of 5.4 cm Typical values of the cyclotron frequency are 80 MHz for Hydrogen and 130 GHz for the elec ...
... For 10 keV and B = 5T. The Larmor radius of the Deuterium ions is around 4 mm for the electrons around 0.07 mm Note that the alpha particles have an energy of 3.5 MeV and consequently a Larmor radius of 5.4 cm Typical values of the cyclotron frequency are 80 MHz for Hydrogen and 130 GHz for the elec ...
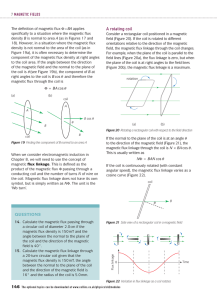
A rotating coil - Collins.co.uk.
... A rotating coil Consider a rectangular coil positioned in a magnetic field (Figure 20). If the coil is rotated to different orientations relative to the direction of the magnetic field, the magnetic flux linkage through the coil changes. For example, when the plane of the coil is parallel to the fie ...
... A rotating coil Consider a rectangular coil positioned in a magnetic field (Figure 20). If the coil is rotated to different orientations relative to the direction of the magnetic field, the magnetic flux linkage through the coil changes. For example, when the plane of the coil is parallel to the fie ...
Electron Configurations
... you may want some extra information on the subject. Most of this below is “borrowed” from Sparknotes.com. The first and most important rule to remember when attempting to determine how electrons will be arranged in the atom is Hund’s rule, which states that the most stable arrangement of electrons i ...
... you may want some extra information on the subject. Most of this below is “borrowed” from Sparknotes.com. The first and most important rule to remember when attempting to determine how electrons will be arranged in the atom is Hund’s rule, which states that the most stable arrangement of electrons i ...
Paper
... KCuF3, La2CuO4 there exists two-ion anisotropy which confines the spins in the CuX2 (X = O, F) besides a small canting from a plane (weak ferromagnetism) for KCuF3 and La2CuO4. Since the classical work by Kanamori [2] on the anisotropic exchange, in a rather large number of publications it have poin ...
... KCuF3, La2CuO4 there exists two-ion anisotropy which confines the spins in the CuX2 (X = O, F) besides a small canting from a plane (weak ferromagnetism) for KCuF3 and La2CuO4. Since the classical work by Kanamori [2] on the anisotropic exchange, in a rather large number of publications it have poin ...
Ferromagnetism

Not to be confused with Ferrimagnetism; for an overview see Magnetism.Ferromagnetism is the basic mechanism by which certain materials (such as iron) form permanent magnets, or are attracted to magnets. In physics, several different types of magnetism are distinguished. Ferromagnetism (including ferrimagnetism) is the strongest type: it is the only one that typically creates forces strong enough to be felt, and is responsible for the common phenomena of magnetism in magnets encountered in everyday life. Substances respond weakly to magnetic fields with three other types of magnetism, paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, but the forces are usually so weak that they can only be detected by sensitive instruments in a laboratory. An everyday example of ferromagnetism is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. The attraction between a magnet and ferromagnetic material is ""the quality of magnetism first apparent to the ancient world, and to us today"".Permanent magnets (materials that can be magnetized by an external magnetic field and remain magnetized after the external field is removed) are either ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic, as are other materials that are noticeably attracted to them. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic. The common ones are iron, nickel, cobalt and most of their alloys, some compounds of rare earth metals, and a few naturally-occurring minerals such as lodestone.Ferromagnetism is very important in industry and modern technology, and is the basis for many electrical and electromechanical devices such as electromagnets, electric motors, generators, transformers, and magnetic storage such as tape recorders, and hard disks.