World Buddhist Directory (Philippines)
... Humanistic Buddhism (Chinese; Pinyin: Rénjiān Fójiào) is a popular modern philosophy practiced mainly in Chinese Mahayana Buddhism. It is the integration of people\'s spiritual practice into all aspects of their daily lives. Buddhist monastics such as Venerable Masters Yin Shun and Hsing Yun pioneer ...
... Humanistic Buddhism (Chinese; Pinyin: Rénjiān Fójiào) is a popular modern philosophy practiced mainly in Chinese Mahayana Buddhism. It is the integration of people\'s spiritual practice into all aspects of their daily lives. Buddhist monastics such as Venerable Masters Yin Shun and Hsing Yun pioneer ...
I live by faith: the religions described
... Buddhism began historically in the sixth centuryBC, as (in part) a protest against a prevailing tendency in Indian religion at that time to rely on sacrifices and rituals to ensure one’s successful progress through life. The term ‘Buddha’ means ‘Enlightened One’. So the main point of departure for B ...
... Buddhism began historically in the sixth centuryBC, as (in part) a protest against a prevailing tendency in Indian religion at that time to rely on sacrifices and rituals to ensure one’s successful progress through life. The term ‘Buddha’ means ‘Enlightened One’. So the main point of departure for B ...
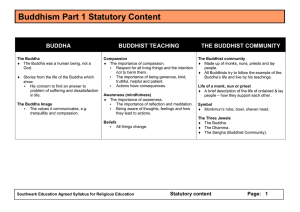
The Buddha - Southwark Schools
... The Buddha teaches about only two things – suffering and the ending of suffering The Five Moral Precepts Important in forming attitudes of mind and as guidance for living. Buddhists should refrain from: Harming and killing living beings; Sexual misconduct; Taking drugs or drink that impair ...
... The Buddha teaches about only two things – suffering and the ending of suffering The Five Moral Precepts Important in forming attitudes of mind and as guidance for living. Buddhists should refrain from: Harming and killing living beings; Sexual misconduct; Taking drugs or drink that impair ...
World Religion-Buddhism - Brookland Baptist Church
... Right Effort: guard against sensual thoughts. This concept aims at preventing unwholesome states that disrupt meditation. ...
... Right Effort: guard against sensual thoughts. This concept aims at preventing unwholesome states that disrupt meditation. ...
How did Buddhism start? What do they believe? How to share to a
... decrepit old man, a corpse, a diseased man and a beggar. He then left home for years or months, stayed in caves, etc, mutilating himself in search for the answer for suffering. Finally he believed he found enlightenment one day while meditating under a tree, then he returned to his home and began to ...
... decrepit old man, a corpse, a diseased man and a beggar. He then left home for years or months, stayed in caves, etc, mutilating himself in search for the answer for suffering. Finally he believed he found enlightenment one day while meditating under a tree, then he returned to his home and began to ...
buddhism - A World of Religions
... wheels that are pulled instead of carried. One of them is always a huge white elephant bearing a small image of Buddha. The small statue of Buddha is found inside. The children come up to the statue and bow and pour sweet tea (hydrangea leaf tea) on the head of the infant. Some believe that it raine ...
... wheels that are pulled instead of carried. One of them is always a huge white elephant bearing a small image of Buddha. The small statue of Buddha is found inside. The children come up to the statue and bow and pour sweet tea (hydrangea leaf tea) on the head of the infant. Some believe that it raine ...
Buddhism
... reformulate this Path as six ‘perfections’ (or paramitas). Though the paramitas encompass what is included under the Eightfold Path, the Mahayana Path is explicitly for the benefit of all beings trapped in samsara, rather than primarily for the individual practitioner (Asian Philosophies, pp.141-42) ...
... reformulate this Path as six ‘perfections’ (or paramitas). Though the paramitas encompass what is included under the Eightfold Path, the Mahayana Path is explicitly for the benefit of all beings trapped in samsara, rather than primarily for the individual practitioner (Asian Philosophies, pp.141-42) ...
Buddhism Projected As One of the Major Religions Of The World
... Theravada Buddhism is the more conservative of the two major divisions within this religion. As such, it believes itself to be closer to the original teachings of the Buddha. According to Theravada Buddhism, people must achieve enlightenment by themselves without reliance on the Gods or any other fo ...
... Theravada Buddhism is the more conservative of the two major divisions within this religion. As such, it believes itself to be closer to the original teachings of the Buddha. According to Theravada Buddhism, people must achieve enlightenment by themselves without reliance on the Gods or any other fo ...
Buddhism – Science and Medicine
... their thinking, their feeling – basically for everything. It is something that is guiding our lives. Different cultures pose different frameworks. Highly developed cultures are complex, complicated and manifold frameworks. Thus it is very difficult to enter and also to get a glimpse beyond cultures. ...
... their thinking, their feeling – basically for everything. It is something that is guiding our lives. Different cultures pose different frameworks. Highly developed cultures are complex, complicated and manifold frameworks. Thus it is very difficult to enter and also to get a glimpse beyond cultures. ...
Ven. Dr. M. Punnaji Nayaka Maha Thera
... 1. A unique and original interpretation of the Paticca samuppada, that explains the arising of dukkha at every moment in our lives as opposed to the traditional explanation which spans three-lives. 2. The path to Nibbana, through the gradual evolution of the Noble Eight-fold Path, for which he uses ...
... 1. A unique and original interpretation of the Paticca samuppada, that explains the arising of dukkha at every moment in our lives as opposed to the traditional explanation which spans three-lives. 2. The path to Nibbana, through the gradual evolution of the Noble Eight-fold Path, for which he uses ...
Gautama The Buddha, The Enlightened One
... The second part, the "Discourses," are the most important in Buddhism. These are discourses by the Buddha and contain the whole of Buddhist philosophy and morality. . Therevada Buddhism holds that Buddha was a historical person who, on his death, ceased to exist. There were, however, strong tendenci ...
... The second part, the "Discourses," are the most important in Buddhism. These are discourses by the Buddha and contain the whole of Buddhist philosophy and morality. . Therevada Buddhism holds that Buddha was a historical person who, on his death, ceased to exist. There were, however, strong tendenci ...
Divine Revelation in Pali Buddhism (Peter Mansfield)
... considers the distinctions between the ariyasavaka and the puthujjana. Masefield has collected a number of passages which suggest that the puthujjana was indeed considered as apart from the Buddhist path (pfihak; see the PTS dictionary, s.v. puthujjana, which says this meaning of separateness "is no ...
... considers the distinctions between the ariyasavaka and the puthujjana. Masefield has collected a number of passages which suggest that the puthujjana was indeed considered as apart from the Buddhist path (pfihak; see the PTS dictionary, s.v. puthujjana, which says this meaning of separateness "is no ...
Cummiskey Chapter IV Buddhist Ethics and Virtue Ethics "I believe
... The root of suffering can be defined as a craving or clinging; the endless seeking for fresh experiences; the thirst for sensual pleasure, for existence, even for nonexistence. When desires are satisfied new desires immediately arise from them and simply replace them, leaving one no more satisfied o ...
... The root of suffering can be defined as a craving or clinging; the endless seeking for fresh experiences; the thirst for sensual pleasure, for existence, even for nonexistence. When desires are satisfied new desires immediately arise from them and simply replace them, leaving one no more satisfied o ...
Pure Land Buddhism
... With the rise of the Mahāyāna came the idea that buddhas are at present teaching in other parts of the universe in their own special ‘buddha fields’ or ‘pure lands’ where the conditions for the practice of the Dharma are extremely favourable. With this came the aspiration to be reborn in these pure ...
... With the rise of the Mahāyāna came the idea that buddhas are at present teaching in other parts of the universe in their own special ‘buddha fields’ or ‘pure lands’ where the conditions for the practice of the Dharma are extremely favourable. With this came the aspiration to be reborn in these pure ...
Buddhism Impact On Korean Culture
... unique wooden gong called the mokt'ak. Korean Buddhist music, while often using sutras commonly found in other countries, is unique in its notation and use of the gong, which is popular tourist souvenir. Other aspects of temple worship, such as showing veneration for the images, giving offerings, bo ...
... unique wooden gong called the mokt'ak. Korean Buddhist music, while often using sutras commonly found in other countries, is unique in its notation and use of the gong, which is popular tourist souvenir. Other aspects of temple worship, such as showing veneration for the images, giving offerings, bo ...
Current Newsletter - Longmont Buddhist Temple
... and effective manner we can offer support to the many victims and disaster-stricken locations of the East Japan Great Earthquake to facilitate their recovery?” Let us always keep in mind the venerable words, jishin kyo ninshin, “secure our own entrusting heart to the Dharma, guiding others to the sa ...
... and effective manner we can offer support to the many victims and disaster-stricken locations of the East Japan Great Earthquake to facilitate their recovery?” Let us always keep in mind the venerable words, jishin kyo ninshin, “secure our own entrusting heart to the Dharma, guiding others to the sa ...
The Foundations Of Japanese Buddhism
... Practice: the nembutsu devotional meditation; no other practices are effective any more. Shin Buddhism (Jōdo Shinshū) A special branch of Pure Land, founded by Shinran (1173-1263), a disciple of Hōnen Teachings: "We are saved by faith, and that by grace." Humans are too corrupt ever to be able to ea ...
... Practice: the nembutsu devotional meditation; no other practices are effective any more. Shin Buddhism (Jōdo Shinshū) A special branch of Pure Land, founded by Shinran (1173-1263), a disciple of Hōnen Teachings: "We are saved by faith, and that by grace." Humans are too corrupt ever to be able to ea ...
Study of Cults and False Religions Week 13: Buddhism
... decided that the true way must lie somewhere between hedonism – which is unbridled pursuit of pleasure – and asceticism – which is intense self-denial and simple living, intentional poverty. Guatama then found the Middle Path or the Middle Way that sought to make the most sense out of reality, suffe ...
... decided that the true way must lie somewhere between hedonism – which is unbridled pursuit of pleasure – and asceticism – which is intense self-denial and simple living, intentional poverty. Guatama then found the Middle Path or the Middle Way that sought to make the most sense out of reality, suffe ...
BUDDHISM, RADICAL CRITIQUE AND REVOLUTIONARY PRAXIS
... think about our way of being and acting in such a world. How do we care for sacred ground? How do we care for the body of the Buddha? We might ask further: How do we respond to those who trample on sacred ground? How do we respond to those who trample on the body of the Buddha? These same ideas have ...
... think about our way of being and acting in such a world. How do we care for sacred ground? How do we care for the body of the Buddha? We might ask further: How do we respond to those who trample on sacred ground? How do we respond to those who trample on the body of the Buddha? These same ideas have ...
Vedas - unoosa
... Ways in which Buddhism and Hinduism are similar: • 1) Both believe in reincarnation. • 2) Both believe there are many different paths to enlightenment. • 3) Both believe that our suffering is caused by excessive attachment to things and people in the physical world. • 4) Both believe in an ultimate ...
... Ways in which Buddhism and Hinduism are similar: • 1) Both believe in reincarnation. • 2) Both believe there are many different paths to enlightenment. • 3) Both believe that our suffering is caused by excessive attachment to things and people in the physical world. • 4) Both believe in an ultimate ...
Eastern philosophies
... systemic suffering within the community • Enlightenment (escape from the cycle) is achieved by fully understanding the cycle, and how it works – As in Hinduism, “salvation” is knowledge-based, not action based ...
... systemic suffering within the community • Enlightenment (escape from the cycle) is achieved by fully understanding the cycle, and how it works – As in Hinduism, “salvation” is knowledge-based, not action based ...
Learning to Read Japanese Paintings: Using Artwork as an Entry Point for Japanese Literature
... suffering; (2) suffering is caused by craving; (3) suffering can have an end, and (4) there is a path that leads to the end of suffering. Karma: The idea that one’s moral choices in life have consequences; how one is reborn depends on one’s deeds and intentions behind the deeds in a former life. Lot ...
... suffering; (2) suffering is caused by craving; (3) suffering can have an end, and (4) there is a path that leads to the end of suffering. Karma: The idea that one’s moral choices in life have consequences; how one is reborn depends on one’s deeds and intentions behind the deeds in a former life. Lot ...
BSTC1001 Introduction to Buddhist teachings (6 Credits)
... BSTC1001 Introduction to Buddhist teachings (6 Credits) Course Description Buddhism, being a major world religion, is an important cultural heritage of mankind. Its teachings have not only influenced art and philosophy throughout history, but have also become a source of inspiration for contemporary ...
... BSTC1001 Introduction to Buddhist teachings (6 Credits) Course Description Buddhism, being a major world religion, is an important cultural heritage of mankind. Its teachings have not only influenced art and philosophy throughout history, but have also become a source of inspiration for contemporary ...
The Buddha
... • 2nd watch: Siddhartha is filled with compassion for all beings because he sees the ways in which they suffer without escape. Even those born in heaven are disturbed by sensual passion and fall from heaven; therefore, no state of existence is free from illusion and death • 3rd watch: Siddhartha und ...
... • 2nd watch: Siddhartha is filled with compassion for all beings because he sees the ways in which they suffer without escape. Even those born in heaven are disturbed by sensual passion and fall from heaven; therefore, no state of existence is free from illusion and death • 3rd watch: Siddhartha und ...
Sample Course Specification MAv2
... nature, special features and importance of the Mahayana in Asian religious culture, and acquire a basic grasp of the Mahayana: its evolution, its relation to the Theravada, its diversity and its influence on Asian civilization. ...
... nature, special features and importance of the Mahayana in Asian religious culture, and acquire a basic grasp of the Mahayana: its evolution, its relation to the Theravada, its diversity and its influence on Asian civilization. ...