Robot Morality and Review of classical logic.
... Analytic philosophy (like proving God’ Existence, free will, the problem of evil, etc) Many other… At this point I should ask all students to give another examples of similar problems that they want to solve ...
... Analytic philosophy (like proving God’ Existence, free will, the problem of evil, etc) Many other… At this point I should ask all students to give another examples of similar problems that they want to solve ...
On Elkan`s theorems: Clarifying their meaning
... omitted from the first version of Elkan’s theorem. As to the rest of the assumptions, both t~A ∧ B! ⫽ min$t~A!, t~B!% and t~¬A! ⫽ 1 ⫺ t~A! are quite reasonable and, in fact, are often used in applications of fuzzy logic. Let us now concentrate on the last assumption, that is, on t~A! ⫽ t~B! if A and ...
... omitted from the first version of Elkan’s theorem. As to the rest of the assumptions, both t~A ∧ B! ⫽ min$t~A!, t~B!% and t~¬A! ⫽ 1 ⫺ t~A! are quite reasonable and, in fact, are often used in applications of fuzzy logic. Let us now concentrate on the last assumption, that is, on t~A! ⫽ t~B! if A and ...
Section 2.4: Arguments with Quantified Statements
... y = 2m2 is an integer and n = 2 ∗ y, it follows that n2 is an even integer. Note that there we actually excluded a number of steps in this argument (because they were similar to the ones we already stated coming from the elementary rules of arithmetic). In order to make a completely formal argument, ...
... y = 2m2 is an integer and n = 2 ∗ y, it follows that n2 is an even integer. Note that there we actually excluded a number of steps in this argument (because they were similar to the ones we already stated coming from the elementary rules of arithmetic). In order to make a completely formal argument, ...
ppt - Dave Reed
... function/operator name & arguments are evaluated in unspecified order note: if argument is a functional expression, evaluate recursively the resulting function is applied to the resulting values (car '(a b c)) ...
... function/operator name & arguments are evaluated in unspecified order note: if argument is a functional expression, evaluate recursively the resulting function is applied to the resulting values (car '(a b c)) ...
ppt - Dave Reed
... function/operator name & arguments are evaluated in unspecified order note: if argument is a functional expression, evaluate recursively the resulting function is applied to the resulting values (car '(a b c)) ...
... function/operator name & arguments are evaluated in unspecified order note: if argument is a functional expression, evaluate recursively the resulting function is applied to the resulting values (car '(a b c)) ...
A logical basis for quantum evolution and entanglement
... evolving, two particles which had been unentangled can become entangled due to an event that is nonlocal to either. The simple linear logic calculus had no effective way to encode this situation. A solution was proposed, using something the authors called entanglement update, but it was felt at the ...
... evolving, two particles which had been unentangled can become entangled due to an event that is nonlocal to either. The simple linear logic calculus had no effective way to encode this situation. A solution was proposed, using something the authors called entanglement update, but it was felt at the ...
Scheme: More function examples, higher
... • Write a function called fixFirst that takes a binary function f and a parameter p, and returns a function that is the same as f except the first parameter is fixed to be p. Examples: > ((fixFirst cons 'z) '(a b c)) (z a b c) > ((fixFirst append '(1 2)) '(3 4)) ...
... • Write a function called fixFirst that takes a binary function f and a parameter p, and returns a function that is the same as f except the first parameter is fixed to be p. Examples: > ((fixFirst cons 'z) '(a b c)) (z a b c) > ((fixFirst append '(1 2)) '(3 4)) ...
Logic and Resolution - Institute for Computing and Information
... Logic and Resolution One of the earliest formalisms for the representation of knowledge is logic. The formalism is characterized by a well-defined syntax and semantics, and provides a number of inference rules to manipulate logical formulas on the basis of their form in order to derive new knowledge ...
... Logic and Resolution One of the earliest formalisms for the representation of knowledge is logic. The formalism is characterized by a well-defined syntax and semantics, and provides a number of inference rules to manipulate logical formulas on the basis of their form in order to derive new knowledge ...
Propositional Logic
... • Somewhat mysterious to non-technical users • Algorithmically simple but more complex than perfect induction. • Not considered appropriate for general problem solving. ...
... • Somewhat mysterious to non-technical users • Algorithmically simple but more complex than perfect induction. • Not considered appropriate for general problem solving. ...
doc - Brown CS
... G(x,y), the relation x = y, or the relation P(…), where “…” represents some fixed number of arguments. Also we now only require that only one or zero non-negated P(…)’s be in each clause, negations of the other atomic expression are unrestricted. Clearly our sentence which represented HAMILTONIAN P ...
... G(x,y), the relation x = y, or the relation P(…), where “…” represents some fixed number of arguments. Also we now only require that only one or zero non-negated P(…)’s be in each clause, negations of the other atomic expression are unrestricted. Clearly our sentence which represented HAMILTONIAN P ...
predicate
... • Some people have more than one brother • x y1 y2 ( B(y1,x) B(y2,x) (y1 = y2) ...
... • Some people have more than one brother • x y1 y2 ( B(y1,x) B(y2,x) (y1 = y2) ...
CSC 533: Programming Languages Spring 2015
... LISP LISP is very simple and orthogonal § only 2 kinds of data objects 1. atoms (identifiers, strings, numbers, …) 2. lists (of atoms and sublists) unlike arrays, lists do not have to store items of same type/size do not have to be stored contiguously do not have to provide random access § al ...
... LISP LISP is very simple and orthogonal § only 2 kinds of data objects 1. atoms (identifiers, strings, numbers, …) 2. lists (of atoms and sublists) unlike arrays, lists do not have to store items of same type/size do not have to be stored contiguously do not have to provide random access § al ...
ppt - Dave Reed
... function/operator name & arguments are evaluated in unspecified order note: if argument is a functional expression, evaluate recursively the resulting function is applied to the resulting values (car '(a b c)) ...
... function/operator name & arguments are evaluated in unspecified order note: if argument is a functional expression, evaluate recursively the resulting function is applied to the resulting values (car '(a b c)) ...
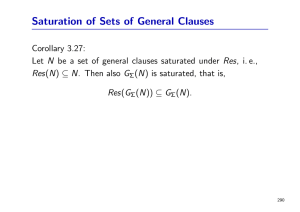
Saturation of Sets of General Clauses
... choose a fixed but arbitrary clause D ∈ N with C ∈ GΣ (D) and define sel′ (C ) to be those occurrences of literals that are ground instances of the occurrences selected by sel in D. Then proceed as in the proof of Cor. 3.27 using the above lifting lemma. ...
... choose a fixed but arbitrary clause D ∈ N with C ∈ GΣ (D) and define sel′ (C ) to be those occurrences of literals that are ground instances of the occurrences selected by sel in D. Then proceed as in the proof of Cor. 3.27 using the above lifting lemma. ...
Haskell Summary Functions • A function takes 1 or more parameter
... A binary operator can be converted into a curried function by enclosing the name of the operator in Useful functions can sometimes be constructed in a simple way using parentheses. For example: sections. Examples: 1+2 can be written as (+) 1 2 (1+) - successor function This convention also allows on ...
... A binary operator can be converted into a curried function by enclosing the name of the operator in Useful functions can sometimes be constructed in a simple way using parentheses. For example: sections. Examples: 1+2 can be written as (+) 1 2 (1+) - successor function This convention also allows on ...
Curry`s paradox, Lukasiewicz, and Field
... form ϕ → ϕ). He then notes that the particular theory which it is his concern to show inconsistent has two different methods of constructing, from any b, a provable identity of the kind u = u → b; one is Russell-like (in effect gets trouble from naive comprehension), one is Epimenides-like (gets tro ...
... form ϕ → ϕ). He then notes that the particular theory which it is his concern to show inconsistent has two different methods of constructing, from any b, a provable identity of the kind u = u → b; one is Russell-like (in effect gets trouble from naive comprehension), one is Epimenides-like (gets tro ...
On Equivalent Transformations of Infinitary Formulas under the
... to check that the equivalence F ↔ G is provable intuitionistically. Some extensions of intuitionistic propositional logic, including the logic of here-and-there, can be used as well. In this note we extend these results to deductive systems of infinitary propositional logic. This goal is closely rel ...
... to check that the equivalence F ↔ G is provable intuitionistically. Some extensions of intuitionistic propositional logic, including the logic of here-and-there, can be used as well. In this note we extend these results to deductive systems of infinitary propositional logic. This goal is closely rel ...
Propositional Logic: Normal Forms
... assign true to all marked atoms, and false to the others. If φ is not true under ν, it means that there exists a conjunct P1 ∧ . . . ∧ Pki → P 0 of φ that is false. By the semantics, this can only mean that P1 ∧ . . . ∧ Pki is true but P 0 is false. However, by the definition of ν, all Pi s are mark ...
... assign true to all marked atoms, and false to the others. If φ is not true under ν, it means that there exists a conjunct P1 ∧ . . . ∧ Pki → P 0 of φ that is false. By the semantics, this can only mean that P1 ∧ . . . ∧ Pki is true but P 0 is false. However, by the definition of ν, all Pi s are mark ...
Reasoning about Programs by exploiting the environment
... would then be incomplete for this new environment. Weakening the assumptions could add feasible behaviors; the logic for the original environment would then become unsound. For example, any of the programming logics for shared-memory concurrency (e.g. [0G76]) could be used to prove that program of F ...
... would then be incomplete for this new environment. Weakening the assumptions could add feasible behaviors; the logic for the original environment would then become unsound. For example, any of the programming logics for shared-memory concurrency (e.g. [0G76]) could be used to prove that program of F ...
Available on-line - Gert
... The new system does not have the theorem S A → S(A & B), so it seems to give a more adequate account of safety than Anderson’s system did, at least in the particular examples that we have discussed. But we cannot conclude from this that it is generally more adequate. The basic problem is that safety ...
... The new system does not have the theorem S A → S(A & B), so it seems to give a more adequate account of safety than Anderson’s system did, at least in the particular examples that we have discussed. But we cannot conclude from this that it is generally more adequate. The basic problem is that safety ...
Chapter 7: Functional Programming Languages
... defined function symbol; in the functional language, it can be any expression (for instance, a lambda abstract or an application). Thus the evaluation of f is not simply a look-up in the function table. But we can just replace the look-up by a step of evaluating the expression f . This evaluation re ...
... defined function symbol; in the functional language, it can be any expression (for instance, a lambda abstract or an application). Thus the evaluation of f is not simply a look-up in the function table. But we can just replace the look-up by a step of evaluating the expression f . This evaluation re ...
Haskell - CIS @ UPenn
... of which makes some changes in the state of the program Instead you evaluate an expression, which can call functions ...
... of which makes some changes in the state of the program Instead you evaluate an expression, which can call functions ...
full text (.pdf)
... DL does not distinguish between these two categories of assertions. The two are freely mixed, and both are treated classically. For this reason, the resulting system is unnecessarily complex for its purposes. The rich-test version of DL, in which one can convert an arbitrary correctness assertion to ...
... DL does not distinguish between these two categories of assertions. The two are freely mixed, and both are treated classically. For this reason, the resulting system is unnecessarily complex for its purposes. The rich-test version of DL, in which one can convert an arbitrary correctness assertion to ...
The gist of side effects in pure functional languages
... whether they are dynamically type-checked or statically type-checked; whether they are pure or impure; and finally whether they are strict or non-strict. Pure functional languages lack assignment constructs, an expression produces the same value independently of when it is evaluated—a property calle ...
... whether they are dynamically type-checked or statically type-checked; whether they are pure or impure; and finally whether they are strict or non-strict. Pure functional languages lack assignment constructs, an expression produces the same value independently of when it is evaluated—a property calle ...