Important Data Since the Midterm Exam (Rel
... called the Hinayana (Deficient or Little Vehicle). The ideal of Theravada piety, the enlightened arhat, is thus judged imperfect because his enlightenment is selforiented only. Kumarajiva : (344-413) half-Indian missionary who taught Nagarjuna’s Madhyamaka doctrine in north China, translating three ...
... called the Hinayana (Deficient or Little Vehicle). The ideal of Theravada piety, the enlightened arhat, is thus judged imperfect because his enlightenment is selforiented only. Kumarajiva : (344-413) half-Indian missionary who taught Nagarjuna’s Madhyamaka doctrine in north China, translating three ...
Buddhism - worldreliefdurham.org
... collections of quotes, histories, grammars, etc. This categorization is not universal, however: there will always be texts that cross boundaries, or that belong in more than one category. Moreover, Zen Buddhism rejects scriptures altogether as an ineffective path to ...
... collections of quotes, histories, grammars, etc. This categorization is not universal, however: there will always be texts that cross boundaries, or that belong in more than one category. Moreover, Zen Buddhism rejects scriptures altogether as an ineffective path to ...
Scouting in the Buddhist Community
... basic tenets of Buddhism as they relate to the activities of daily life. The program stresses the importance of both harmonious relationships and the universal brotherhood of all living beings. ...
... basic tenets of Buddhism as they relate to the activities of daily life. The program stresses the importance of both harmonious relationships and the universal brotherhood of all living beings. ...
Buddhism - Spartan Geography
... rebirth of a living being after death into a new body that is either a human, animal or a supernatural being. ...
... rebirth of a living being after death into a new body that is either a human, animal or a supernatural being. ...
Core Beliefs Buddhism
... Karma is not an external force, not a system of punishment or reward dealt out by a god. The concept is more accurately understood as a natural law similar to gravity. Buddhists believe that people are in control of their ultimate fates. The problem is that most people are ignorant of this, which ca ...
... Karma is not an external force, not a system of punishment or reward dealt out by a god. The concept is more accurately understood as a natural law similar to gravity. Buddhists believe that people are in control of their ultimate fates. The problem is that most people are ignorant of this, which ca ...
Buddhist identities
... Buddhism was first introduced to Australia in the mid to late 1800s with the arrival of Chinese, Sri Lankan and Japanese gold miners, pearl divers and sugar plantation workers. A small number of Buddhists from the Anglo-European community settled in Australia during the 1920s. The first Buddhist monas ...
... Buddhism was first introduced to Australia in the mid to late 1800s with the arrival of Chinese, Sri Lankan and Japanese gold miners, pearl divers and sugar plantation workers. A small number of Buddhists from the Anglo-European community settled in Australia during the 1920s. The first Buddhist monas ...
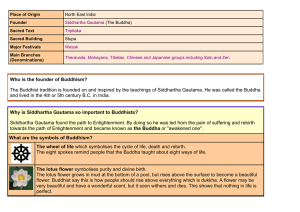
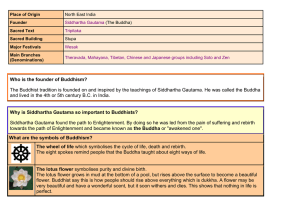
Who is the founder of Buddhism? The Buddhist tradition is founded
... flowers, candles, incense and pure water at a shrine. People thank Buddha for his teachings. When Buddhist worship alone they usually meditate and read from the Buddhist holy books. Every month most Buddhists have special religious days. These are often days when there is a full moon. Many Buddhists ...
... flowers, candles, incense and pure water at a shrine. People thank Buddha for his teachings. When Buddhist worship alone they usually meditate and read from the Buddhist holy books. Every month most Buddhists have special religious days. These are often days when there is a full moon. Many Buddhists ...
The Buddhist tradition is founded on and inspired by the teachi
... flowers, candles, incense and pure water at a shrine. People thank Buddha for his teachings. When Buddhist worship alone they usually meditate and read from the Buddhist holy books. Every month most Buddhists have special religious days. These are often days when there is a full moon. Many Buddhists ...
... flowers, candles, incense and pure water at a shrine. People thank Buddha for his teachings. When Buddhist worship alone they usually meditate and read from the Buddhist holy books. Every month most Buddhists have special religious days. These are often days when there is a full moon. Many Buddhists ...
Buddhism
... • Stupas are Buddhist monuments in India, and are generally domes that cover relics of Buddha and his followers. • The Great Stupa of Sanchi is the oldest and largest Stupa, and also one of the best preserved. It is a pilgrimage site. • The Stupa is decorated on the outside with four gates, each ado ...
... • Stupas are Buddhist monuments in India, and are generally domes that cover relics of Buddha and his followers. • The Great Stupa of Sanchi is the oldest and largest Stupa, and also one of the best preserved. It is a pilgrimage site. • The Stupa is decorated on the outside with four gates, each ado ...
The picture above shows the Eightfold Path as a wheel. This is to
... Please note that the word ‘right’ in this Buddhist context does not mean the opposite of wrong or ‘bad. ‘Right’ means ‘that which leads to freedom from suffering ...
... Please note that the word ‘right’ in this Buddhist context does not mean the opposite of wrong or ‘bad. ‘Right’ means ‘that which leads to freedom from suffering ...
Steven Collins. Nirvana and Other Buddhist Felicities: Utopias of the
... In defining the concept of nirvana, Collins explicitly disavows the quest for the Òoriginal Buddhism,Ó Òwhat the Buddha taught,Ó and Òwhat Buddhism Ôteaches,Õ essentially and ahistoricallyÓ (p. 418). At the outset he spells out what Buddhist systematic thought says about the concept of nirvana: It i ...
... In defining the concept of nirvana, Collins explicitly disavows the quest for the Òoriginal Buddhism,Ó Òwhat the Buddha taught,Ó and Òwhat Buddhism Ôteaches,Õ essentially and ahistoricallyÓ (p. 418). At the outset he spells out what Buddhist systematic thought says about the concept of nirvana: It i ...
Buddhism Quiz
... 15. Each of these is part of Buddhism except a. Five Precepts c. Four Noble Truths b. Eight Fold Path d. Four Jewels 16. Each of these is a type of Buddhism except a. Pure Light c. Mahayana b. Theravada d. Zen 17. Which of these was not one of the four sights that the founder saw a. dead man c. sick ...
... 15. Each of these is part of Buddhism except a. Five Precepts c. Four Noble Truths b. Eight Fold Path d. Four Jewels 16. Each of these is a type of Buddhism except a. Pure Light c. Mahayana b. Theravada d. Zen 17. Which of these was not one of the four sights that the founder saw a. dead man c. sick ...
Buddhism Quiz
... 15. Each of these is part of Buddhism except a. Five Precepts c. Four Noble Truths b. Eight Fold Path d. Four Jewels 16. Each of these is a type of Buddhism except a. Pure Light c. Mahayana b. Theravada d. Zen 17. Which of these was not one of the four sights that the founder saw a. dead man c. sick ...
... 15. Each of these is part of Buddhism except a. Five Precepts c. Four Noble Truths b. Eight Fold Path d. Four Jewels 16. Each of these is a type of Buddhism except a. Pure Light c. Mahayana b. Theravada d. Zen 17. Which of these was not one of the four sights that the founder saw a. dead man c. sick ...
10 Buddhism Notes PowerPoint
... the Buddha Three jewels of Buddhism: Buddha, the teacher Dharma, the teachings Sangha, the community ...
... the Buddha Three jewels of Buddhism: Buddha, the teacher Dharma, the teachings Sangha, the community ...
Chapter 9 Lesson 2 Religions of Ancient India BLANKS
... 1. Another religion also came to India at this time called Jainism. The main teacher of Jainism was named Mahavira. 2. Mahavira’s title was “the Jina,” or “the Conqueror” and his followers are called Jains. 3. Much of Jainism is like Buddhism. 4. _________ Jainism and Buddhism taught that people sho ...
... 1. Another religion also came to India at this time called Jainism. The main teacher of Jainism was named Mahavira. 2. Mahavira’s title was “the Jina,” or “the Conqueror” and his followers are called Jains. 3. Much of Jainism is like Buddhism. 4. _________ Jainism and Buddhism taught that people sho ...
Making Sense of Ch`an - 羅致廉醫生| DR. Robert CL Law
... •Reign of Indian Emperor Asoka (272231) who converted and established the Buddha's Dharma on a national level for the first time in Buddhist history. •He ruled from Burma to Iran and from Nepal to South India • In the 3rd Century B.C. during the time of Emperor Asoka, the Third Council was held at P ...
... •Reign of Indian Emperor Asoka (272231) who converted and established the Buddha's Dharma on a national level for the first time in Buddhist history. •He ruled from Burma to Iran and from Nepal to South India • In the 3rd Century B.C. during the time of Emperor Asoka, the Third Council was held at P ...
The Buddhist Core Values and Perspectives for Protection
... In reincarnation, the individual may recur repeatedly. In rebirth, a person does not necessarily return to Earth as the same entity ever again. He compares it to a leaf growing on a tree. When the withering leaf falls off, a new leaf will eventually replace it. It is similar to the old leaf, but it ...
... In reincarnation, the individual may recur repeatedly. In rebirth, a person does not necessarily return to Earth as the same entity ever again. He compares it to a leaf growing on a tree. When the withering leaf falls off, a new leaf will eventually replace it. It is similar to the old leaf, but it ...
Introductory Notes
... how to achieve gradual self-improvement in order to end the cycle of rebirth and attain Nirvana. Eightfold Path2: the “middle” path to Nirvana that avoids the extremes of selfindulgence (hedonism) and self-mortification (asceticism) 1. Right View: to see and understand things as they really are, and ...
... how to achieve gradual self-improvement in order to end the cycle of rebirth and attain Nirvana. Eightfold Path2: the “middle” path to Nirvana that avoids the extremes of selfindulgence (hedonism) and self-mortification (asceticism) 1. Right View: to see and understand things as they really are, and ...
An Outline of Buddhist Traditions
... confusion – to think of others and their needs and to dedicate ourselves to them. At other times, even the word ‘others’ we will not be able to hear – the thought of others might seem too remote, or that it is just a concept, whereas our own difficulty is what is right in front of us… It’s my feelin ...
... confusion – to think of others and their needs and to dedicate ourselves to them. At other times, even the word ‘others’ we will not be able to hear – the thought of others might seem too remote, or that it is just a concept, whereas our own difficulty is what is right in front of us… It’s my feelin ...
Buddhism and psychiatry: confluence and conflict
... fastest growing religion; a lot of this growth is in new converts to Buddhism among previously nonBuddhist Australians. Increasingly, people working in clinical practice may encounter Buddhists, including Buddhists of Australian origin. As with any of the many cultural settings of practice, it may b ...
... fastest growing religion; a lot of this growth is in new converts to Buddhism among previously nonBuddhist Australians. Increasingly, people working in clinical practice may encounter Buddhists, including Buddhists of Australian origin. As with any of the many cultural settings of practice, it may b ...
7286 A lacquer and gilt-wood figure of Amida Nyorai seated in jō
... zenjō (ecstatic thought) for it is the gesture which indicates the suppression of all spiritual disquiet in order to arrive finally at the complete concentration on the truth. The position of the hands in the mudra of concentration derives, in accordance with the tradition, from the attitude which ...
... zenjō (ecstatic thought) for it is the gesture which indicates the suppression of all spiritual disquiet in order to arrive finally at the complete concentration on the truth. The position of the hands in the mudra of concentration derives, in accordance with the tradition, from the attitude which ...
H.W. Schumann, The Historical Buddha, The Times, Life and
... 'The title The Historical Buddha' - writes the author in his Preface, p. xi 'indicates both the subject of the present work and the limits of its scope. It excludes any treatment of the non-historical Buddhas of the past and the future who are frequently mentioned in Buddhist scriptures; it also exc ...
... 'The title The Historical Buddha' - writes the author in his Preface, p. xi 'indicates both the subject of the present work and the limits of its scope. It excludes any treatment of the non-historical Buddhas of the past and the future who are frequently mentioned in Buddhist scriptures; it also exc ...
Powerpoint - John Provost, PhD
... any other being that can feel hurt, including animals; I avoid stealing and sexual conduct that would bring hurt. Unwholesome actions lead to unsound states of mind, while wholesome actions lead to sound states of mind. ...
... any other being that can feel hurt, including animals; I avoid stealing and sexual conduct that would bring hurt. Unwholesome actions lead to unsound states of mind, while wholesome actions lead to sound states of mind. ...